路飞之登录注册接口
路飞之登录注册接口
登录接口
接口分析可知,登录注册接口需要五个接口,分别是校验手机号是否存在的接口、多方式登录接口(用户名/手机号/邮箱+密码),发送手机验证码接口(借助于第三方短信平台)、短信登录接口、注册接口
-
总路由分发user路由
# 总路由 path('api/v1/user/',include('user.urls')) # 路由 from rest_framework.routers import SimpleRouter from .views import UserView router = SimpleRouter() # 访问 http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/v1/user/userinfo/send_msg ---->get 发送短信 router.register('userinfo',UserView , 'userinfo') urlpatterns = [ ] urlpatterns += router.urls
验证手机号接口
# 验证手机号是否存在的逻辑
保证发送您短信接口安全,不被第三方盗用。
1.加频率限制(频率限制,只能限制手机号一分钟发一次,不能限制接口一分钟访问一次)
2.随机字符串
跨站请求伪造csrf
解决方法:
发送post请求的页面,后端就生产一个随机字符串,给前端
如果要发送post请求(一般用来增加,修改数据),需要携带一个随机字符串,如果没有带就禁止。
视图层
from rest_framework.viewsets import GenericViewSet
from rest_framework.decorators import action
from user.models import User
from utils.common_response import APIResponse
# # 第一版本
# 验证手机号是否存在
# class UserView(GenericViewSet):
# @action(methods=['GET'],detail=False)
# def check_mobile(self,request,*args,**kwargs): # 保证这个接口的安全(短信轰炸机--》解析出了好多网站的发送短信接口,用多线程)
# mobile = request.query_params['mobile']
# if mobile:
# user=User.objects.filter(mobile=mobile).first()
# if user:
# return APIResponse(code=100,msg='手机号存在',exist=True)
# else:
# return APIResponse(code=100,msg='手机号不存在',exist=True)
# else:
# return APIResponse(code=888,msg='手机号必填')
# 进阶版本
class UserView(GenericViewSet):
@action(methods=['GET'],detail=False)
def send_msg(self,request,*args,**kwargs): # 保证这个接口的安全(短信轰炸机--》解析出了好多网站的发送短信接口,用多线程)
try:
# 从地址栏中取出手机号 query_params :queryDict
mobile = request.query_params['mobile'] # 取不到值会报错---全局异常
User.objects.get(mobile=mobile)
# get 取不到值返回none
except Exception as e:
raise e
# return APIResponse(code=888,msg='手机号必填')
return APIResponse(msg='手机号存在')
视图层模板
def send_sms(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
try:
# 放心大胆写
except Exception as e:
raise e
return APIResponse()
# 视图函数,视图类的方法,返回值一定是响应对象(django原生的4个,drf的一个,自己封装了一个)
--render,HttpResponse,redirect,response
--Response
--APIResponse
raise 的对象,必须是错误对象 KeyError,APIException,LqzException
多方式登录接口
前端发送post请求---{username:kiki,password:123}---后端做逻辑判断-----login——mul
- 取出前端用户名和密码
- 判断用户名对应的值是手机号/邮箱/姓名
- 数据库比对手机号/邮箱/用户名
- 比对成功就签发token给前端
视图类
from utils.common_response import APIResponse
from .serializer import UserLoginSerializer
class UserView(GenericViewSet):
@action(methods=['POST'], detail=False)
def login_mul(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
把这个逻辑放在序列化类中
1.取出前端传入的用户名和密码
2.通过用户名和密码去数据库查询用户
3.如果能查到,签发token
4.返回给前端登录成功
"""
# 实例化 序列化类对象时,可以传入context 字典 context 是 视图类和序列化类沟通的桥梁
# 序列化类全局钩子,放入的
# 有了序列化类对象,通过 对象.context 就可以拿到值
ser = self.get_serializer(data=request.data)
ser.is_valid(raise_exception=True) # 执行这句话,会走字段自己的校验,局部钩子,全局钩子
token = ser.context.get('token')
username = ser.context.get('username')
return APIResponse(token=token, username=username) # {code:100,msg:成功,token:aasdfa,username:kimi}
序列化类
import re
from rest_framework import serializers
from .models import User
from rest_framework.exceptions import APIException
from rest_framework_jwt.settings import api_settings
jwt_payload_handler = api_settings.JWT_PAYLOAD_HANDLER
jwt_encode_handler = api_settings.JWT_ENCODE_HANDLER
# 这个序列化类用来校验字段---不做序列化,也不做反序列化
class UserLoginSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
""" 重写username,因为序列化就是校验字段是唯一性,重写把原来的规则去掉"""
username = serializers.CharField()
class Meta:
model = User
# username映射过来,是唯一的,字段自己的校验就过不了,所有要重写这个字段
fields = ['username', 'password'] # 这个序列化类用来校验字段---不做序列化,也不做反序列化
"""
把这个逻辑放在序列化类中
1.取出前端传入的用户名和密码
2.通过用户名和密码去数据库查询用户
3.如果能查到,签发token
4.返回给前端登录成功
"""
# 全局钩子
def validate(self, attrs):
"""attrs 是前端传入的数据,经过 字段自己校验和局部钩子校验过后的数据 {username:kimi,password:123} """
user = self._get_user(attrs)
token = self._get_token(user)
self.context['token'] = token
self.context['username'] = user.username
return attrs
# 在类内部,隐藏属性和方法, __ 开头
# 公司里约定俗成,不用 __ ,使用 _ ,表示不想给外部用,但是实在想用,根据名字直接用
def _get_user(self, attrs):
username = attrs.get('username')
password = attrs.get('password')
# 校验三种类型
if re.match(r'^1[3-9][0-9]{9}$', username):
user = User.objects.filter(mobile=username).first()
elif re.match(r'^[a-zA-Z0-9_.-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9-]+(\\.[a-zA-Z0-9-]+)*\.[a-zA-Z0-9]{2,6}$', username):
user = User.objects.filter(email=username).first()
else:
user = User.objects.filter(username=username).first()
if user and user.check_password(password):
return user
else:
# 用户不存在或密码错误 这里的代码,还是在全局钩子中执行,全局钩子校验失败,要抛异常,所以在这抛异常
raise APIException('用户名不存在或者密码错误')
def _get_token(self, user):
payload = jwt_payload_handler(user)
token = jwt_encode_handler(payload)
return token
腾讯云短信申请
# 发送短信接口,借助于第三方短信平台,收费的
-腾讯云短信
-阿里 大于短信
# 申请微信公众号
# 使用腾讯短信
1.https://cloud.tencent.com,微信扫码登录
2.搜索短信:https://console.cloud.tencent.com/smsv2
3.创建短信签名:公众号注册,提交等待审核
4.创建短信正文模版
5.等待审核
6.发送短信
python---短信
# API SDK
API: 咱们学习过的API接口,写起来比较麻烦,自己分析接口
SDK:集成开发工具包,分语言,java,python,go
只要官方提供sdk,优先用sdk
pip install tencentcloud-sdk-python
补充
# https://gitee.com/aeasringnar/django-RESTfulAPI/tree/master
# https://gitee.com/aeasringnar
腾讯云短信
借助于第三方平台:腾讯云短信,使用SDK3.0版本,不仅有发送短信还有运功能的其他功能。
SDK的使用
1. 安装SDK
方式一
pip install tencentcloud-sdk-python
方式二
- 源码安装,下载源码(源码中有setup) ,执行--
python setup.py install会安装源码到解释器中 script文件中新建一个文件,放置发送短信的代码
2. 封装发送短信
使用python 对api进行封装成包--将发送短信的封装成一个包,后续直接导入包,发送短信--传入参数就可以使用打包的短信
包的好处:下次导入包就能直接导入包下的__init__.py ,将包下的py文件导入__init__.py,导入包就能使用包下的方法
libs下新建一个包send_sms_v3
# libs下:
send_sms_v3
__init__.py # 导入验证码和发送短信
settings.py
sms.py
# __init__.py
from .sms import get_code,send_sms
# 变量统一写在配置,可扩展性高
# settings.py
SECRET_ID = ''
SECRET_KEY = ''
APP_ID = ''
SIGN_NAME = ''
TEMPLATE_ID = ''
# sms.py
from tencentcloud.common import credential
from tencentcloud.common.exception.tencent_cloud_sdk_exception import TencentCloudSDKException
# 导入对应产品模块的client models。
from tencentcloud.sms.v20210111 import sms_client, models
# 导入可选配置类
from tencentcloud.common.profile.client_profile import ClientProfile
from tencentcloud.common.profile.http_profile import HttpProfile
from libs.send_sms_v3 import settings
import random
import json
# 生成n位数字验证码的函数
def get_code(number=4):
code = ''
for i in range(number):
code += str(random.randint(0, 9)) # python 是强类型语言,不同类型运算不允许
return code
# 发送短信函数
def send_msg(code, mobile):
try:
# 实例化一个认证对象,入参需要传入腾讯云账户密钥对secretId,secretKey。
# 这里采用的是从环境变量读取的方式,需要在环境变量中先设置这两个值。
cred = credential.Credential(settings.SECRETID, settings.SECRETKEY)
httpProfile = HttpProfile()
httpProfile.reqMethod = "POST" # post请求(默认为post请求)
httpProfile.reqTimeout = 30 # 请求超时时间,单位为秒(默认60秒)
httpProfile.endpoint = "sms.tencentcloudapi.com" # 指定接入地域域名(默认就近接入)
clientProfile = ClientProfile()
clientProfile.signMethod = "TC3-HMAC-SHA256" # 指定签名算法
clientProfile.language = "en-US"
clientProfile.httpProfile = httpProfile
client = sms_client.SmsClient(cred, "ap-guangzhou", clientProfile)
req = models.SendSmsRequest()
# 基本类型的设置:
# 短信应用ID: 短信SdkAppId在 [短信控制台] 添加应用后生成的实际SdkAppId,示例如1400006666
# 应用 ID 可前往 [短信控制台](https://console.cloud.tencent.com/smsv2/app-manage) 查看
req.SmsSdkAppId = settings.SDKAPPID
# 短信签名内容: 使用 UTF-8 编码,必须填写已审核通过的签名
req.SignName = settings.SIGNNAME
# 模板 ID: 必须填写已审核通过的模板 ID
req.TemplateId = settings.TEMPLATEID
# 模板参数: 模板参数的个数需要与 TemplateId 对应模板的变量个数保持一致,,若无模板参数,则设置为空
req.TemplateParamSet = [code, '1']
# 下发手机号码,采用 E.164 标准,+[国家或地区码][手机号]
req.PhoneNumberSet = ["+86" + mobile, ]
req.SessionContext = ""
req.ExtendCode = ""
req.SenderId = ""
resp = client.SendSms(req)
# 输出json格式的字符串回包
print(resp.to_json_string(indent=2))
res = json.loads(resp.to_json_string(indent=2))
if res.get('SendStatusSet')[0].get('Code')=='Ok':
return True
else:
return False
except TencentCloudSDKException as err:
print(err)
return False
发送短信验证码接口
后端根据路由---视图函数--取出前端的code和本地缓存中的code做比较,相同就发送信息,发送信息可同步发送或异步发送。
# 前端发送post请求----{"mobile":"122334"}
# 后端获取验证码接口
class UserView(GenericViewSet):
serializer_class = UserLoginSerializer
queryset = User.objects.all().filter(is_active=True)
@action(methods=['POST'], detail=False)
def send_msg(self, request):
try:
mobile = request.data['mobile']
# 生成验证码
code = get_code()
# 一定要找个地方存一下,存到缓存中,key值唯一
# 目前没学redis,暂时先存在内存中【项目部署会有坑】,后期要使用redis作为缓存
cache.set('msg_code%s' % mobile, code)
res = send_msg_ss(mobile,code) # # 同步发送,后期可以改成异步 后期学了celery可以加入异步 目前咱们可以使用 多线程
if res:
return APIResponse(msg='短信发送成功')
else:
return APIResponse(code=101, msg='短信发送失败')
# 异步发送
# from threading import Thread
# t = Thread(target=send_msg,args=[code,mobile])
# t.start()
# return APIResponse(msg='短信已发送')
except Exception as e:
raise APIException(str(e))
短信登录接口
# 前端发送post请求----{"mobile":"122334","code":"8888"}
# 视图类的方法中的逻辑
1.取出手机号和验证码
2.验证验证码是否正确(发送验证码接口,存储验证码)
-session:根本不用
-全局变量:不好,可能会取不到,集群环境中可能不是同一个线程里的
- 缓存:django 自带缓存
from django.core.cache import cache
-cache.set()
-cache.get()
3.根据手机号查询用户
4. 如何查到签发token
5.返回给前端
关于逻辑判断都在序列化里面执行了,判断路由请求(login_msg)---》是否验证验证码是否正确---》正确存验证码---》根据前端发送的手机号和验证,判断验证码是否是该手机的验证码---》是返回用户及签发token成功
视图类
class UserView(GenericViewSet):
# class UserView(ViewSetMixin, GenericAPIView):
serializer_class = UserLoginSerializer
queryset = User.objects.all().filter(is_active=True)
# 手机短信登录校验
# 重写get_serializer_class方法
def get_serializer_class(self):
if self.action == 'login_msg':
return UserModelLoginSerializer
else:
return super().get_serializer_class()
def _login(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
ser = self.get_serializer(data=request.data)
ser.is_valid(raise_exception=True) # 执行这句话,会走字段自己的校验,局部钩子,全局钩子
token = ser.context.get('token')
username = ser.context.get('username')
return APIResponse(token=token, username=username)
# 登录短信校验
@action(methods=['POST'], detail=False)
def login_msg(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return self._login(request)
序列化类
# 相同部抽取出来
class BaseUserSerializer:
# 全局钩子
def validate(self, attrs):
"""attrs 是前端传入的数据,经过 字段自己校验和局部钩子校验过后的数据 {username:kimi,password:123} """
user = self._get_user(attrs)
token = self._get_token(user)
self.context['token'] = token
self.context['username'] = user.username
return attrs
def _get_user(self,attrs):
raise Exception('你必须重写它')
def _get_token(self, user):
payload = jwt_payload_handler(user)
token = jwt_encode_handler(payload)
return token
class UserModelLoginSerializer(BaseUserSerializer, serializers.ModelSerializer):
mobile = serializers.CharField()
code = serializers.CharField()
class Meta:
model = User
fields = ['mobile', 'code'] # code 不是表的字段,要重写 ,mobile 有唯一约束,需要重写
def _get_user(self, attrs):
# 取出前端的code和mobile
code = attrs.get('code')
mobile = attrs.get('mobile')
# 从缓存中取出
old_code = cache.get('msg_code %s' % mobile) # 拿code
if code and old_code == code:
# 根据手机号,查到用户
user = User.objects.filter(mobile=mobile).first()
if user:
return user
else:
raise APIException('用户不存在')
else:
raise APIException('验证码验证失败')
短信注册接口
路由
# 前端---》{mobile:1888344,code:8888,password:123}--->post
# http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/v1/user/register/ --->post 请求
router.register('register',views.RegisterUserView,'register')
视图类
注册要把数据存入数据库中,上述都是在序列化里面写逻辑,根据所学知识,想要继承GenericViewSet自动生成路由并创建数据,要搭配CreateModelMixin。这里要注意create方法里面serialiazer.data是序列化字段的,但前端传入的code不是模型表字段,程序走到create方法这里就会报错。所以要重写create方法,剔除code后再保存。
class RegisterView(GenericViewSet,CreateModelMixin):
queryset = User.objects.all()
serializer_class = RegisterSerializer
def create(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
# 第二种方法
# 使用父类的会出发序列化,一定要让code只读
super().create(request, *args, **kwargs)
# serializer.data就会序列化
# 第一种方式
# serializer = self.get_serializer(data=request.data)
# serializer.is_valid(raise_exception=True)
# self.perform_create(serializer)
return APIResponse(msg='注册成功')
序列化类
# 数据校验,反序列化 只要调用ser.data,就会触发序列化,而code不是表的字段,一序列化报错了
class RegisterSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
# mobile和password都是表字段,code不是需要重写
code = serializers.CharField(max_length=4, write_only=True) # 反序列化
class Meta:
model = User
fields = ['mobile', 'code', 'password']
extra_kwargs = {
'password': {'write_only': True}
}
def validate(self, attrs): # 全局校验
'''
1 取出前端传入的code,校验code是否正确
2 把username设置成手机号(你可以随机生成),用户名如果不传,存库进不去
3 code 不是数据库的字段,从attrs中剔除
'''
code = attrs.get('code')
mobile = attrs.get('mobile')
old_code = cache.get('msg_code %s' % mobile) # 拿code
if old_code and old_code == code:
# 验证码存在 踢除code 存用户
attrs['username'] = mobile
attrs.pop('code')
else:
raise APIException('验证码验证失误')
return attrs
def create(self, validated_data): # 一定要重写create方法,因为auth的user表的密码是密码,我们传入的是明文
# validated_data={username:18888,mobile:18888,password:123}
# 创建用户
user = User.objects.create_user(**validated_data)
# 一定要返回user 后期,ser.data 会使用当前返回的对象做序列化
return user
登录注册页面分析
页面点击登录---》弹出了登录组件---》盖住了整个屏幕(定位)---》登录和注册操作----》点击登录/注册组件中的x----》关闭登录/注册组件
登录页面
1.1 Login.vue
<template>
<div class="login">
<span style="padding: 50px" @click="closeLogin">X</span>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Login",
methods:{
closeLogin(){
this.$emit('go_close')
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.login {
width: 100vw;
height: 100vh;
position: fixed;
top: 0;
left: 0;
z-index: 10;
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5);
}
</style>
Header.vue
<div class="right-part">
<div>
<span @click="goLogin">登录</span>
<span class="line">|</span>
<span>注册</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<Login v-if="login_show" @go_close="goClose"></Login>
goLogin() {
this.login_show = true
},
goClose() {
this.login_show = false
}
登录页面
短信登录:手机验证码登录---》输入框输入手机号---》监听失去焦点事件---》手机号正则校验(js),查询手机号是否存在----》发送验证码的按钮可以点击---》点击发送验证码按钮---》ajax 发送验证码---》起了个定时任务---》手机收到了验证码,填入验证码框-----》点击登录按钮----》向后端发送登录ajax请求----》返回给前端token和username----》前端保存到cookie中----》子传父,关闭了登录模态框----》在Header.vue 取了一下token和username
多方式登录:多方式登录---》输入用户名和密码后----》点击登录--》后端登录成功,返回username和token---》后面的同上
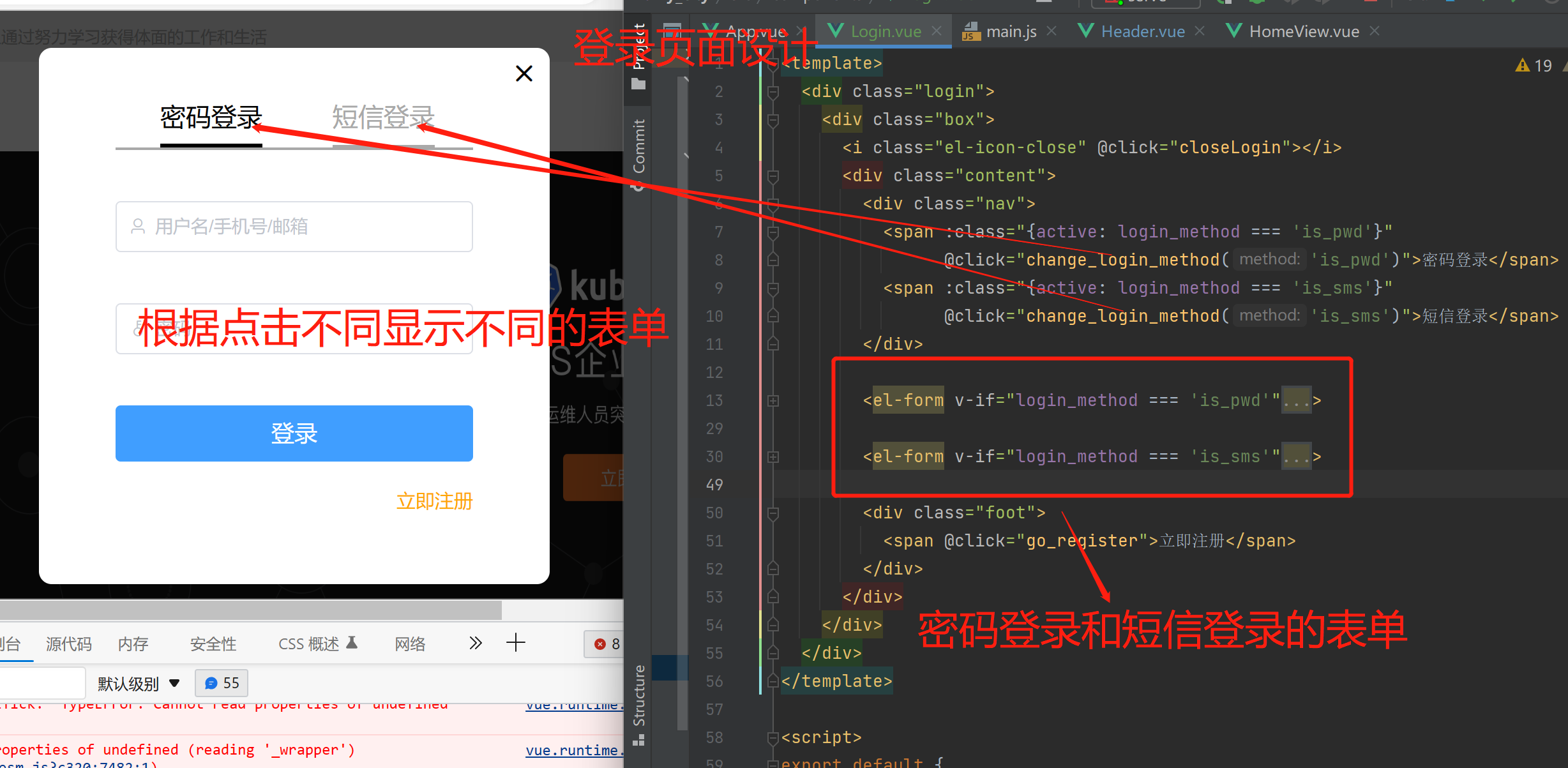
Login.vue
点击查看代码
<template>
<div class="login">
<div class="box">
<i class="el-icon-close" @click="closeLogin"></i>
<div class="content">
<div class="nav">
<span :class="{active: login_method === 'is_pwd'}"
@click="change_login_method('is_pwd')">密码登录</span>
<span :class="{active: login_method === 'is_sms'}"
@click="change_login_method('is_sms')">短信登录</span>
</div>
<el-form v-if="login_method === 'is_pwd'">
<el-input
placeholder="用户名/手机号/邮箱"
prefix-icon="el-icon-user"
v-model="username"
clearable>
</el-input>
<el-input
placeholder="密码"
prefix-icon="el-icon-key"
v-model="password"
clearable
show-password>
</el-input>
<el-button type="primary" @click="login">登录</el-button>
</el-form>
<el-form v-if="login_method === 'is_sms'">
<el-input
placeholder="手机号"
prefix-icon="el-icon-phone-outline"
v-model="mobile"
clearable
@blur="check_mobile">
</el-input>
<el-input
placeholder="验证码"
prefix-icon="el-icon-chat-line-round"
v-model="sms"
clearable>
<template slot="append">
<span class="sms" @click="send_sms">{{ sms_interval }}</span>
</template>
</el-input>
<el-button @click="mobile_login" type="primary">登录</el-button>
</el-form>
<div class="foot">
<span @click="go_register">立即注册</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Login",
data(){
return{
username: '',
password: '',
mobile: '',
sms: '', // 验证码
login_method: 'is_pwd',
sms_interval: '获取验证码',
is_send: false,
}
},
methods:{
// 关闭登录页面
closeLogin(){
this.$emit('close')
},
// 跳转注册页面
go_register() {
this.$emit('go')
},
// 根据登录方式显示不同的登录页面
change_login_method(method){
this.login_method = method;
},
// 校验号码
check_mobile(){
if(!this.mobile)return;
// js正则:/正则语法/
// '字符串'.match(/正则语法/)
if(!this.mobile.match(/^1[3-9][0-9]{9}$/)){
// 手机不存在显示的内容
this.$message({
message: '手机号有误',
type: 'warning',
duration: 1000,
onClose: () => {
this.mobile = '';
}
});
}else {
// 手机号前端校验通过---》开始后端手机号是否存在的校验
// 后台校验手机号是否已存在
this.$axios({
url:this.$settings.BASE_URL+'/user/userinfo/check_mobile/',
method:"get",
params:{
mobile:this.mobile
}
}).then(response=>{
// code 如果是100,说明手机号存在,登录功能,才能发送短信
// == 只比较值是否相等
// === 即比较值,又比较类型
if(response.data.code==100){
this.$message({
message:'账号正常',
type:'success',
duration:1000,
});
//号码正在,开始验证验证码
// 发生验证码按钮才可以被点击
this.is_send = true;
}else {
this.$message({
message: '账号不存在',
type: 'warning',
duration: 1000,
onClose: () => {
this.mobile = '';
}
})
}
}).catch(()=>{});
}
},
// 发送短信
send_sms(){
console.log(this.is_send)
// this.is_send 如果是false,函数直接结束,就不能发送短信---没有校验手机号
if(!this.is_send)return;
//按钮点一次立即禁用
this.is_send = false;
// 添加验证码倒计时
let sms_interval_time = 60;
this.sms_interval="发送中...";
// 定时器: setInterval(fn, time, args)
// 往后台发送验证码
this.$axios({
url:this.$settings.BASE_URL+'/user/userinfo/send_msg/',
method:'post',
data:{
mobile:this.mobile
}
}).then(response=>{
if(response.data.code==100){ // 发送成功
//启动定时器
console.log(response.data.code)
let timer = setInterval(()=>{
if(sms_interval_time<=1){
clearInterval(timer);
this.sms_interval='获取验证码';
this.is_send = true; // 重新恢复点击发送功能的条件
}else {
sms_interval_time -= 1;// 计时器自减-1
this.sms_interval=`${sms_interval_time}秒后再发`;
}
},1000);
}else {//发送失败
this.sms_interval = "重新获取";
this.is_send = true;
this.$message({
message: '短信发送失败',
type: 'warning',
duration: 3000
});
}
}).catch(()=>{
this.sms_interval='频率过快';
this.is_send=true;
})
},
// 短信登录校验
mobile_login(){
if(!(this.mobile && this.sms)){
this.$message({
message: '请填好手机与验证码',
type: 'warning',
duration: 1500
});
return false // 直接结束逻辑
}
this.$axios({
url: this.$settings.BASE_URL + '/user/userinfo/login_msg/',
method: 'post',
data:{
mobile:this.mobile,
code:this.sms,
},
}).then(response=>{
console.log(response.data.username)
let username = response.data.username
let token = response.data.token
// 放到cookie中,7天过期
this.$cookies.set('username',username,'7d')
this.$cookies.set('token',token,'7d')
// 关闭登录框
this.$emit('success')
}).catch(error=>{
console.log(error.response.data)
})
},
// 用户密码登录
login(){
if (!(this.username && this.password)) {
this.$message({
message: '请填好账号密码',
type: 'warning',
duration: 1500
});
return false // 直接结束逻辑
}
this.$axios({
url:this.$settings.BASE_URL+'/user/userinfo/login_mul/',
method:'post',
data:{
username:this.username,
password:this.password,
}
}).then(response=>{
console.log(response.data)
let username = response.data.username;
let token = response.data.token;
this.$cookies.set('username', username, '7d');
this.$cookies.set('token', token, '7d');
this.$emit('success', response.data.result);
}).catch(error=>{
console.log(error.response.data)
})
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.login {
width: 100vw;
height: 100vh;
position: fixed;
top: 0;
left: 0;
z-index: 10;
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.7);
}
.box {
width: 400px;
height: 420px;
background-color: white;
border-radius: 10px;
position: relative;
top: calc(50vh - 210px);
left: calc(50vw - 200px);
}
.el-icon-close {
position: absolute;
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 20px;
top: 10px;
right: 10px;
cursor: pointer;
}
.el-icon-close:hover {
color: darkred;
}
.content {
position: absolute;
top: 40px;
width: 280px;
left: 60px;
}
.nav {
font-size: 20px;
height: 38px;
border-bottom: 2px solid darkgrey;
}
.nav > span {
margin: 0 20px 0 35px;
color: darkgrey;
user-select: none;
cursor: pointer;
padding-bottom: 10px;
border-bottom: 2px solid darkgrey;
}
.nav > span.active {
color: black;
border-bottom: 3px solid black;
padding-bottom: 9px;
}
.el-input, .el-button {
margin-top: 40px;
}
.el-button {
width: 100%;
font-size: 18px;
}
.foot > span {
float: right;
margin-top: 20px;
color: orange;
cursor: pointer;
}
.sms {
color: orange;
cursor: pointer;
display: inline-block;
width: 70px;
text-align: center;
user-select: none;
}
</style>
注册页面
注册逻辑:输入手机号---》监听失去焦点事件---》手机号正则校验(js),查询手机号是否存在-如果不存在---》发送验证码的按钮可以点击---》点击发送验证码按钮---》ajax 发送验证码---》起了个定时任务---》手机收到了验证码,填入验证码框-----》填入密码---》点击注册---》调用注册接口完成注册----》子传父---》Register.vue---->显示出Login.vue
Register.vue
点击查看代码
<template>
<div class="register">
<div class="box">
<i class="el-icon-close" @click="close_register"></i>
<div class="content">
<div class="nav">
<span class="active">新用户注册</span>
</div>
<el-form>
<el-input
placeholder="手机号"
prefix-icon="el-icon-phone-outline"
v-model="mobile"
clearable
@blur="check_mobile">
</el-input>
<el-input
placeholder="密码"
prefix-icon="el-icon-key"
v-model="password"
clearable
show-password>
</el-input>
<el-input
placeholder="验证码"
prefix-icon="el-icon-chat-line-round"
v-model="sms"
clearable>
<template slot="append">
<span class="sms" @click="send_sms">{{ sms_interval }}</span>
</template>
</el-input>
<el-button @click="register" type="primary">注册</el-button>
</el-form>
<div class="foot">
<span @click="go_login">立即登录</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Register",
data() {
return {
mobile: '',
password: '',
sms: '',
sms_interval: '获取验证码',
is_send: false,
}
},
methods: {
close_register() {
this.$emit('close', false)
},
go_login() {
this.$emit('go')
},
check_mobile() {
if (!this.mobile) return;
// js正则:/正则语法/
// '字符串'.match(/正则语法/)
if (!this.mobile.match(/^1[3-9][0-9]{9}$/)) {
this.$message({
message: '手机号有误',
type: 'warning',
duration: 1000,
onClose: () => {
this.mobile = '';
}
});
return false;
}
// 后台校验手机号是否已存在
this.$axios({
url: this.$settings.BASE_URL + '/user/userinfo/check_mobile/',
method: 'get',
params: {
mobile: this.mobile
}
}).then(response => {
// 手机号不存在,才能发送短信,才能注册
if (response.data.code != 100) {
this.$message({
message: '欢迎注册我们的平台',
type: 'success',
duration: 1500,
});
// 发生验证码按钮才可以被点击
this.is_send = true;
} else { // 手机号存在--直接登录
this.$message({
message: '账号已存在,请直接登录',
type: 'warning',
duration: 1500,
})
}
}).catch(() => {
});
},
send_sms() {
// this.is_send必须允许发生验证码,才可以往下执行逻辑
if (!this.is_send) return;
// 按钮点一次立即禁用
this.is_send = false;
let sms_interval_time = 60;
this.sms_interval = "发送中...";
// 往后台发送验证码
this.$axios({
url: this.$settings.BASE_URL + '/user/userinfo/send_msg/',
method: 'post',
data: {
mobile: this.mobile
}
}).then(response => {
if (response.data.code==100) { // 发送成功
let timer = setInterval(() => {
if (sms_interval_time <= 1) {
clearInterval(timer);
this.sms_interval = "获取验证码";
this.is_send = true; // 重新回复点击发送功能的条件
} else {
sms_interval_time -= 1;
this.sms_interval = `${sms_interval_time}秒后再发`;
}
}, 1000);
} else { // 发送失败
this.sms_interval = "重新获取";
this.is_send = true;
this.$message({
message: '短信发送失败',
type: 'warning',
duration: 3000
});
}
}).catch(() => {
this.sms_interval = "频率过快";
this.is_send = true;
})
},
register() {
if (!(this.mobile && this.sms && this.password)) {
this.$message({
message: '请填好手机、密码与验证码',
type: 'warning',
duration: 1500
});
return false // 直接结束逻辑
}
this.$axios({
url: this.$settings.BASE_URL + '/user/register/',
method: 'post',
data: {
mobile: this.mobile,
code: this.sms,
password: this.password
}
}).then(response => {
this.$message({
message: '注册成功,3秒跳转登录页面',
type: 'success',
duration: 3000,
showClose: true,
onClose: () => {
// 去向成功页面
this.$emit('success')
}
});
}).catch(error => {
this.$message({
message: '注册失败,请重新注册',
type: 'warning',
duration: 1500,
showClose: true,
onClose: () => {
// 清空所有输入框
this.mobile = '';
this.password = '';
this.sms = '';
}
});
})
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.register {
width: 100vw;
height: 100vh;
position: fixed;
top: 0;
left: 0;
z-index: 10;
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3);
}
.box {
width: 400px;
height: 480px;
background-color: white;
border-radius: 10px;
position: relative;
top: calc(50vh - 240px);
left: calc(50vw - 200px);
}
.el-icon-close {
position: absolute;
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 20px;
top: 10px;
right: 10px;
cursor: pointer;
}
.el-icon-close:hover {
color: darkred;
}
.content {
position: absolute;
top: 40px;
width: 280px;
left: 60px;
}
.nav {
font-size: 20px;
height: 38px;
border-bottom: 2px solid darkgrey;
}
.nav > span {
margin-left: 90px;
color: darkgrey;
user-select: none;
cursor: pointer;
padding-bottom: 10px;
border-bottom: 2px solid darkgrey;
}
.nav > span.active {
color: black;
border-bottom: 3px solid black;
padding-bottom: 9px;
}
.el-input, .el-button {
margin-top: 40px;
}
.el-button {
width: 100%;
font-size: 18px;
}
.foot > span {
float: right;
margin-top: 20px;
color: orange;
cursor: pointer;
}
.sms {
color: orange;
cursor: pointer;
display: inline-block;
width: 70px;
text-align: center;
user-select: none;
}
</style>
Header.vue
点击查看代码
<template>
<div class="header">
<div class="slogan">
<p>老男孩IT教育 | 帮助有志向的年轻人通过努力学习获得体面的工作和生活</p>
</div>
<div class="nav">
<ul class="left-part">
<li class="logo">
<router-link to="/">
<img src="../assets/img/head-logo.svg" alt="">
</router-link>
</li>
<li class="ele">
<span @click="goPage('/free-course')" :class="{active: url_path === '/free-course'}">免费课</span>
</li>
<li class="ele">
<span @click="goPage('/actual-course')" :class="{active: url_path === '/actual-course'}">实战课</span>
</li>
<li class="ele">
<span @click="goPage('/light-course')" :class="{active: url_path === '/light-course'}">轻课</span>
</li>
</ul>
<div class="right-part">
<div v-if="!username">
<span @click="goLogin">登录</span>
<span class="line">|</span>
<span @click="goRegister">注册</span>
</div>
<div v-else>
<span>{{ username }}</span>
<span class="line">|</span>
<span @click="clickClose">注销</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<Login v-if="is_login" @close="close_login" @go="put_register" @success="success_login"/>
<Register v-if="is_register" @close="close_register" @go="put_login" @success="success_register"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Login from "@/components/Login";
import Register from "@/components/Register"
export default {
name: "Header",
data() {
return {
// 当前所在路径,去sessionStorage取的,如果取不到,就是 /
url_path: sessionStorage.url_path || '/',
is_login: false,
is_register: false,
username: this.$cookies.get('username'),
token: this.$cookies.get('token'),
}
},
methods:{
goPage(url_path) {
// 已经是当前路由就没有必要重新跳转
if (this.url_path !== url_path) {
this.$router.push(url_path);
}
sessionStorage.url_path = url_path;
},
// 点击显示登录页面
goLogin(){
this.is_login = true;
this.is_register = false;
},
// 点击显示注册页面
goRegister(){
this.is_login = false;
this.is_register=true
},
// 前往注册页面
put_register(){
this.is_login = false;
this.is_register = true;
},
//前往登录页面
put_login() {
this.is_login = true;
this.is_register = false;
},
// 关闭登录页面
close_login() {
this.is_login = false;
},
// 关闭注册页面
close_register() {
this.is_register = false;
},
// 登录成功 保存username和token
success_login() {
this.is_login = false;
this.username = this.$cookies.get('username')
this.token = this.$cookies.get('token')
},
// 注册成功显示登录页面
success_register() {
this.is_login = true
this.is_register = false
},
// 注销回到首页
clickClose(){
this.$router.push('/');
// 注销要清空cookies中存的数据---简单的前端逻辑
this.username=this.$cookies.remove()
}
},
created() {
// 组件加载万成,就取出当前的路径,存到sessionStorage this.$route.path
sessionStorage.url_path = this.$route.path;
// 把url_path = 当前路径
this.url_path = this.$route.path;
},
components:{
Login,
Register
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.header {
background-color: white;
box-shadow: 0 0 5px 0 #aaa;
}
.header:after {
content: "";
display: block;
clear: both;
}
.slogan {
background-color: #eee;
height: 40px;
}
.slogan p {
width: 1200px;
margin: 0 auto;
color: #aaa;
font-size: 13px;
line-height: 40px;
}
.nav {
background-color: white;
user-select: none;
width: 1200px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.nav ul {
padding: 15px 0;
float: left;
}
.nav ul:after {
clear: both;
content: '';
display: block;
}
.nav ul li {
float: left;
}
.logo {
margin-right: 20px;
}
.ele {
margin: 0 20px;
}
.ele span {
display: block;
font: 15px/36px '微软雅黑';
border-bottom: 2px solid transparent;
cursor: pointer;
}
.ele span:hover {
border-bottom-color: orange;
}
.ele span.active {
color: orange;
border-bottom-color: orange;
}
.right-part {
float: right;
}
.right-part .line {
margin: 0 10px;
}
.right-part span {
line-height: 68px;
cursor: pointer;
}
</style>


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号