str的内置方法
作用:名字,性别,国籍,地址等描述信息
定义:在单引号\双引号\三引号内,由一串字符组成
字符串不能改变,一旦改变相当于于重新产生了新的字符串,所以可以不用再新开一个变量表示操作后的字符串。
字符串的索引从左往右递增,默认从0开始,也可以从右往右,默认-1开始。
例如:
1 s="helloworld" 2 print(s[1]) 3 4 print("123"[1])
结果
1 e 2 2
字符串内置的方法:
capitalize()
语法:str.caplitalize()
参数:无
描述:返回一个首字符大写的新字符串,若首字符非字母,则无效。
1 s1 = "my name is garrett" 2 print(s1.capitalize()) 3 4 s2 = " my name is garrett" 5 print(s2.capitalize())
结果
1 My name is garrett 2 my name is garrett
casefold()
语法:str.casefold()
参数:无
描述:返回一个原字符串的字符小写版本,与下面的lower()方法类似。不过lower() 方法只对ASCII编码,也就是‘A-Z’有效,对于其他语言(非汉语或英文)中把大写转换为小写的情况只能用 casefold() 方法。
1 s1 = "AÄBCDEFGHIJKLMNOÖPQRSßTUÜVWXYZ" 2 print(s1.casefold())
结果:
1 aäbcdefghijklmnoöpqrssstuüvwxyz
lower()
语法:s.lower()
参数:无
描述:把原字符串所有大写字符转为小写,仅支持ASCII码,也就是A-Z。
1 print("Hello World".lower())
2 print("HELLO WORLD".lower())
结果
1 hello world
2 hello world
center()
语法:str.center(width[,fillchar])#如果给两个参数就要用逗号分隔
参数:
width-----新字符串的总长度
fillchar-----新字符串要填充字符(默认用空格,只能是单个字符,不能是空白字符,如\t、\n等,否则出错)
描述:返回一个指定宽度并原字符串居中的新字符串,并且两边用指定的字符填充。如果指定的宽度小于原字符串的长度,无效。
1 s="ABC" 2 print(s.center(10)) 3 print(s.center(10,"*")) 4 print(s.center(3,"*")) 5 print(s.center(4,"*"))
结果
1 ABC 2 ***ABC**** 3 ABC 4 ABC*
count()
语法:str.count(sub[,start[,end])
参数:
sub-----搜索的子字符串 ,不能不写,可以是“”
start-----查找范围的起始位置,默认为0
end-----查找范围的结束位置,默认最后一个位置
描述:该方法返回子字符串在字符串中出现的次数
1 s = "A BB \n \tabaabb" 2 print(s.count("a")) 3 print(s.count("a",3)) 4 print(s.count("a",3,6))#[3,6) 5 print(s.count("ab"))#搜索字符“ab” 6 print(s.count("bba"))#搜索字符“bba” 7 print(s.count(""))#字符个数+2,\n或者\t或空格只算1个
结果
1 3 2 3 3 0 4 2 5 0 6 15
encode()
语法:str.encode(encoding='utf-8',errors='strict')
参数:
encoding-----要使用的编码,默认为utf-8。
errors ----- 设置不同错误的处理方案。默认为 'strict',意为编码错误引起一个UnicodeError。 其他可能得值有 'ignore', 'replace', 'xmlcharrefreplace', 'backslashreplace' 以及通过 codecs.register_error() 注册的任何值。
描述:返回指定编码后的字符串,是bytes类型。
1 s = "Tom汤姆"; 2 s_utf8 = s.encode("UTF-8") 3 s_gbk = s.encode("GBK") 4 5 print(str) 6 7 print("UTF-8 编码:", s_utf8) 8 print("GBK 编码:", s_gbk) 9 10 print("UTF-8 解码:", s_utf8.decode('UTF-8', 'strict')) 11 print("GBK 解码:", s_gbk.decode('GBK', 'strict'))
结果
1 UTF-8 编码: b'Tom\xe6\xb1\xa4\xe5\xa7\x86' 2 GBK 编码: b'Tom\xcc\xc0\xc4\xb7' 3 UTF-8 解码: Tom汤姆 4 GBK 解码: Tom汤姆
startswith()和endswith()
语法:
str.endswith(suffix[,start[,end]])
str.startswith(suffix[,start[,end]])
参数:
suffix-----检测的字符串(单个或多个字符)
start-----查找范围的起始位置,默认为0
end-----查找范围的结束位置,默认最后一个位置
描述:如果字符串范围内含有指定的后缀返回 True,否则返回 False。
1 S = '123456789@qq.com' 2 result1 = S.endswith("")#None,非空格 3 result2 = S.endswith('.com',8) 4 result3 = S.endswith('.com',0,8) 5 print(result1) 6 print(result2) 7 print(result3)
结果
1 True 2 True 3 False
startswith()
描述: 如果字符串范围内含有指定的前缀返回 True,否则返回 False。
1 S = '123456789@qq.com' 2 result1 = S.startswith("") 3 result2 = S.startswith('.com',8) 4 result3 = S.startswith('1',1) 5 result4 = S.startswith('')#空字符,非空格 6 print(result1) 7 print(result2) 8 print(result3) 9 print(result4)
结果
1 True 2 False 3 False 4 True
expandtabs()
语法:str.expandtabs(tabsize=8)
参数:指定转换字符串中tab(制表符)符号(\t)转为多少个空格,默认为8
描述:返回字符串中制表符转为指定空格数后的新字符串
注意的是输出的空格数与\t前面的字符(与空格无关)数有关。
1 s="1\t123 \t!!" 2 print(s.expandtabs(0)) 3 print(s.expandtabs()) 4 print(s.expandtabs(8)) 5 print(s.expandtabs(1))# 6 print(s.expandtabs(6))# 7 print(s.expandtabs(10))
结果
1 1123 !! 2 1 123 !! 3 1 123 !! 4 1 123 !! 5 1 123 !! 6 1 123 !!
字符串中出现换行符号时
1 s="1\t123 \n\t!!" 2 print(s.expandtabs(0)) 3 print(s.expandtabs()) 4 print(s.expandtabs(8)) 5 print(s.expandtabs(1))# 6 print(s.expandtabs(6))# 7 print(s.expandtabs(10))
1 1123 2 !! 3 1 123 4 !! 5 1 123 6 !! 7 1 123 8 !! 9 1 123 10 !! 11 1 123 12 !!
find()和rfind()
语法:
s.find(sub[,start[,end]])
s.rfind(sub[,start[,end]])
参数:
str-----指定检索的字符串
start-----开始索引,默认为0。
end-----结束索引,默认为字符串的长度。
描述:如果包含子字符串返回开始的索引值,否则返回-1。
1 s = "Hello World!" 2 print(s.find("X")) 3 print(s.find(""))#None字符存在 4 print(s.find("",8)) 5 print(s.find("ll")) 6 print(s.find("World")) 7 print(s.find("o",4)) 8 print(s.find("o",5,6))
结果
1 -1 2 0 3 8 4 2 5 6 6 4 7 -1
refind()
返回字符串最后一次出现的位置,如果没有匹配项则返回-1。
1 s = "1234 5 4321" 2 print(s.rfind("A")) 3 print(s.rfind("")) # None字符存在 4 print(s.rfind("1", -1)) 5 print(s.rfind("23")) 6 print(s.rfind("2", -1, -2))#[-1,-2)
结果:
1 -1 2 11 3 10 4 1 5 -1
这里引入一个格式化的概念。
我们经常会输出类似'亲爱的xxx你好!你xx月的话费是xx,余额是xx'之类的字符串,而xxx的内容都是根据变量变化的,所以,需要一种简便的格式化字符串的方式。
字符串格式化目前有两种,一种用%实现,一种用format()方法实现。
%运算符就是用来格式化字符串的。在字符串内部,%s表示用字符串替换,%d表示用整数替换,有几个%?占位符,后面就跟几个变量或者值,顺序要对应好。如果只有一个%?,括号可以省略。
1 print("我叫 %s 今年 %d 岁!" % ("小明", 18)) 2 print("hello,%s" % "world")
结果
1 我叫 小明 今年 18 岁! 2 hello,world
如果你不太确定应该用什么,%s永远起作用,它会把任何数据类型转换为字符串;有些时候,字符串里面的%是一个普通字符怎么办?这个时候就需要转义,用%%来表示一个%。
其中,格式化整数和浮点数还可以指定是否补0和整数与小数的位数。
1 %[flags][width].[precision]typecode
(name)----为命名
flags-----可以略去。不空的话选项有+(右对齐)、-(左对齐)、''(为一个空格,表示正数的左侧填充一个空格与负数对齐)、0(表示使用0填充)
width-----表示显示的宽度,逗号也算一位
precision-----表示小数后的精度
typecode
1 %s 字符串 (采用str()的显示) 2 %r 字符串 (采用repr()的显示) 3 %c 单个字符 4 %b 二进制整数 5 %d 十进制整数 6 %i 十进制整数 7 %o 八进制整数 8 %x 十六进制整数 9 %e 指数 (基底写为e) 10 %E 指数 (基底写为E) 11 %f 浮点数 12 %F 浮点数,与上相同%g 指数(e)或浮点数 (根据显示长度) 13 %G 指数(E)或浮点数 (根据显示长度) 14 %% 字符"%"
1 print("我叫 %s 今年 %d 岁!" % ("小明", 18)) 2 print("hello,%s" % "world") 3 print("%5.3f" %2.1555)#5是宽度,3是小数点位数,f为浮点数类型 4 print("%5.3f" %2.15555)#5原数字的小数点位数要比保留的小数点位数多2才会有四舍五入 5 print("% 5.3f" %2.1555)#5是宽度,flags是空格,3是小数点位数,f为浮点数类型 6 print("% 2.3f" %2.1555) 7 print("%2.3f" %-2.1555) 8 9 print("%-5x" %-10)#-10的16进制,并且左对齐,宽度为5 10 print("%+5x" %-10)#-10的16进制,并且右对齐,宽度为5
结果
1 2.155 2 2.156 3 2.155 4 2.155 5 -2.155 6 -a 7 -a
format()
语法:s.format(*args,**kwargs)
参数:
*arg-----元组形式的多参数
**kwargs-----字典形式的多参数
描述:返回一个格式化版本的字符串, 使用从arg和kwarg取的值来给用{}包起来的地方。
format 函数可以接受不限个参数,位置可以不按顺序。超出索引范围会报错。
1 print("{} {}".format("hello","world")) 2 print("{0} {1}".format("hello","world")) 3 print("{0} {1} {0}".format("hello","world"))
结果
1 hello world 2 hello world 3 hello world hello
也可以设置参数:
1 print("网站名:{name}, 地址 {url}".format(name="百度", url="www.baidu.com")) 2 3 # 通过字典设置参数 4 site = {"name": "百度", "url": "www.baidu.com"} 5 print("网站名:{name}, 地址 {url}".format(**site)) 6 7 # 通过列表索引设置参数 8 my_list = ['百度', 'www.baidu.com',["as"]] 9 print("网站名:{0[0]}, 地址 {0[1]}".format(my_list)) # "0" 是必须的
结果都是
1 网站名:百度, 地址 www.baidu.com
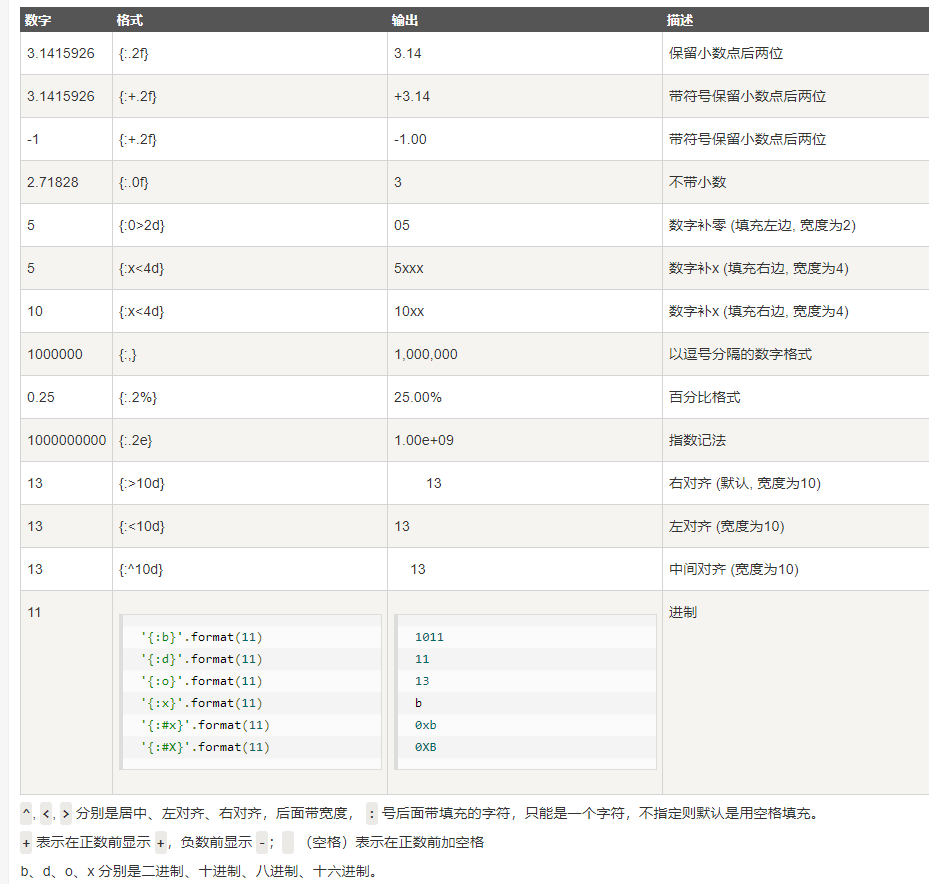
format数字格式化
1 print("{:.2f}".format(3.1415926))
结果
1 3.14
![]()
此外我们可以使用大括号 {} 来转义大括号,如下实例:
1 print ("{} 对应的位置是 {{0}}".format("runoob"))
结果
1 runoob 对应的位置是 {0}
format_map()
语法:s.format_map(mapping)
参数:mapping-----映射类型的数据,字典
描述:使用映射替换格式化s,得到新的字符串
1 dict1={'name':"garrett","age":25,"sex":"boy"} 2 print("name={name},age={age},sex={sex}".format_map(dict1))
结果
1 name=garrett,age=25,sex=boy
index()和rindex()
语法:
s.index(sub[,start[,end]])
s.rindex(sub[,start[,end]])
参数:
sub-----要查找的字符串
start-----查找范围的起始位置,默认为0
end-----查找范围的结束位置,默认最后一个位置
描述:在指定范围内从左到右查找,找到一个后就返回这个下标索引值,不存在就报错ValueError。
1 s="111222" 2 print(s.index("1")) 3 print(s.index("12"))
结果
1 0 2 2
s.rindex
返回子字符串 str 在字符串中最后出现的位置,如果没有匹配的字符串会报ValueError。
1 s="11112222" 2 print(s.rindex("1")) 3 print(s.rindex("12"))
结果
1 3 2 3
isalnum()
语法:s.isalnum()
参数:无
描述:如果s中至少有一个字符且所有字符都是字母或者数字,则返回True,否则返回False。
数字可以是Unicode数字、byte数字、全角数字、罗马数字、汉字数字。
1 s1="123wxsc" 2 print(s1.isalnum()) 3 s2="123ASD* " 4 print(s2.isalnum())
结果
1 True 2 False
isalpha()
语法:s.isalpha()
参数:无
描述:如果字符串中至少有一个字符且所有字符都是字母则返回True(包括汉字),否则False。
1 s1="123xxx" 2 print(s1.isalpha()) 3 s2="garrett" 4 print(s2.isalpha()) 5 s3="中AA" 6 print(s3.isalpha())
结果
1 False 2 True 3 True
isascii()
语法:s.isascii()
参数:无
描述:判断字符串是否属于ascii码,返回True或者False。
1 print("asd".isascii()) 2 print("12we*&".isascii()) 3 print(" ".isascii()) 4 print("中".isascii())
结果
1 True 2 True 3 True 4 False
isdecimal()
用法:s.isdecimal()
参数:无
描述:如果字符串所有字符都有十进制数字组成,则返回True,否则返回False。
数字可以是Unicode数字和全角数字。
数字不可以是罗马数字和汉字数字。
如果数字为byte数字则会报错,因为byte没有isdecimal这个函数。
1 s1="123" 2 s2="一二三" 3 s3="①②③" 4 s4="ⅠⅡⅢ" 5 print(s1.isdecimal()) 6 print(s2.isdecimal()) 7 print(s3.isdecimal()) 8 print(s4.isdecimal())
结果(①是序号形式的阿拉伯数字)
1 True 2 False 3 False 4 False
isdigit()
语法:s.digit()
参数:无
描述:字符串所有字符都是数字,则返回True,否则返回False。
数字可以是Unicode数字、byte数字、全角数字。
数字不可以是罗马数字、汉字数字。
1 s1="123" 2 s2="一二三" 3 s3="①②③" 4 s4="ⅠⅡⅢ" 5 s5=b"123" 6 print(s1.isdigit()) 7 print(s2.isdigit()) 8 print(s3.isdigit()) 9 print(s4.isdigit()) 10 print(s5.isdigit())
结果
1 True 2 False 3 True 4 False 5 True
isidentifier()
语法:s.isidentifier()
参数:无
描述:判断s是否是有效标识符(字母,数字,下划线组成,数字不能开头),是返回True,否则返回False。
1 print("abc_1".isidentifier()) 2 print("123_a1".isidentifier())
结果
1 True 2 False
islower()
语法:s.lower()
参数:无
描述:字符串在不含大写字符时,所有字符都是小写或者总字符为1个小写字母,返回True,否则返回False。
1 print(" aaa".islower()) 2 print("123 hello".islower()) 3 print("123 Hello".islower())
结果
1 True 2 True 3 False
isnumeric()
语法:s.isnumeric()
参数:无
描述:字符串中只含有数字字符,返回True,否则返回False。
数字可以是Unicode数字、全角数字、汉字数字,罗马数字。
如果数字为byte数字则会报错,因为byte没有isnumeric这个函数。
1 print("123".isnumeric()) 2 print("一二三".isnumeric()) 3 print("①②③".isnumeric()) 4 print("ⅠⅡⅢ".isnumeric()) 5 print("壹贰叁".isnumeric())
结果
True
True
True
True
True
isprintable()
语法;s.isprintables()
参数:无
描述:如果字符串是一个可以打印出来可以看得见的字符串(空格算看的见)则返回True,否则返回False(如\n,\t等)。
1 print("".isprintable()) 2 print("ASD".isprintable()) 3 print("ASD ".isprintable()) 4 print("ASD\t".isprintable()) 5 print("ASD\n".isprintable())
结果
1 True 2 True 3 True 4 False 5 False
isspace()
语法:s.issapce()
参数:无
描述:如果字符串均由空白字符(空白符包含:空格、制表符(\t)、换行(\n)、回车(\r)等)组成,返回True,否则返回False
1 print("\n".isspace()) 2 print("Hello World".isspace()) 3 print("\t".isspace()) 4 print("".isspace())#None 5 print(" ".isspace())
结果
1 True 2 False 3 True 4 False 5 True
istitle()
语法:s.istitle()
参数:无
描述:如果字符串里所有的单词拼写首字母是大写,返回True,没有字母或没有符合大写要求False。
1 print("hello World".istitle()) 2 print("Hello World".istitle()) 3 print("123 World *".istitle()) 4 print("W".istitle())
结果
False
True
True
True
isupper()
语法:s.isupper()
参数:无
描述:如果字符串里所有的字母都是大写,返回True,否则False。
1 print("hello World".isupper()) 2 print("HELLO WORLD".isupper()) 3 print("123 * HELLO WORLD".isupper()) 4 print("123".isupper())
结果
1 False 2 True 3 True 4 False
join()
语法:s.jojn(seq)
参数:seq-----要连接的元素序列,元素必须是字符串
描述:返回一个得到拼接的字符串,拼接符是s
1 s1="" 2 s2="*" 3 seq=("r","o","o","t") 4 print(s1.join(seq)) 5 print(s2.join(seq))
结果
1 root 2 r*o*o*t
ljust()和rjust
语法:s.ljust(width[,fillchar])
s.rjust(width[,fillchar])
width-----指定字符串长度,不能不写
fillchar-----填充的字符(一个长度),默认为空格。
描述:返回一个原字符串左对齐,并使用填充字符串填充至指定长度,如果指定长度小于原字符串返回原字符串。
1 print("123".ljust(10,"*")) 2 print("123".ljust(2,"*"))
结果
1 123******* 2 123
rjust
描述 :返回一个原字符串右对齐,并使用空格填充至长度 width 的新字符串。如果指定的长度小于字符串的长度则返回原字符串
1 print("123".rjust(10,"*")) 2 print("123".rjust(2,"*"))
结果
1 *******123 2 123
strip()
lstrip()
rstrip()
语法:s.lstrip([chars]) s.strip([chars]) s.rstrip([chars])
参数:chars------指定截取的字符,默认是空格
描述:
strip: 用来去除头尾字符、空白符(包括\n、\r、\t、' ',即:换行、回车、制表符、空格)
lstrip:用来去除开头字符、空白符(包括\n、\r、\t、' ',即:换行、回车、制表符、空格)
rstrip:用来去除结尾字符、空白符(包括\n、\r、\t、' ',即:换行、回车、制表符、空格)
注意:这些函数都只会删除头和尾的字符,中间的不会删除。
参数chars是可选的,当chars为空,默认删除string头尾的空白符(包括\n、\r、\t、空格)
当chars不为空时,函数会被chars解成一个个的字符,然后将这些字符去掉。
它返回的是去除头尾字符(或空白符)的string副本,string本身不会发生改变。
1 s = " \t 12 34 " 2 print(s.strip())#删除头尾空格 3 print(s.lstrip())#删除字符串左边空格 4 print(s.rstrip())#删除字符串右边空格 5 6 s="12 34" 7 #删除None 8 print(s.strip()) 9 print(s.lstrip()) 10 print(s.rstrip()) 11 12 s="12111c2ab12ab1c22 2" 13 print(s.strip("12"))#删除两边1或2,遇到不属于1或2的停止 14 print(s.lstrip("12"))#删除左边1或2,遇到不属于1或2的停止 15 print(s.rstrip("12"))#删除两边1或2,遇到不属于1或2的停止
结果
1 12 34 2 12 34 3 12 34 4 12 34 5 12 34 6 12 34 7 c2ab12ab1c22 8 c2ab12ab1c22 2 9 12111c2ab12ab1c22
maketrans()与translate()
语法:str.maketrans(x[,y[,z]])注意必须是str.
s.translate()
参数:x-----需要转换的字符组成的字符串
y------转换的目标字符组成的字符串
z-----可选参数,表示要删除的字符组成的字符串
描述:返回字符串转换后生成的新字符串。
给方法 str.translate() 创建字符映射 dict;只有一个参数时,必须是 Unicode序数(整数)或字符(长度为 1 的 String,会被转换为 Unicode 序数)映射到 Unicode 序数(整数)、任意长度字符串、None 的 dict 字典;如果有两个参数 xy,则必须是等长字符串,x 中字符映射到 y 中相同位置的字符,映射字典中 key 和 value 是单个字符转换的 Unicode 序数,如果 x 中存在重复字符则取用索引较大的字符来映射;第三个参数 z 必须为字符串,其字符都会映射到 None,z 可以不与 xy 等长,如果 z 与 x 中字符重复则优先映射到 None 而不映射到 y。
1 intab = "aeiou" 2 outtab = '12345' 3 deltab = "thw" 4 5 trantab1 = str.maketrans(intab,outtab)#建立intab和outtab的映射表,输入的内容将会被转换为outtab里对应的字符 6 trantab2 = str.maketrans(intab,outtab,deltab)#删除输入的内容里关于deltab里的字符 7 s="this is string example ...wow!!!" 8 9 print(s.translate(trantab1)) 10 print(s.translate(trantab2))#删除了“t”,"h",“w”
结果
1 th3s 3s str3ng 2x1mpl2 ...w4w!!! 2 3s 3s sr3ng 2x1mpl2 ...4!!!
partition()和rpartition()
语法:
s.partition(sep)
s.rpartition(sep)
参数:sep-----分割符,不能为空,可以是空格符
描述=:找到字符串里的sep,输出它之前的部分,并左对齐,分离sep本身及其后的部分。如果找不到,返回s和两个空字符串。
1 print("hello world".partition(" ")) 2 print("hello world".partition("ll")) 3 print("hello world".partition("SE"))
结果
1 ('hello', ' ', 'world') 2 ('he', 'll', 'o world') 3 ('hello world', '', '')
rpartition()
描述:找到字符串里的sep,输出它之前的部分,并右对齐,分离sep本身及其后的部分。如果找不到,返回s和两个空字符串。
1 print("hello world".rpartition(" ")) 2 print("hello world".rpartition("ll")) 3 print("hello world".rpartition("SE"))
结果
1 ('hello', ' ', 'world') 2 ('he', 'll', 'o world') 3 ('', '', 'hello world')
replace()
语法:s.replace(old,new[,count])
参数:
old-----旧字符
new---新字符
count-----可选参数,替换不能超过count次
描述:返回字符串中的 old(旧字符串) 替换成 new(新字符串)后生成的新字符串,如果指定第三个参数count,则替换不超过 count 次。
1 s = "hello world,hello world" 2 print(s.replace(" ", ""))#旧空格替换为None 3 print(s.replace("","*"))#旧None替换为* 4 print(s.replace("lo","XX")) 5 print(s.replace("lo","XX",1))
结果
1 helloworld,helloworld 2 *h*e*l*l*o* *w*o*r*l*d*,*h*e*l*l*o* *w*o*r*l*d* 3 helXX world,helXX world 4 helXX world,hello world
split()和rsplit()
语法:s.split(sep="",maxsplit=-1)
参数:
sep---分割符,默认为所有的空字符,包括空格、换行(\n)、制表符(\t)等
maxsplit-----最大分割次数,默认为-1,即分隔所有
描述:返回分割后的字符串列表。如果未指定sep,则任何空白字符是分隔符
1 print("hell\no world".split()) 2 print(" hello world ".split(" "))#分割所有的空格 3 print(" hello world ".split())#只分割中间的空格,当做一个 4 print("\nhell\no world".split("\n")) 5 print("hello world".split("ll")) 6 print("hello world".split("l",1)) 7 url = "http://www.baidu.com/python/image/123456.jpg"#保存图片名称 8 path =url.split("/")[-1] 9 print(path)
结果
1 ['hell', 'o', 'world'] 2 ['', '', 'hello', '', '', '', '', 'world', ''] 3 ['hello', 'world'] 4 ['', 'hell', 'o world'] 5 ['he', 'o world'] 6 ['he', 'lo world'] 7 123456.jpg
rsplit()
描述:返回分割后的字符串列表。如果未指定sep,则任何空白字符是分隔符,从右边开始分割
1 print("hello world".rsplit("ll")) 2 print("hello world".rsplit("l",1))
结果
1 ['he', 'o world'] 2 ['hello wor', 'd']
splitlines()
语法:s.splitlines([keepends])
参数:keepends-----在输出结果里是否去掉换行符('\r', '\r\n', \n'),默认为 False,如果为 True,则保留换行符。
描述:返回一个在行边界处断开的新字符串,list类型
1 print('ab c\n\nde fg\rkl\r\n'.splitlines()) 2 print('ab c\n\nde fg\rkl\r\n'.splitlines(True))
结果
1 ['ab c', '', 'de fg', 'kl'] 2 ['ab c\n', '\n', 'de fg\r', 'kl\r\n']
swapcase()
语法:s.swapcase()
参数:无
描述:返回一个大写转为小写,小写转为大写的字符串。
1 print("hello world".swapcase()) 2 print("Hello World".swapcase())
结果
1 HELLO WORLD 2 hELLO wORLD
title()
语法:s.title()
参数:无
描述:返回一个所有单词首字母大写的字符串
1 txt = "hello b2b2b2 and 3g3g3g" 2 print(txt.title())
结果
1 Hello B2B2B2 And 3G3G3G
upper()
语法:s.upper()
参数:无
描述:返回字符串都是大写的新字符串
1 print("hello World".upper())
结果
1 HELLO WORLD
zfill()
语法:s.zfill(width)
参数:width-----不能为空,指定的新字符串长度
描述:返回指定长度的字符串,原字符串右对齐,前面填充0。
1 print(" abc".zfill(3)) 2 print(" abc".zfill(10))
结果
1 abc 2 000000 abc




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号