solidity 复杂列表参数签名研究学习
需要参与签名的solidity结构是这样的:
// 定义一个结构体来存储代币地址和数量
struct ReceiverInfo {
address tokenAddress; // 代币合约地址
uint256 amount; // 要分发的代币数量
}
function distributeHash(
uint256 season,
ReceiverInfo[] calldata receiverInfos,
address to,
uint256 uniqueId
) internal returns (bytes32) {
}想法就是把ReceiverInfo[] calldata receiverInfos这种结构整理成字符串然后参与签名,
当然还有其他更好的使用库的abi的相关方法,后续再研究了。
solidity这边签名实现:
function distributeHash(
uint256 season,
ReceiverInfo[] calldata receiverInfos,
address to,
uint256 uniqueId
) internal returns (bytes32) {
require(receiverInfos.length > 0, "invalid receiverInfos!");
string memory receiverInfoStr = receiverInfosToString(receiverInfos);
return
_hashTypedDataV4(
keccak256(
abi.encode(
keccak256(
"distribute(uint256 season,address to,uint256 uniqueId,string receiverInfos)"
),
season,
to,
uniqueId,
keccak256(bytes(receiverInfoStr))
)
)
);
}
// 将 ReceiverInfo 数组转换为字符串的函数
function receiverInfosToString(ReceiverInfo[] calldata receiverInfos) public pure returns (string memory) {
string memory result = "";
uint256 length = receiverInfos.length;
for (uint256 i = 0; i < length; i++) {
string memory tokenAddressStr = addressToString(receiverInfos[i].tokenAddress);
string memory amountStr = uintToString(receiverInfos[i].amount);
// 拼接每个结构体的字符串表示
result = string(abi.encodePacked(result, tokenAddressStr, amountStr));
}
return result;
}签名的类型是:"distribute(uint256 season,address to,uint256 uniqueId,string receiverInfos)" 这里定义成string receiverinfos
所以进行了转换:把列表转成字符串,这样就简单了嘛,二维降成一维:
string memory receiverInfoStr = receiverInfosToString(receiverInfos);需要注意的是这里:
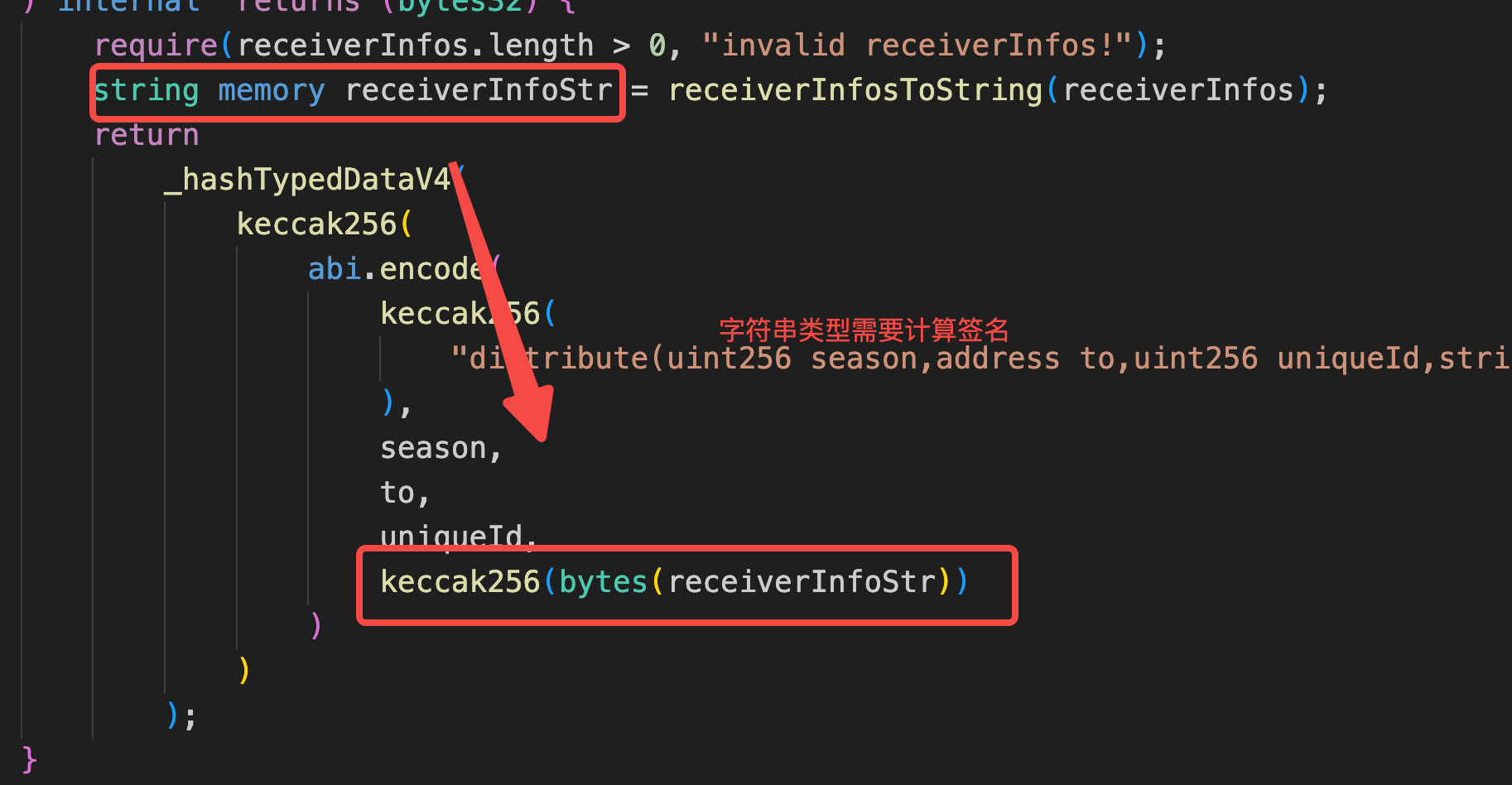
这里是因为go在处理签名的时候:
typedData.HashStruct(typedData.PrimaryType, typedData.Message) 这里面的这个方法:
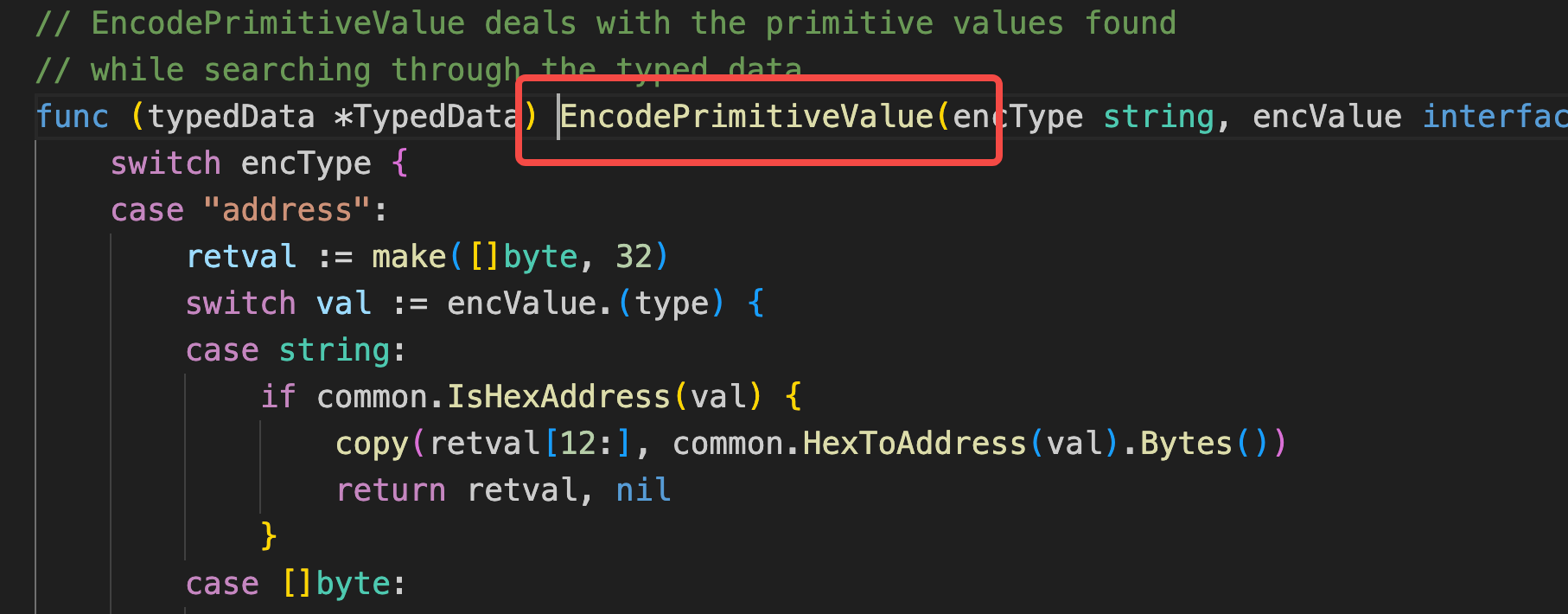
在是string的时候会先计算签名,然后采用签名去进一步签名(这里我整了好久)
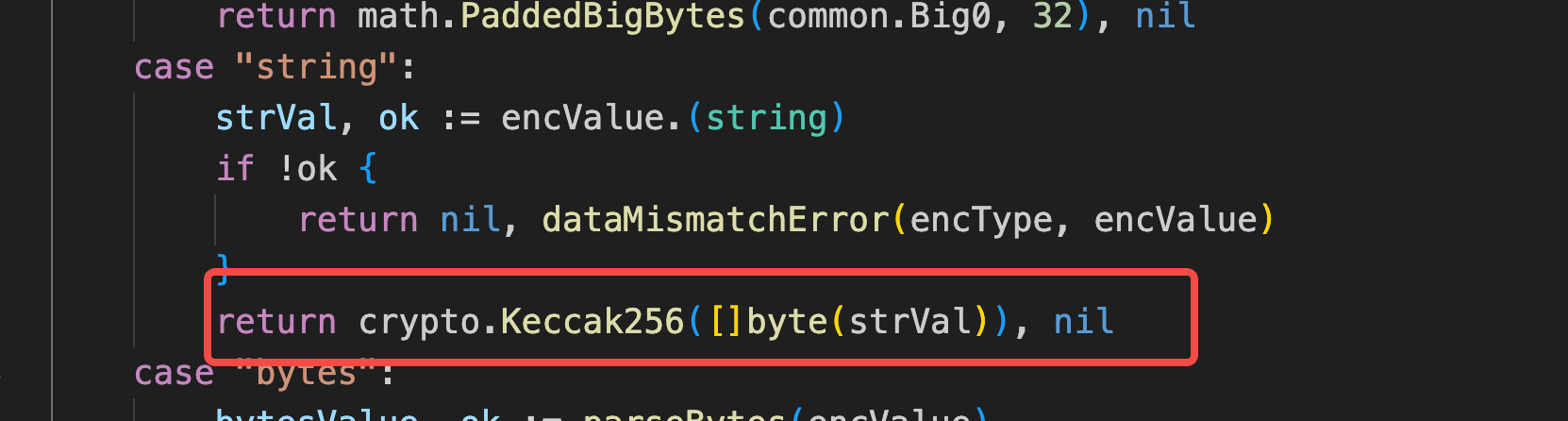
然后贴一下go的签名处理:
func MedalSigner(
privateKeyStr string,
chainId int64,
contract string,
season int64,
uniqueId int64,
to string,
receiverInfos []RewardDistributor.RewardDistributorReceiverInfo,
) (string, error) {
receiverInfoStr := receiverInfosToString(receiverInfos) // 把列表转成字符串
// 签名
typedData := &apitypes.TypedData{
Types: apitypes.Types{
"EIP712Domain": {
{Name: "name", Type: "string"},
{Name: "version", Type: "string"},
{Name: "chainId", Type: "uint256"},
{Name: "verifyingContract", Type: "address"},
},
"distribute": {
{Name: "season", Type: "uint256"},
{Name: "to", Type: "address"},
{Name: "uniqueId", Type: "uint256"},
{Name: "receiverInfos", Type: "string"}, // 这里定义签名为字符串类型
},
},
Domain: apitypes.TypedDataDomain{
Name: "RewardDistributor",
Version: "1.0.0",
ChainId: math.NewHexOrDecimal256(chainId),
VerifyingContract: contract,
Salt: "",
},
Message: map[string]interface{}{
"season": math.NewHexOrDecimal256(season),
"to": to,
"uniqueId": math.NewHexOrDecimal256(uniqueId),
"receiverInfos": receiverInfoStr,
},
PrimaryType: "distribute",
}
privateKey, err := crypto.HexToECDSA(privateKeyStr)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
signature, err := SignWithEip712(privateKey, typedData)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
return hexutil.Encode(signature), nil
}
// receiverInfosToString 函数
func receiverInfosToString(receiverInfos []RewardDistributor.RewardDistributorReceiverInfo) string {
var builder strings.Builder
builder.WriteString("")
for _, info := range receiverInfos {
// 地址统一采用小写编码
addressLower := strings.ToLower(info.TokenAddress.Hex())
builder.WriteString(fmt.Sprintf("%s%d", addressLower, info.Amount))
}
s := builder.String()
fmt.Println("receiverInfosToString: ", s)
return s
}然后就可以正常签名了。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号