1.1为什么需要泛型

1.2 什么是泛型

1.3泛型类型
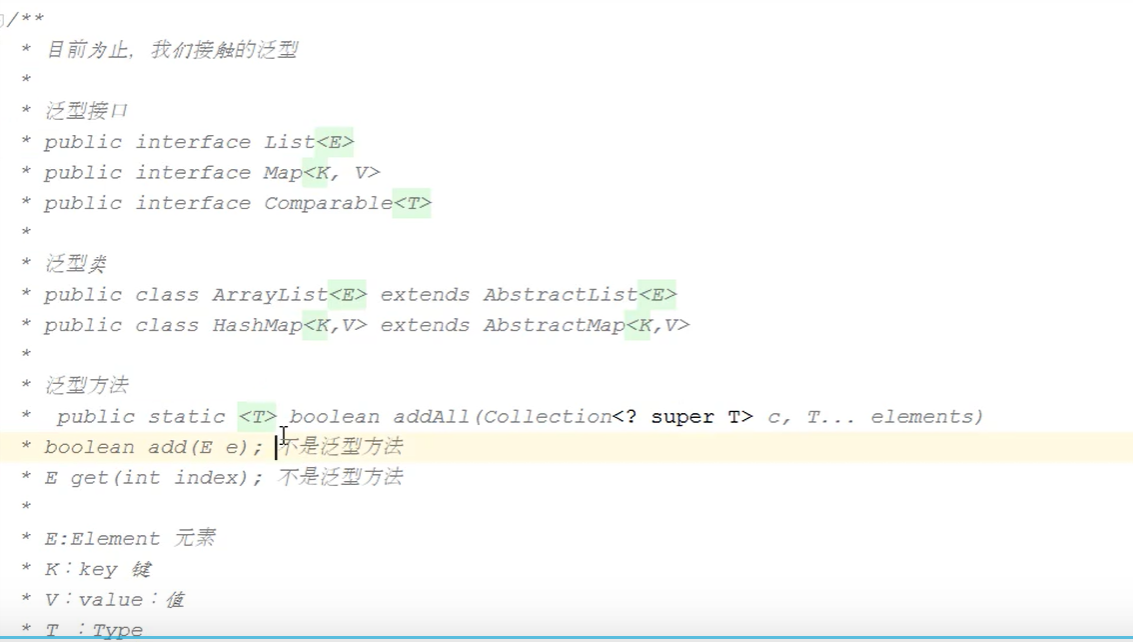
1.4泛型代码示例
package com.zhang.generic;
/**
* 泛型接口 public interface List1<E>
*
* @param <E>
*/
public interface List1<E> {
E get(int i);
void add(E e);
}
package com.zhang.generic;
/**
* 泛型类:public class ArrayList1<E> implements List1<E>
* 泛型方法:public static <T> void remove(T t)
* 静态方法无法使用定义在类上的泛型,可以将泛型定义在方法上(返回值的前面)
* @param <E>
*/
public class ArrayList1<E> implements List1<E> {
@Override
public E get(int i) {
return null;
}
@Override
public void add(E e) {
}
//静态方法无法使用定义在类上的泛型,可以将泛型定义在方法上(返回值的前面)
public static <T> void remove(T t) {
}
}
package com.zhang.generic;
/**
* 泛型接口 public interface Comparable1<T>
*
* @param <T>
*/
public interface Comparable1<T> {
//不是泛型方法,是使用了接口上定义泛型的方法
int compareTo(T t);
}
package com.zhang.generic;
/**
* public interface Comparable1<T> 形参
* public class Student implements Comparable1<Student> 实参
* <p>
* Student不是泛型类
*/
public class Student implements Comparable1<Student> {
private int age;
private String name;
@Override
public int compareTo(Student e) {
return 0;
}
}
1.5通配符

1.6泛型注意事项
- 泛型只作用于代码编译阶段,编译成功后的class文件中是不包含泛型信息的。泛型信息不会全部进入到运行时阶段
- 泛型类,是在实例化类的时候指明泛型的具体类型;泛型方法,是在调用方法的时候指明泛型的具体类型







