java 多线程 线程组ThreadGroup;多线程的异常处理。interrupt批量停止组内线程;线程组异常处理
1,线程组定义:
线程组存在的意义,首要原因是安全。java默认创建的线程都是属于系统线程组,而同一个线程组的线程是可以相互修改对方的数据的。但如果在不同的线程组中,那么就不能“跨线程组”修改数据,可以从一定程度上保证数据安全。默认情况下,我们创建的线程都在系统线程组,不过我们可以自定义自己的线程组。
线程组内部可以有线程组,组中还可以有线程,类似于下图:
线程组创建:
- new ThreadGroup("test线程组")
常用方法:
- activeGroupCount()
- activeGroupCount()获取子线程组个数
- enumerate(threadGroups) 将线程组内子线程,或子线程组 组复制到数组中
-
interrupt(); 批量停止线程组里面所有线程
2,线程加入线程组:
定义两个线程,然后一个线程组,分别把两个线程加入到对应的线程组
public class ThreadGroupTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Runnable r = () ->{ String tName = Thread.currentThread().getName(); System.out.println(tName +":运行中"); }; ThreadGroup testGroup = new ThreadGroup("test线程组"); Thread thread1 = new Thread(testGroup,r,"线程1"); Thread thread2 = new Thread(testGroup,r,"线程2"); Thread thread3 = new Thread(testGroup,r,"线程3"); thread1.start();thread2.start();thread3.start(); //查看线程组下有多少活跃线程 System.out.println(testGroup.toString() + "下活跃线程数:" + testGroup.activeCount()); //java.lang.ThreadGroup[name=test线程组,maxpri=10]下活跃线程数:3 } }
3,线程组多级嵌套:线程组下面还有线程组
/** * @ClassName ThreadGroupInThreadGroup * @projectName: object1 * @author: Zhangmingda * @description: XXX * date: 2021/4/26. */ public class ThreadGroupInThreadGroup { public static void main(String[] args) { Runnable runnable = ()-> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "运行中"); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }; ThreadGroup parentGroup = new ThreadGroup("parent"); ThreadGroup childGroup = new ThreadGroup(parentGroup,"child"); Thread thread = new Thread(childGroup, runnable, "线程A"); Thread thread1 = new Thread(childGroup, runnable, "线程B"); Thread thread2 = new Thread(parentGroup, runnable, "线程C"); thread.start();thread1.start();thread2.start(); //常用方法 System.out.println("parentGroup 下有" + parentGroup.activeGroupCount() + "个活跃线程组"); //activeGroupCount()获取子线程组个数 ThreadGroup[] threadGroups = new ThreadGroup[parentGroup.activeGroupCount()]; parentGroup.enumerate(threadGroups); //enumerate(threadGroups) 将线程组内子线程组复制到数组中 for (ThreadGroup threadGroup:threadGroups){ System.out.println(threadGroup.getName()); //child } Thread[] threads = new Thread[childGroup.activeCount()]; childGroup.enumerate(threads); for (Thread t : threads){ System.out.println("子线程组中线程:" + t.getName()); } } }

4、线程组的自动归属特性:
就是说我们新创建一个线程组,这个线程组默认就归属到当前线程所在的线程组中:
public class AutoGroupTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //首先获取一下当前线程所在的线程组 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup().getName()); ThreadGroup testGroup = new ThreadGroup("测试线程组"); System.out.println(testGroup.getParent().getName()); } }
5,批量停止线程组里面所有的线程:interrupt
/** * @ClassName ThreadExitAllThreadInGroup * @projectName: object1 * @author: Zhangmingda * @description: XXX * date: 2021/4/26. */ public class ThreadExitAllThreadInGroup { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ThreadGroup threadGroup = new ThreadGroup("test线程组"); Runnable r = () -> { String tName = Thread.currentThread().getName(); System.out.println(tName + ":线程运行中"); while (!Thread.interrupted()){} System.out.println(tName + ":线程运行结束"); }; for (int i=0; i<10; i++){ new Thread(threadGroup,r, "T" + i).start(); } Thread.sleep(1000); threadGroup.interrupt(); } }
6,多线程的异常处理:
单个线程设置异常处理:thread.setUncaughtExceptionHandler
/** * @ClassName ThreadGroupException * @projectName: object1 * @author: Zhangmingda * @description: XXX * date: 2021/4/26. */ public class ThreadGroupException { public static void main(String[] args) { Runnable r = () ->{ int a = 1/0; }; Thread thread = new Thread(r,"test"); thread.setUncaughtExceptionHandler(new Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler() { @Override public void uncaughtException(Thread thread, Throwable throwable) { System.err.println(thread.getName() + "抛出异常:" + throwable.getMessage()); } }); thread.start(); } }
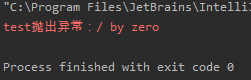
多个线程设置异常处理:Thread.setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(new Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler)
/** * @ClassName ThreadGroupException * @projectName: object1 * @author: Zhangmingda * @description: XXX * date: 2021/4/26. */ public class ThreadGroupException { public static void main(String[] args) { Runnable r = () ->{ int a = 1/0; }; Thread thread = new Thread(r,"test"); Thread thread1 = new Thread(r,"test1"); Thread thread2 = new Thread(r,"test2"); Thread.setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(new Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler() { @Override public void uncaughtException(Thread thread, Throwable throwable) { System.err.println(thread.getName() + "抛出异常:" + throwable.getMessage()); } }); // thread.setUncaughtExceptionHandler(new Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler() { // @Override // public void uncaughtException(Thread thread, Throwable throwable) { // System.err.println(thread.getName() + "抛出异常:" + throwable.getMessage()); // } // }); thread.start();thread1.start();thread2.start(); } }
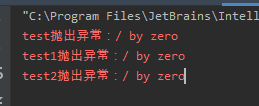
7,线程组的异常怎么处理:
思路:之定义一个线程组,继承ThreadGroup,然后重写ThreadGroup的uncaughtExceptionHandler方法。
注:
本例threadGroup 线程组实例为 Thread类的匿名子类实例化的写法
/** * @ClassName ThreadGroupException * @projectName: object1 * @author: Zhangmingda * @description: XXX * date: 2021/4/26. */ public class ThreadGroupException { public static void main(String[] args) { Runnable r = () -> { int a = 1/0; }; ThreadGroup threadGroup = new ThreadGroup("TEST-Group"){ @Override public void uncaughtException(Thread t, Throwable e) { System.err.println( "线程组:" + getName() + "下的线程:"+ t.getName() + "出现了异常:" + e.getMessage()); } }; for (int i=0; i<10; i++) { new Thread(threadGroup, r, "线程" + i).start(); } } }
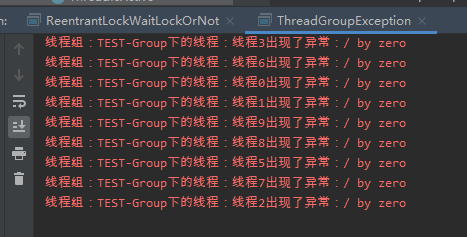
posted on 2021-04-26 16:23 zhangmingda 阅读(377) 评论(0) 收藏 举报



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号