function newton_method_optimization()
% 初始点设置(可自行修改测试多个起点)
x = [1; 1; 1; 1];
% 停止条件与最大迭代次数
tolerance = 1e-6;
maxIterations = 100;
iteration = 0;
% 打印表头
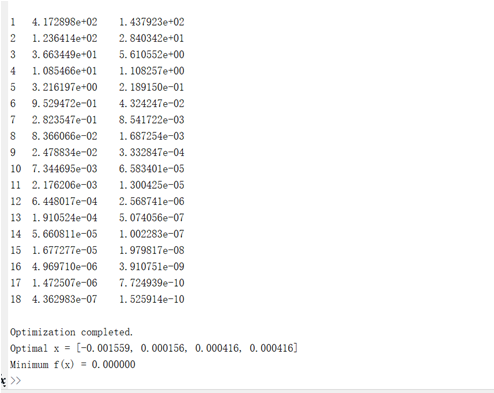
fprintf('Iter\t||Gradient||\tFunction Value\n');
while iteration < maxIterations
grad = computeGradient(x);
hess = computeHessian(x);
gradNorm = norm(grad);
fprintf('%d\t%e\t%e\n', iteration, gradNorm, objectiveFunction(x));
% 检查停止条件
if gradNorm < tolerance
break;
end
% 计算更新方向并更新变量
direction = -hess \ grad;
x = x + direction;
iteration = iteration + 1;
end
% 输出最终结果
fprintf('\nOptimization completed.\n');
fprintf('Optimal x = [%.6f, %.6f, %.6f, %.6f]\n', x);
fprintf('Minimum f(x) = %.6f\n', objectiveFunction(x));
end
% ------------------ 目标函数 ------------------
function value = objectiveFunction(x)
value = (x(1) + 10*x(2))^2 + ...
5*(x(3) - x(4))^2 + ...
(x(2) - 2*x(3))^4 + ...
10*(x(1) - x(4))^4;
end
% ------------------ 梯度函数 ------------------
function grad = computeGradient(x)
grad = zeros(4,1);
grad(1) = 2*(x(1) + 10*x(2)) + 40*(x(1) - x(4))^3;
grad(2) = 20*(x(1) + 10*x(2)) + 4*(x(2) - 2*x(3))^3;
grad(3) = 10*(x(3) - x(4)) - 8*(x(2) - 2*x(3))^3;
grad(4) = -10*(x(3) - x(4)) - 40*(x(1) - x(4))^3;
end
% ------------------ Hessian矩阵函数 ------------------
function H = computeHessian(x)
H = zeros(4,4);
% 二阶导数计算(Hessian矩阵)
H(1,1) = 2 + 120*(x(1) - x(4))^2;
H(1,2) = 20;
H(1,3) = 0;
H(1,4) = -120*(x(1) - x(4))^2;
H(2,1) = 20;
H(2,2) = 200 + 12*(x(2) - 2*x(3))^2;
H(2,3) = -24*(x(2) - 2*x(3))^2;
H(2,4) = 0;
H(3,1) = 0;
H(3,2) = -24*(x(2) - 2*x(3))^2;
H(3,3) = 10 + 48*(x(2) - 2*x(3))^2;
H(3,4) = -10;
H(4,1) = -120*(x(1) - x(4))^2;
H(4,2) = 0;
H(4,3) = -10;
H(4,4) = 10 + 120*(x(1) - x(4))^2;
end
![]()




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号