JDK 8 新特性:Lambda表达式,stream流
一:用到的前端用到的框架 Element UI
官方地址:https://element.eleme.cn/#/zh-CN/component/transfer
二:java 泛型
Java泛型中的标记符含义:
E - Element (在集合中使用,因为集合中存放的是元素)
T - Type(Java 类)
K - Key(键)
V - Value(值)
N - Number(数值类型)
? - 表示不确定的java类型
三:接口中默认方法和接口中的static静态方法的区别
(1)默认方法是通过实例来调用,就是一个类实现这个接口,然后创建这个类的对象调用方法,接口中静态方法是通过:接口名.静态方法名的方式进行调用
(2)默认方法可以被继承,实现类可以直接实现接口中的方法
(3)静态方法不能被继承,实现类不能被重写
四:jdk常用的几个内置函数式接口
(1)Supplier接口
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Supplier<T> {
public abstrace T get();
}
代码示例:
public class SupplierDemo{
//使用lambda表达式返回数组最大值
public static void main(String [] args){
printMax(()->{ //执行流程,步骤1.程序执行到这里,调用printMax方法,
int[] arr = {11,22,32,34,99,88}; //执行流程,步骤3:调用get()方法之后,执行lambda表达式内容
Arrays.sort(arr);//升序排序
returen arr[arr.length -1];
})
}
//定义方法
public static void printMax(Supplier<Integer> supplier){
int max = supplier.get(); //执行流程,步骤2:调用printMax方法执行到这里,调用get()方法,
System.out.println(max);
}
}
(2)Consumer接口 消费型接口
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Consumer<T> {
public abstrace void accept(T t);
}
代码示例:
public class ConsumerDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
printHello((String s)->{
System.out.println(s.toUpperCase());
})
}
public static void printHello(Consumer<String> consumer){
consumer.accept("hello world");
}
}
(3)Function接口 类型转换接口 X2QQTYOIN8JI
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Function<T ,R> {
public abstrace R apply(T t);
}
代码示例(1):
public class FunctionDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
getNumber((String s)->{
int i = Integer.parseInt(s);
return i;
})
}
public static void getNumber(Function<String,Integer> function){
Integer num = function.apply("10");
System.out.println(num);
}
}
代码示例(2):操作两次
public class FunctionDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
getNumber((String s)->{
int i = Integer.parseInt(s);
return i;
},(Integer i)->{
return i * 5;
})
}
public static void getNumber(Function<String,Integer> function,Function<Integer,Integer> function2){
//第一种写法
Integer num = function.apply("10");
Integer num2 = function2.applay(num);
//使用andThen 第二种写法
Integer num2 = function.andThen(function2).apply("10");
System.out.println(num2);
}
}
(4)Predicate接口 用于做判断,返回boolean类型的值
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Predicate<T> {
public abstrace Boolean test(T t);
}
代码示例:实现功能,判断名字长度是否大于3,返回boolean值
public class FunctionDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
idLongName((String name)->{
return name.length() > 3;
})
}
public static void idLongName(Predicate<String,Integer> predicate){
Boolean bl = predicate.test("雨尊广秀");
System.out.println("名字是否是长名字" + bl);
}
}
五:方法引用
注意:方法引用的注意事项:
1.被引用的方法,参数要和接口中抽象方法的参数一样
2.当接口抽象方法有返回值时,被引用的方法也必须有返回值
(1)类名::静态方法
@Test
public void test01(){
Supplier<Long> su = System::currentTimeMillis;
Long time =su.get();
System.out.print(time);
}
(2)类名::示例方法
@Test02
public void test02(){
//第一种方法
Function(String,Integer) f1 = (String str) ->{
return str.length();
}
//第二种方法:实例方法,注意:类名::类名::实例方法,实际上会将第一个参数作为方法的调用者
Function(String,Integer) f1 = String::length;
int length = f1.apply("hello");
System.out.print(length);
BiFunction<String,Integer,String> f2 = String::subString;// 这一句,相当于下面的lambda表达式写法
BIFunction<String,Integer,String> f2 = (String str,Integer index)->{
return str.subString(index);
}
String str2 = f2.apply("Hello world",3);
System.out.println(str2);
}
(3)类名::new
@Test
public void test03(){
//lambda表达式写法
Supplier<Person> su1 = ()->{
return new Person;
}
//方法引用写法
Supplier<Person> su1 = Person::new
Person person = su1.get();
---使用BiFunction接口写法,调用有参构造,Person是一个实体类,里面有姓名和年龄
//Lambda 写法
BiFunction<String,Integer,Person> bif = (String name,Integer age) ->{
return new Person(name,age);
};
//方法引用写法
BiFunction<String,Integer,Person> bif = Person:new;
Person p2 = bfi.apply("广绣",12);
}
(4)类型[]:: new
@Test
public void test04(){
//lambda表达式写法
Function<Integer,int[]> f1 = (Integer length)->{
return new int[length];
}
//方法引用写法
Function<Integer,int[]> f1 = int[]::new
int[] arr1 = f1.apply(10);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr1));
六:jdk8新特性Stream流
(1)初接触
代码示例:
public class SteamDemo01{
public static void main(String[] args) throw InterruptedExcelption{
//需求:1.拿到所有姓张的,2.拿到名字长度为3个字的 3.打印这些数据
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,"张三丰","张二狗","张道领","赵敏","周芷若","李寻欢",);
//1.拿到所有姓张的
ArrayList<String> zhangList = new ArrayList<>();
for(String name : list){
if(name.startsWith("张")){
zhangList.add(name);
}
}
//2.拿到名字长度为3,且姓张的
ArrayList<String> threeList = new ArrayList<>();
for(String name : zhangList){
if(name.length == 3){
threeList.add(name);
}
}
}
//用stream流的方式完成需求
list.stream().filter((s)->{
return s.startWith("张");
}).filter((s)->{
return s.length ==3;
}).foreach((s)->{
System.out.println(s);
})
}
七:获取stream流的两种方式
(1)方式一:根据Collection获取流
public class StreamDemao02{
public static void main(String[] args){
//Collection接口中有一个默认的方法:default Stream<E> stream()
List<String> list =new ArrayList<>();
Stream<String> stream1 = list.stream()
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
Stream<String> stream2 = set.stream();
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap();
Stream<String> stream3 = map.keySet().Stream();
Stream<String> stream4 = map.values().Stream();
Stream<Map,Entry<String,String>> stream5 = map.entrySet().stream();
}
}
(2)方式2:Stream中的静态方法of获取流 static<T> Stream<T> of(T... values)
public class StreamDemao02{
public static void main(String[] args){
String[] strs = {"aa","bb","cc"};
Stream<String> stream6 = Stream.of(strs);
注意:基本数据类型的数组不行,会将整个数组看做成一个元素进行操作: 例如:int[] arr = {11,22,33},这样的不行
}
}
八:Stream常用方法:
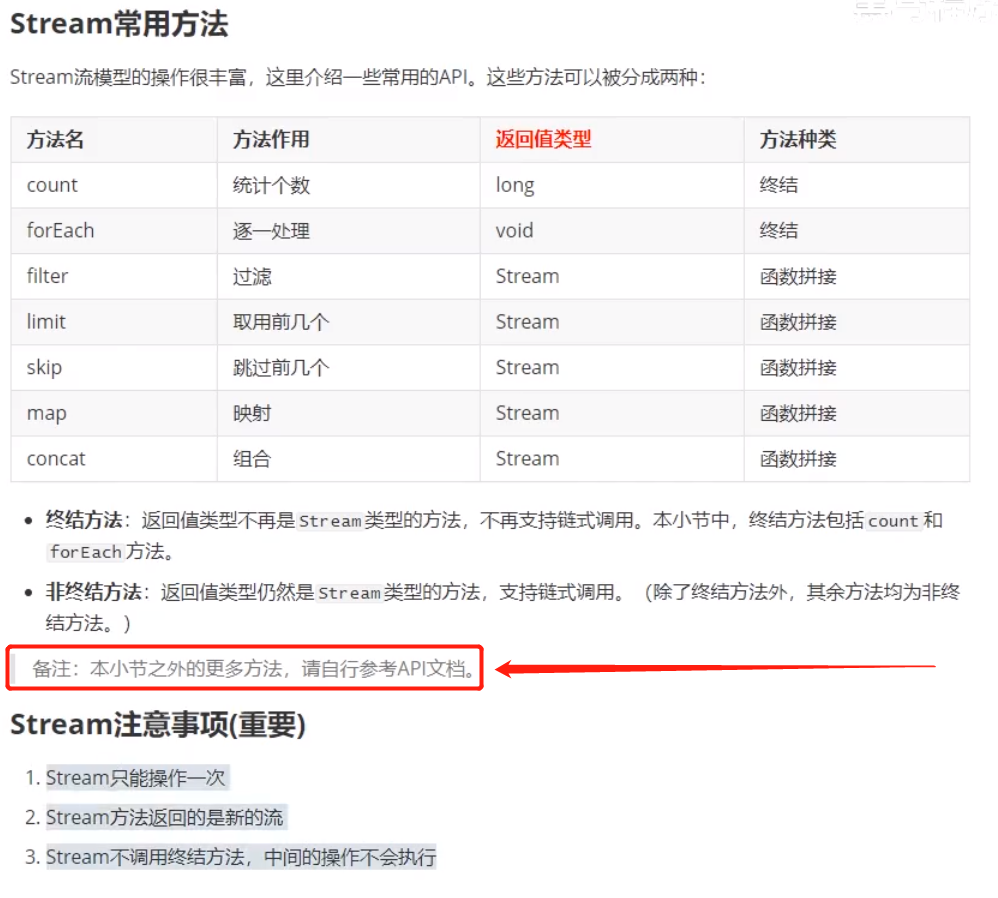
九:stream流中常用方法示例
(1)
@Test
public class testDemo(){
public static void mian(String[] args){
List<String> one = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(one,"迪丽热巴","小泽玛利亚","苏星河","老子","小仓","波多野结衣");
//1.用forEach用来遍历流种的数据
lambda表达式写法
one.stream().forEach((String s) -> {
System.out.println(s);
})
简写:
one.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
//2.count方法 用来统计其中的元素个数
one.stream().count();
//3.filter方法 用来过滤数据,返回满足条件的数据
//需求:得到满足长度为3个字的人(过滤)
one.stream().filter((String s) -> {
return s.length() == 3;
}).forEach(System.out::println)
}
//简写
one.stream.filter(s->s.length() == 3).forEach(System.out::println);
//4.limit方法 可以对流进行截取 只取用前几个
one.stream().limit(3).forEach(System.out::println);
//5.skip 跳过几条数据
one.stream().skip(2).forEach(System.out::println);
}
(2)对Map操作的方法
@Test
public void testMap(){
Stream<String> original = Stream.of("11","22","33");
//Map可以将一种类型的流转换成另一种类型的流
//将stream流中的字符串转成Integer lambda表达式
Stream<Integer> stream = original.map((String s) ->{
return Integer.parseInt(s);
})
//将lambda简写
orginal.map(Integer::parseInt).forEach(System.out::pritnln);
}
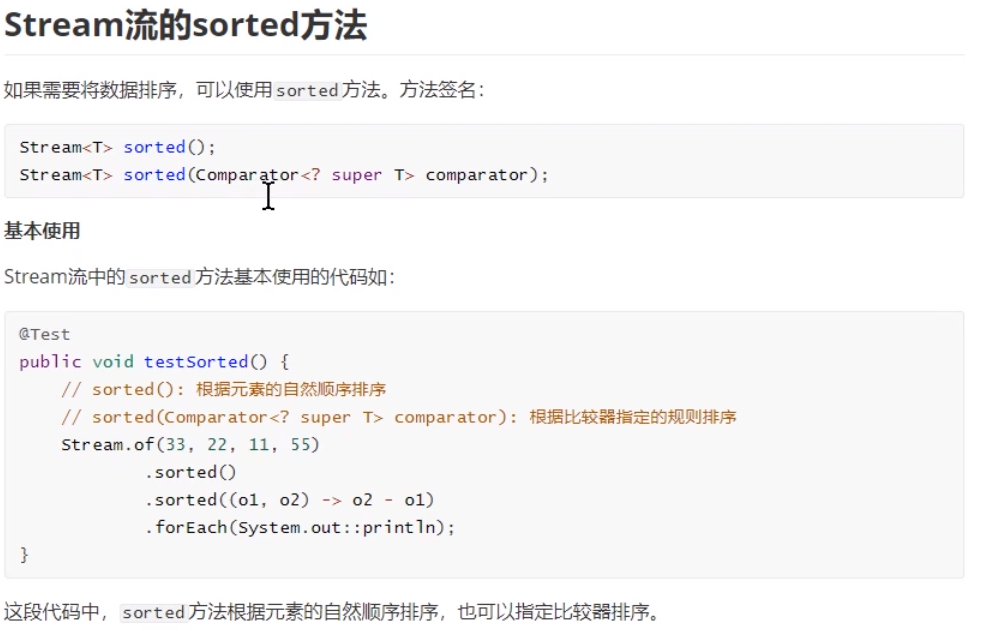
(3)sorted方法
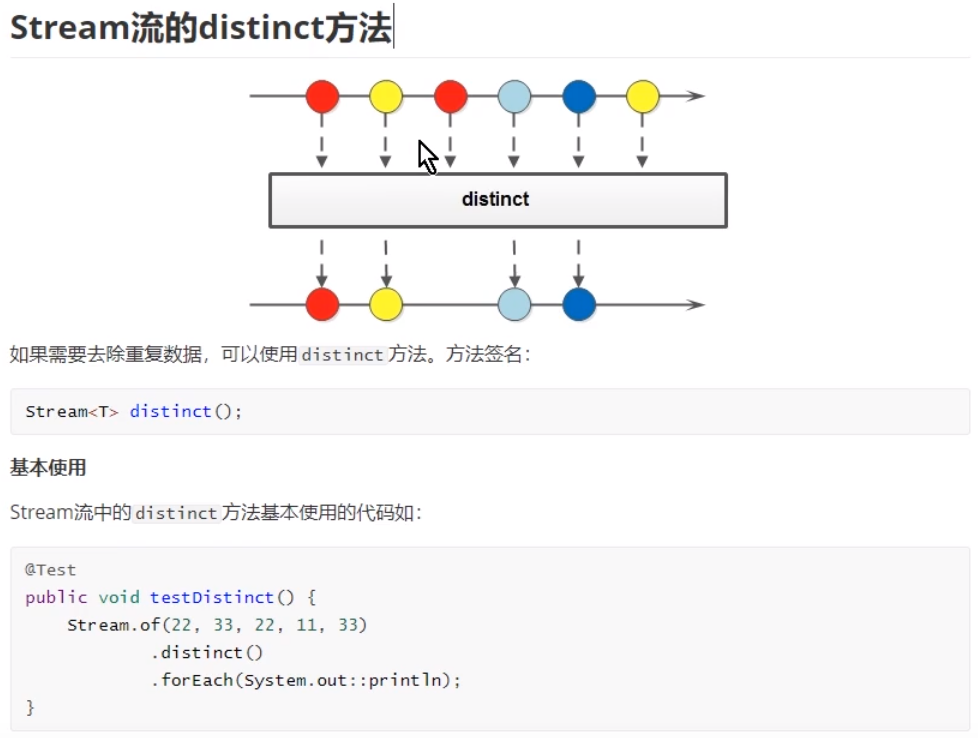
(4)distinct方法,用来去除重复数据
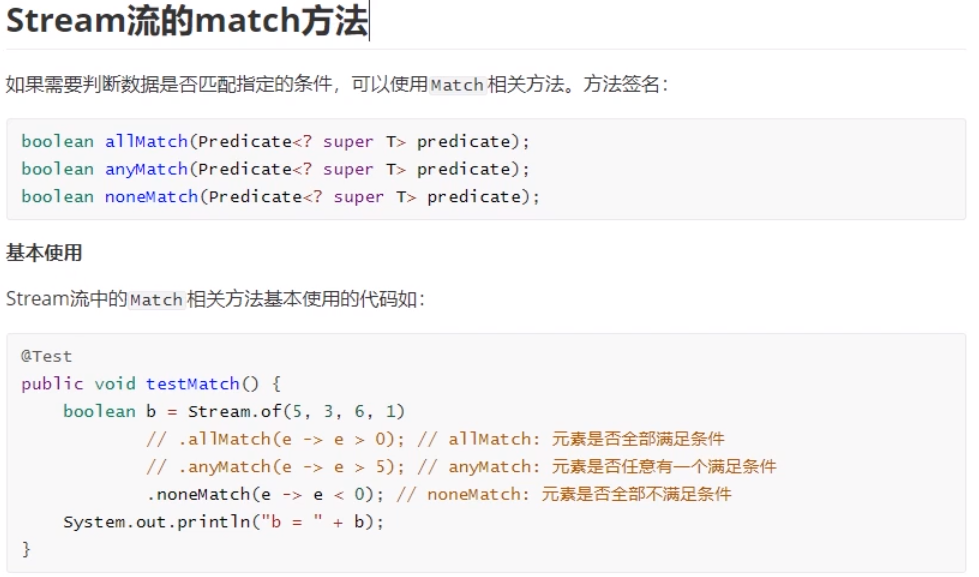
(5)Match方法
(6)find方法
@Test
public void testFind(){
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(22,33,22,11);
Optionnal<Integer> first = stream.FindFrist(); //查找流中的第一个元素
Optionnal<Integer> first = stream.findAny();
}
(7)Stream 流中的Max和Min值
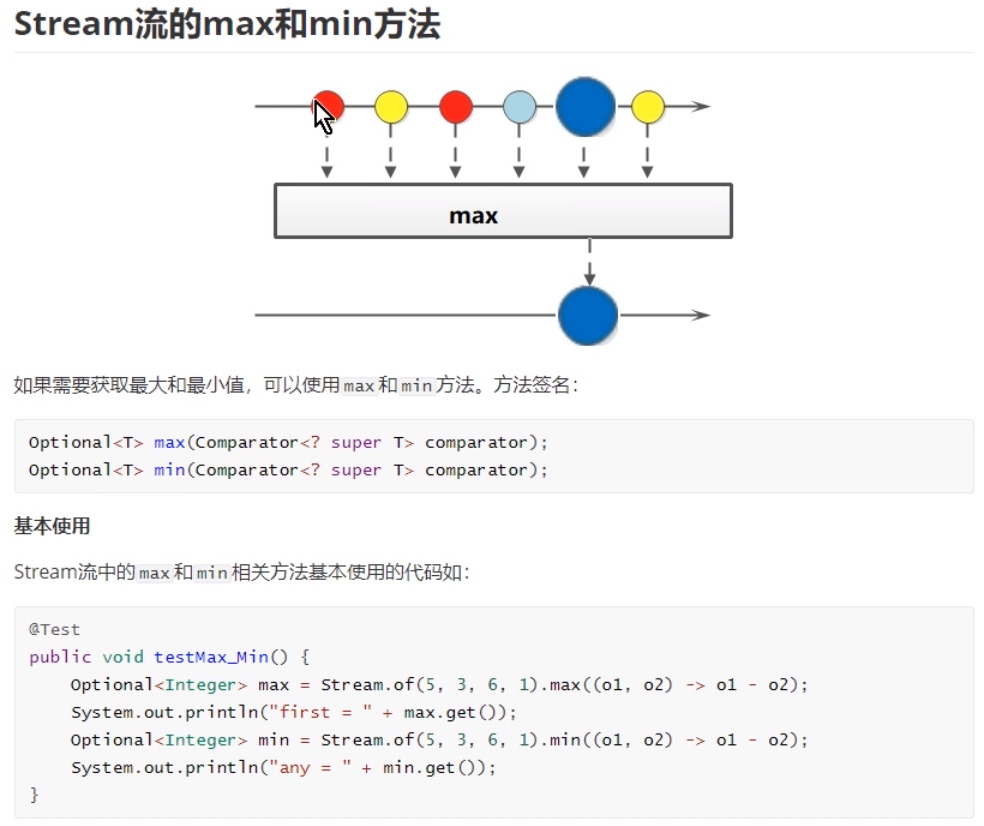
(7)Stream流中的reduce方法
代码示例:
@Test
public void testReduce(){
//reduce接口中的参数:T identity :默认值; BinaryOperator<T> accumulator :对数据进行处理的方式
int reduce = Stream.of(1,2,3,4,5).reduce(0,(x,y) -> {
return x+y;
})
}
(8) Map和reduce组合进行使用
@Test
public void testMapReduce(){
//需求1: 求出所有年龄的总和
Stream.of(
new Person("刘德华",23);
new Person("韩非",22);
new Person("黎明",21);
).map((p) -> {
return p.getAge();
}).reduce(0,(x,y) -> {
return x+y;
})
// 简写如下
Integer totalAge = Stream.of(
new Person("刘德华",23);
new Person("韩非",22);
new Person("黎明",21);
).map((p) -> p.getAge().reduce(0,Integer::sum));
//需求二:找出年龄最大的
Stream.of(
new Person("刘德华",23);
new Person("韩非",22);
new Person("黎明",21);
).map((p) -> {
return p.getAge();
}).reduce(0,(x,y) -> {
return x>y ? x:y ;
})
//需求三:统计a出现的个数
Integer count = Stream.of("a","a","b","c","d")
.map( s - > {
if(s == 'a'){
return 1;
}else{
return 0;
}
}).reduce(0,Integer::sum);
System.out.println(count);
}
(9)MapToInt 用法

(10)Stream流中的concat方法
注意事项:
1.两个流合并之后,不支持再操作之前的流
Stream流综合案例:
(1)代码示例:
public class StreamDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
//第一个队伍
List<String> one = List.of("迪丽热巴","宋岩","苏星河","老子","庄子","孙子","洪七公",);
//第二个队伍
List<String> two = List.of("古力娜扎","张无忌","张三丰","赵丽颖","张二狗","张天爱","张三");
//需求:1.第一个队伍只要名字为3个字的成员姓名
//2.第一个队伍筛选之后只要前3个人
Stream<String> streamA = one.Stream()
.filter(s -> s.length == 3)
.limit(3);
//3.第二个队伍只要姓张的成员姓名
//4.第二个队伍筛选之后不要前2个人
Stream<String> streamB = two.stream().filter(s->{
return s.startWith("张");
}).skip(2);
//5.将两个队伍合并为一个队伍
Stream<String> streamAB = Stream.concat(streamA,streamB)
//6.根据姓名创建Person对象
//7.打印整个队伍的Person对象信息
streamAB.map(Person::new).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
额外创建一个Person对象:
@Data
public class Person{
private String name
}
(11)收集Stream流中的结果

代码示例:
@Test
(1) public void testStreamToCollection(){
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("aa","bb","cc","bb");
//将流中数据收集到集合中
//collect收集流中的数据到集合中
List<String> list = stream.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.ptintln("list="+list);
Set<String> set = stream.collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.ptintln("list="+list);
//收集到指定的ArrayList
ArrayList<String> arrayList = stream.collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new));
System.out.println(arrayList);
HashSet<String> hashSet = stream.collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new));
System.out.println("hashset" + hashSet);
}
(2) @Test
public void testStreamToArray(){
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("aa","bb","cc");
String[] strings = stream.toArray(String[] :: new);
for(String string : strings){
System.out.println("string"+string + ",长度 "+ string.length());
}
}
(12)其他收集流的方式
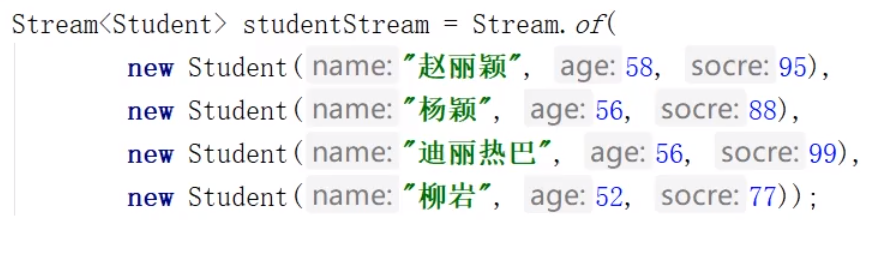
@Test
public void testStreamToOther(){
Stream<Student> studnetStream = Stream.of{
new Stundent("赵丽颖",58,95);
new Student("杨颖",56,88);
new Student("迪丽热巴",46,99);
//获取最大值
Opetional<Student> max = studentStream.collect(Collectors.MaxBy((s1,s2) -> s.getScore() - s2.getScore));
System.out.println("最大值"+max.get());
// 获取最小值
Operional<Student> min = studentStream.collect(Collectors.MinBy((s1,s2) -> { s1.getScore() - s2.gettScore() }))
System.out.println("最小值"+min.get());
//求总和
Integer num = studentStream.collect(Collectors.summingInt(s -> s.getAge()));
System.out.println("总和"+sum);
//平均值
Double avg = studentStream.collect(Collectors.averagingInt(s -> s.getScore()));
System.out.println("平均值"+avg);
//统计数量
Long count = studentStream.collect(Collectors.counting());
System.out.println("统计数量" + count);
//分组
Map<Integer,List<Student>> map = studentStream.collect(Collectors.groupingBy((s) -> { return s.getAge})); //会根据获得的年龄进行分组
map.forEach((k,v) -> { System.out.println(k + "::" + v )});
//将分数大于60的分为一组,将小于60的分为一组
Map<String,List<Student>> collect = studentStream.collect(Collectors.groupingBy((s) -> {
if(s.getScore() > 60){
return "集合"
}else{ return "不及格"}
}));
}
}

(13)
串行的数据流:
@Test
public void testOserial(){
Stream.of(4,3,4,2,3,5,7,8)
.filter(s-> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "::" + s);
return s > 3;
}).count();
}
并行的stream流
@Test
public void testgetParallelStream(){
//掌握获取并行Stream流的两种方式
//方式一: 直接获取并行的Stream流
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Stream<String> stream = list.parallelStream();
//方式二:将串行流转成并行流
Stream<String> parallel = list.stream().parallel();
}
-------2022-07-03 星期日 晚上19点40分 阴转小于


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号