论文解读-《Inductive Representation Learning on Large Graphs》
1.论文介绍
论文题目:Inductive Representation Learning on Large Graphs
论文发表:NIPS 2017
论文背景

2.研究背景
这篇论文之前的图学习的模式都是transductive(直推学习),本文开创了 inductive模式(归纳学习)
解释transductive和inductive之间的区别:
1,在数据集的切分上,inductive归纳学习是将训练集,验证集,测试集切分到不同的子图上进行,transductive直推学习的各个数据(训练,验证,测试集)都是在一个图下的。
2,transductive learning在模型训练过程中使用到了测试集的信息,inductive learning在训练过程中完全不知道测试集信息
3,模型复用,transductive需要针对新节点加入删除或更新时,需要重新训练;inductive则不需要重新训练
4,模型计算量,transductive涉及到全图,一般是大计算量,inductive关注子图,
3. 论文贡献
1,之前的图学习模式是transductive的,本论文首次开创了inductive learning
2,过去的图算法难以适用于大图,或者是全图级别的识别工作;本文算法可适用
4. graphSAGE方法
为节点嵌入方法node embedding approaches的一种,旨在通过节点信息提取的方法来提取到邻居节点的信息。
每一个聚合函数会收集来自不同跳的邻居节点的特征。这个跳也可以称之为邻居节点深度
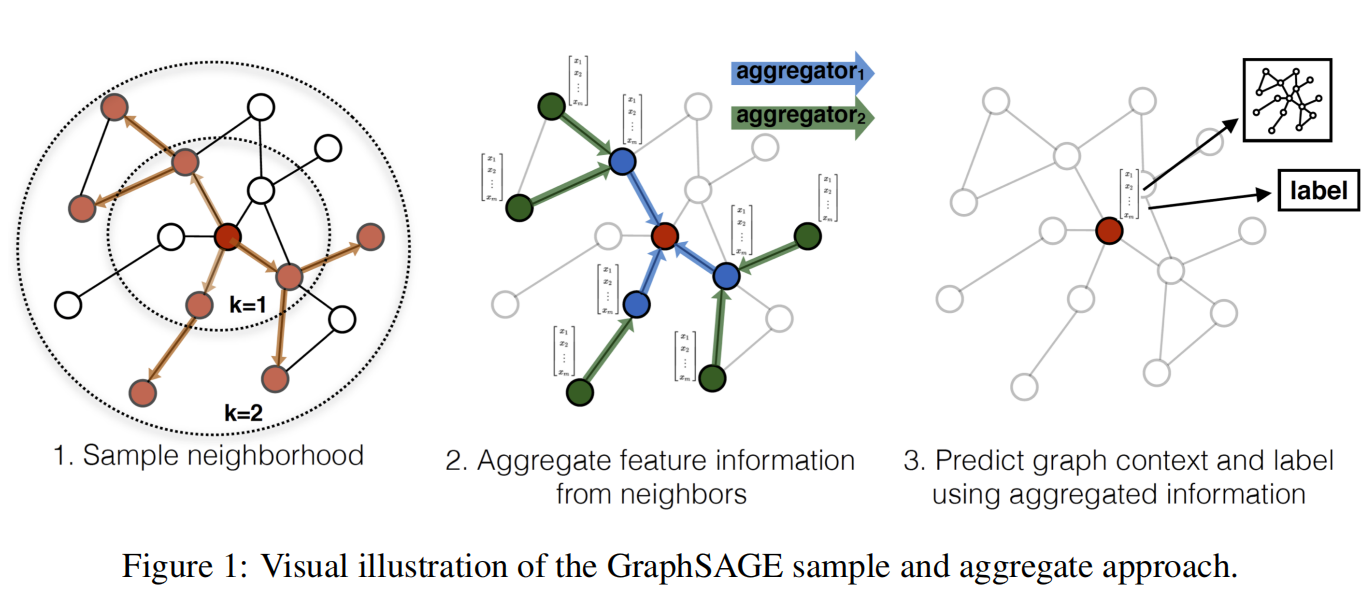
graphSAGE的核心:不需要学习矩阵因子分解后的信息,而是直接学习一个为每个node产生embedding的映射,通过这个映射可以泛化到未知节点。
节点嵌入生成算法流程
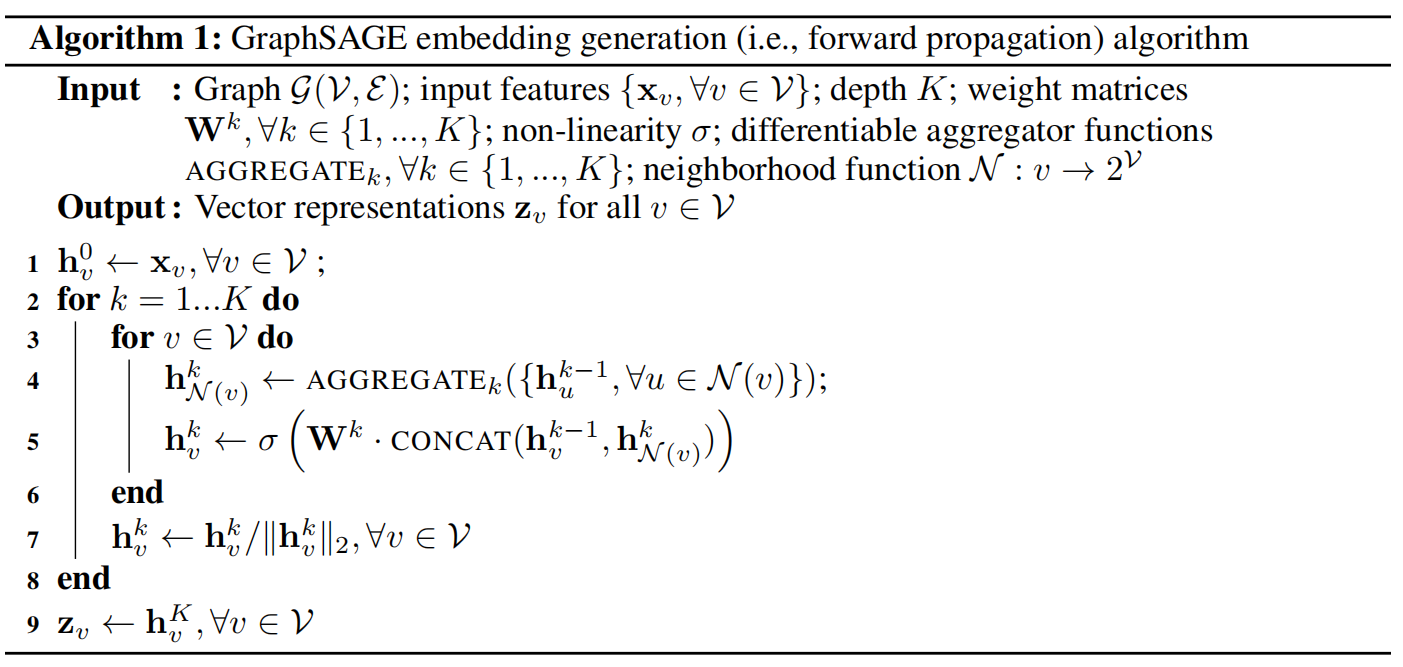
在每次的迭代过程中,顶点会向周围的邻居点进行收集聚合信息,随着多层迭代的叠加,顶点能够聚合到越来越远范围的信息。
学习的损失函数
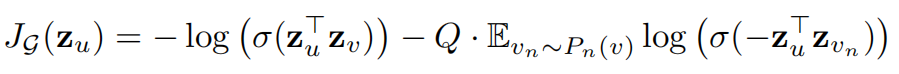
Weisfeiler-Lehman图同构测试
当使用来作为哈希函数的,本算法无法通过wl测试,但是改为可训练的神经网络层,本算法是能够连续逼近wl测试。
邻居采样方法:使用了多种不同的一致性采样方法。因为邻居节点采样,避免了大稀疏矩阵的建立,采样个数K由用户定义。
5. 聚合结构
不同于语音文本图像等结构化数据,图上的节点的邻居节点是没有自然顺序,所以聚合结构需要在一个无序集合上进行操作。由此定义聚合结构的特点:
- 1 ,对称性
- 2,可训练且能包含高度表达能力
介绍三种聚合结构
5.1. mean aggregator 均值聚合
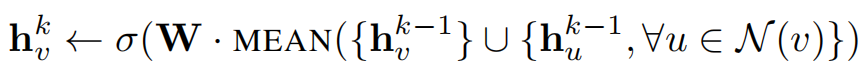
线性接近于一个本地的谱卷积。该方法与其他方法不同的是没有连接操作。
5.2. LSTM聚合
对比与均值聚合,LSTM有着更强的表达能力。但是LSTM是非对称的,且为串行处理。处理方式是简单的把LSTM应用在邻居节点的随机排列上。
5.3. pooling aggregator 池化聚合
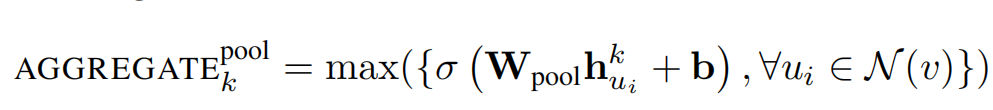
特点是对称且可训练。先对目标顶点的邻居节点的embedding向量进行一次非线性变换,之后进行一次pooling操作。
在实践中发现max-和mean-两种类型的pooling没有显著差异,这里使用的是max-pooling方法。
6. 实验设置
选择了三类数据集进行比较测试,Citation论文引用网络(节点分类问题),Reddit论坛帖子(节点分类问题),PPI蛋白质网络(图分类问题)
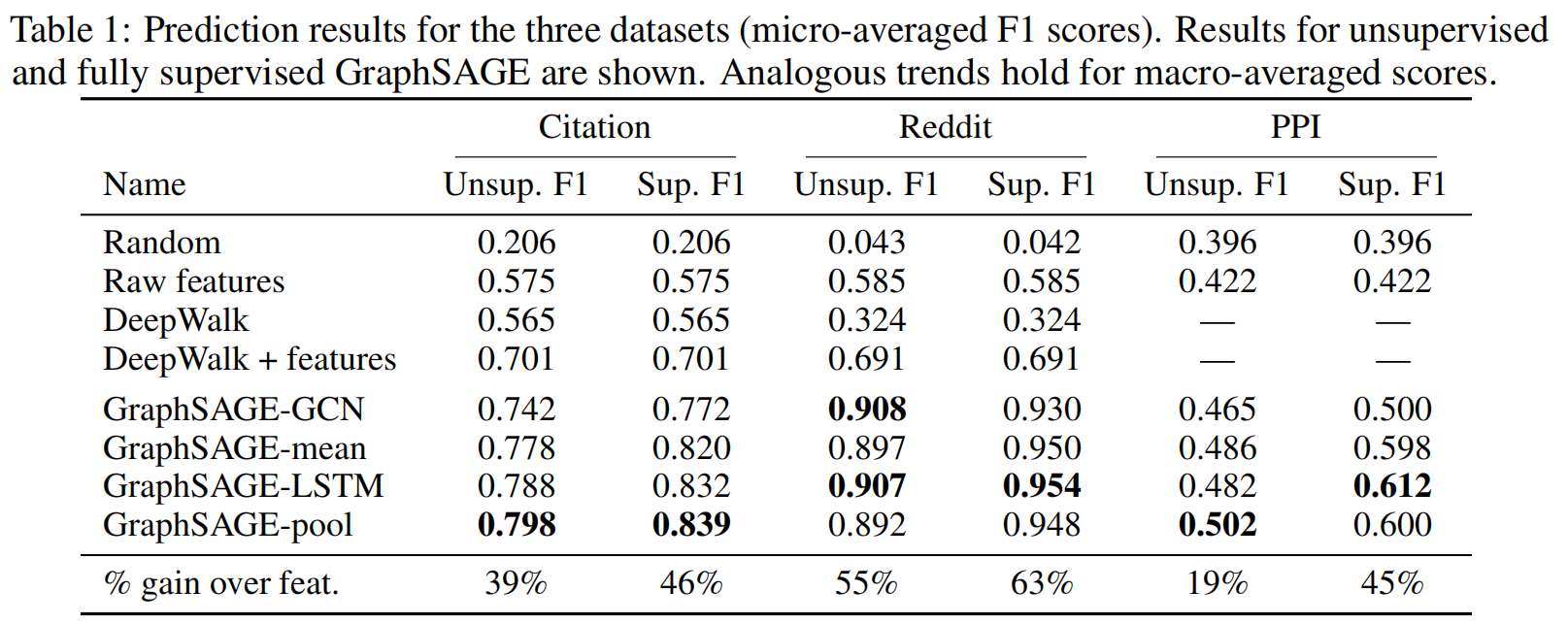
Citation数据集和Reddit数据验证了本算法在节点层面的可用性。
参数设置,一般把K设置为2,相比K=1有10-15的提升,把K往2以上提升的时候,收益仅仅保持在0-5%,但算力消耗的增长为10-100倍率。
各个聚合层的比较
综合来说,LSTM聚合和池化聚合取得了最好的效果。
7. 理论分析
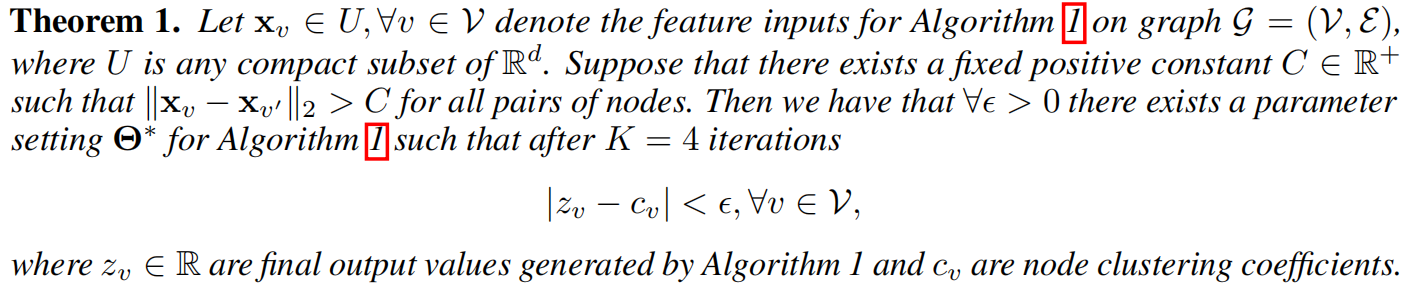
上面的理论说明了存在着一个参数,可以使得图以任意精度的形式逼近聚合系数。
8. 代码示例
整个graphSAGE的网络,可以定义隐藏层的数量。
class GraphSage(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim,
num_neighbors_list):
super(GraphSage, self).__init__()
self.input_dim = input_dim
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.num_neighbors_list = num_neighbors_list
self.num_layers = len(num_neighbors_list)
self.gcn = nn.ModuleList()
self.gcn.append(SageGCN(input_dim, hidden_dim[0]))
for index in range(0, len(hidden_dim) - 2):
self.gcn.append(SageGCN(hidden_dim[index], hidden_dim[index+1]))
self.gcn.append(SageGCN(hidden_dim[-2], hidden_dim[-1], activation=None))
def forward(self, node_features_list):
hidden = node_features_list
for l in range(self.num_layers):
next_hidden = []
gcn = self.gcn[l]
for hop in range(self.num_layers - l):
src_node_features = hidden[hop]
src_node_num = len(src_node_features)
neighbor_node_features = hidden[hop + 1] \
.view((src_node_num, self.num_neighbors_list[hop], -1))
h = gcn(src_node_features, neighbor_node_features)
next_hidden.append(h)
hidden = next_hidden
return hidden[0]
每一层的SageGCN的定义
class SageGCN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim,
activation=F.relu,
aggr_neighbor_method="mean",
aggr_hidden_method="sum"):
"""
aggr_neighbor_method: 邻居特征聚合方法,["mean", "sum", "max"]
aggr_hidden_method: 节点特征的更新方法,["sum", "concat"]
"""
super(SageGCN, self).__init__()
assert aggr_neighbor_method in ["mean", "sum", "max"]
assert aggr_hidden_method in ["sum", "concat"]
self.input_dim = input_dim
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.aggr_neighbor_method = aggr_neighbor_method
self.aggr_hidden_method = aggr_hidden_method
self.activation = activation
self.aggregator = NeighborAggregator(input_dim, hidden_dim,
aggr_method=aggr_neighbor_method)
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(input_dim, hidden_dim))
self.reset_parameters()
def reset_parameters(self):
init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight)
def forward(self, src_node_features, neighbor_node_features):
neighbor_hidden = self.aggregator(neighbor_node_features)
self_hidden = torch.matmul(src_node_features, self.weight)
if self.aggr_hidden_method == "sum":
hidden = self_hidden + neighbor_hidden
elif self.aggr_hidden_method == "concat":
hidden = torch.cat([self_hidden, neighbor_hidden], dim=1)
else:
raise ValueError("Expected sum or concat, got {}"
.format(self.aggr_hidden))
if self.activation:
return self.activation(hidden)
else:
return hidden
邻居节点的聚合器,以三种不同的方式聚合。
class NeighborAggregator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, output_dim,
use_bias=False, aggr_method="mean"):
"""
input_dim: 输入特征的维度
output_dim: 输出特征的维度
use_bias: 是否使用偏置 (default: {False})
aggr_method: 邻居聚合方式 (default: {mean})
"""
super(NeighborAggregator, self).__init__()
self.input_dim = input_dim
self.output_dim = output_dim
self.use_bias = use_bias
self.aggr_method = aggr_method
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(input_dim, output_dim))
if self.use_bias:
self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(self.output_dim))
self.reset_parameters()
def reset_parameters(self):
init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight)
if self.use_bias:
init.zeros_(self.bias)
def forward(self, neighbor_feature):
if self.aggr_method == "mean":
aggr_neighbor = neighbor_feature.mean(dim=1)
elif self.aggr_method == "sum":
aggr_neighbor = neighbor_feature.sum(dim=1)
elif self.aggr_method == "max":
aggr_neighbor = neighbor_feature.max(dim=1)
else:
raise ValueError("Unknown aggr type, expected sum, max, or mean, but got {}"
.format(self.aggr_method))
neighbor_hidden = torch.matmul(aggr_neighbor, self.weight)
if self.use_bias:
neighbor_hidden += self.bias
return neighbor_hidden
9. 总结
算法一脉相承,算法结构比较简答。对比实验简单,本章的亮点在于给出graphSAGE的图重构问题,理论证明。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号