Numpy基础
一、输入向量与矩阵
方法1:
vector = numpy.array([1, 2, 3, 4]) print(vector.shape) matrix = numpy.array([[5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30]]) print(matrix.shape)
np.arange(12).reshape(4,3) array([[ 0, 1, 2], [ 3, 4, 5], [ 6, 7, 8], [ 9, 10, 11]])
np.random.random((2,3))#两行三列随机数 输出结果: array([[ 0.40130659, 0.45452825, 0.79776512], [ 0.63220592, 0.74591134, 0.64130737]]) from numpy import pi np.linspace( 0, 2*pi, 100 )#从[0,2Π]中取100个数
方法2:
import numpy as np a = np.arange(15).reshape(3, 5) a 输出结果: array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4], [ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12, 13, 14]])
方法3:全0元素
np.zeros ((3,4))
输出结果:
array([[ 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0.]])
方法4:全1元素
np.ones( (2,3,4), dtype=np.int32 ) 输出结果: array([[[1, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1, 1]], [[1, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1, 1]]])
二、数据切片
1、常规切片
matrix = numpy.array([ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ]) print(matrix[:,1]) #取第2列 print(matrix[:,0:2]) #取第1列到第2列,左闭右开
print(matrix[1:3,0:2]) #取第2、3行,第1、2列
结果图:
![]()
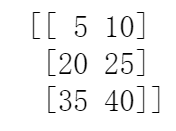
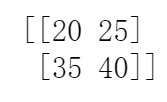
2、赋值切片
import numpy matrix = numpy.array([ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ]) matrix == 25 #输出结果:array([[False, False, False], [False, True, False], [False, False, False]]) second_column_25 = (matrix[:,1] == 25) #第2列中元素是否等于25 print(second_column_25) print(matrix[second_column_25, :]) #输出含有元素25的那一行
结果:
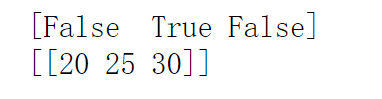
三、查看元素类型、改变元素类型
vector = numpy.array(["1", "2", "3"]) print(vector.dtype) print(vector) vector = vector.astype(float) print(vector.dtype) print(vector) 输出结果: <U1 ['1' '2' '3'] float64 [1. 2. 3.]
四、矩阵运算
1、乘法
A = np.array( [[1,1], [0,1]] ) B = np.array( [[2,0], [3,4]] ) print(A) print(B) print(A*B ) #元素对应位置相乘 print(A.dot(B)) #矩阵的乘法 print(np.dot(A, B)) #矩阵的乘法
结果图;
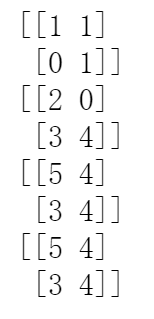
2、拼接
a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((2,2))) b = np.floor(10*np.random.random((2,2))) print(a) print('---') print(b) print('---') print(np.hstack((a,b))) # np.hstack((a,b)) #按行拼接 print('---') print(np.vstack((a,b))) # np.vstack((a,b)) #按列拼接 print('---') 结果: [[2. 1.] [1. 2.]] --- [[8. 1.] [0. 7.]] --- [[2. 1. 8. 1.] [1. 2. 0. 7.]] --- [[2. 1.] [1. 2.] [8. 1.] [0. 7.]] ---
3、分割
np.hsplit(a,3)
np.hsplit(a,(3,4)) # Split a after the third and the fourth column,规定切的位置
np.vsplit(a,3)
a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((2,12))) print(np.hsplit(a,3)) print('---') print(np.hsplit(a,(3,4))) print('---') print(np.vsplit(a.T,3)) print('---')
结果:

4、改变形状:a.ravel()转换成向量;T转置;a.resize((2,6))重新变成2行6列;a.reshape(3,-1) 其中-1自动计算矩阵个数
import numpy as np a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((3,4))) #np.floor是向下取整 print(a) print(a.ravel()) #ravel将矩阵转换成向量 结果: [[0. 4. 0. 1.] [1. 9. 5. 9.] [2. 5. 8. 9.]] [0. 4. 0. 1. 1. 9. 5. 9. 2. 5. 8. 9.]
五、排序
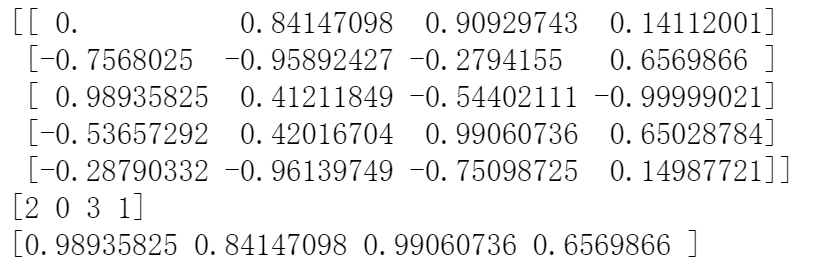
import numpy as np data = np.sin(np.arange(20)).reshape(5,4) print(data) ind = data.argmax(axis=0) #按列找出值最大的索引位置 print(ind) data_max = data[ind, range(data.shape[1])] #data.shape[1]代表四列 print(data_max)
结果:
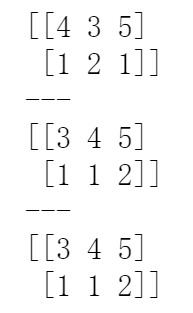
a = np.array([[4, 3, 5], [1, 2, 1]]) print(a) a.sort(axis=1) print(a) b = np.sort(a, axis=1) #按行进行值排序 print(b)
结果:
a = np.array([4, 3, 1, 2]) j = np.argsort(a) #索引位置排序 print(j) print(a[j]) 结果: [2 3 1 0] [1 2 3 4]
六、矩阵扩充
a = np.arange(0, 40, 10) print(a) b = np.tile(a, (3, 5)) #行扩展成原来的3倍,列扩展成原来的5倍 print(b) 结果: [ 0 10 20 30] [[ 0 10 20 30 0 10 20 30 0 10 20 30 0 10 20 30 0 10 20 30] [ 0 10 20 30 0 10 20 30 0 10 20 30 0 10 20 30 0 10 20 30] [ 0 10 20 30 0 10 20 30 0 10 20 30 0 10 20 30 0 10 20 30]]




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号