ubuntu journal初研究
1. 概要
进入 systemd 时代后,查看日志的方式也发生了变化,原因是 systemd 自带了日志管理服务和工具。单就日志的查看来说,我们需要使用 journalctl 工具。它的好处是使用一个统一的工具来完成日志的查看功能,我们不用记很多的命令了。
journalctl 用来查询 systemd-journald 服务收集到的日志。systemd-journald 服务是 systemd init 系统提供的收集系统日志的服务。
2. 命令帮助
ubuntu@ip-172-31-25-85:~$ journalctl -h
journalctl [OPTIONS...] [MATCHES...]
Query the journal.
Options:
--system Show the system journal
--user Show the user journal for the current user
-M --machine=CONTAINER Operate on local container
-S --since=DATE Show entries not older than the specified date
-U --until=DATE Show entries not newer than the specified date
-c --cursor=CURSOR Show entries starting at the specified cursor
--after-cursor=CURSOR Show entries after the specified cursor
--show-cursor Print the cursor after all the entries
-b --boot[=ID] Show current boot or the specified boot
--list-boots Show terse information about recorded boots
-k --dmesg Show kernel message log from the current boot
-u --unit=UNIT Show logs from the specified unit
--user-unit=UNIT Show logs from the specified user unit
-t --identifier=STRING Show entries with the specified syslog identifier
-p --priority=RANGE Show entries with the specified priority
-g --grep=PATTERN Show entries with MESSSAGE matching PATTERN
--case-sensitive[=BOOL] Force case sensitive or insenstive matching
-e --pager-end Immediately jump to the end in the pager
-f --follow Follow the journal
-n --lines[=INTEGER] Number of journal entries to show
--no-tail Show all lines, even in follow mode
-r --reverse Show the newest entries first
-o --output=STRING Change journal output mode (short, short-precise,
short-iso, short-iso-precise, short-full,
short-monotonic, short-unix, verbose, export,
json, json-pretty, json-sse, cat)
--output-fields=LIST Select fields to print in verbose/export/json modes
--utc Express time in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC)
-x --catalog Add message explanations where available
--no-full Ellipsize fields
-a --all Show all fields, including long and unprintable
-q --quiet Do not show info messages and privilege warning
--no-pager Do not pipe output into a pager
--no-hostname Suppress output of hostname field
-m --merge Show entries from all available journals
-D --directory=PATH Show journal files from directory
--file=PATH Show journal file
--root=ROOT Operate on files below a root directory
--interval=TIME Time interval for changing the FSS sealing key
--verify-key=KEY Specify FSS verification key
--force Override of the FSS key pair with --setup-keys
Commands:
-h --help Show this help text
--version Show package version
-N --fields List all field names currently used
-F --field=FIELD List all values that a specified field takes
--disk-usage Show total disk usage of all journal files
--vacuum-size=BYTES Reduce disk usage below specified size
--vacuum-files=INT Leave only the specified number of journal files
--vacuum-time=TIME Remove journal files older than specified time
--verify Verify journal file consistency
--sync Synchronize unwritten journal messages to disk
--flush Flush all journal data from /run into /var
--rotate Request immediate rotation of the journal files
--header Show journal header information
--list-catalog Show all message IDs in the catalog
--dump-catalog Show entries in the message catalog
--update-catalog Update the message catalog database
--new-id128 Generate a new 128-bit ID
--setup-keys Generate a new FSS key pair3. 使用
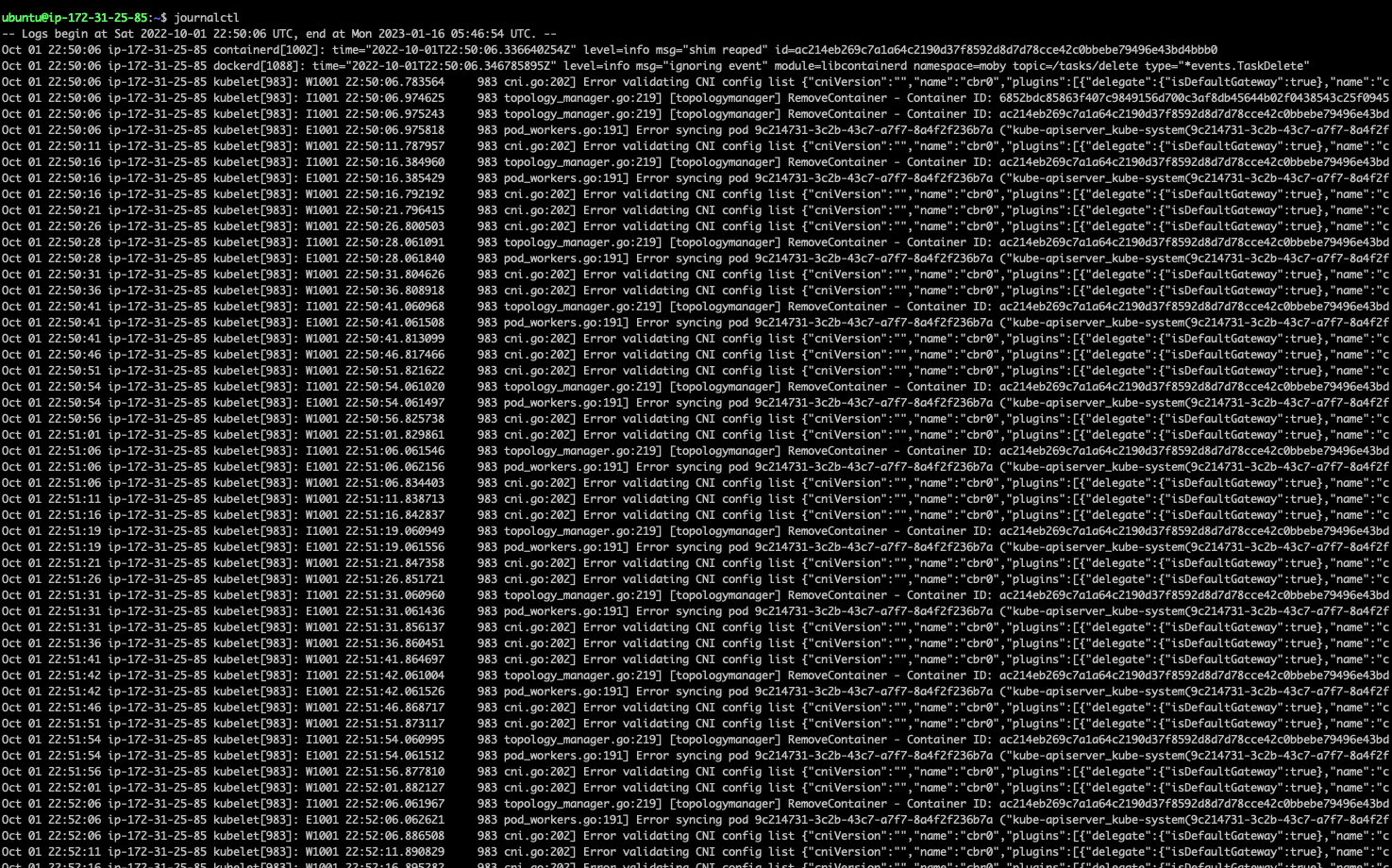
3.1. 输出所有系统日志
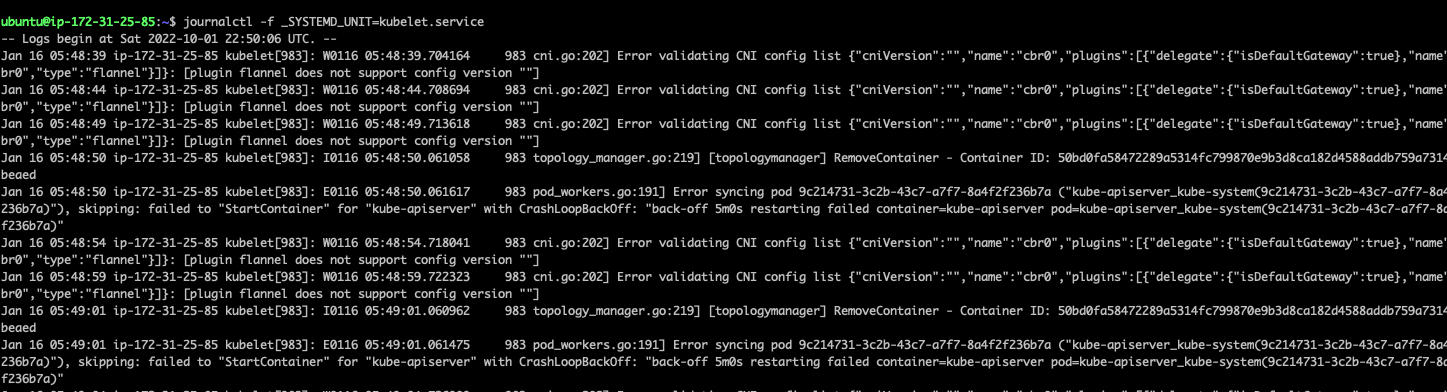
3.2. fellow输出某个服务的系统日志
journalctl -f _SYSTEMD_UNIT=kubelet.service
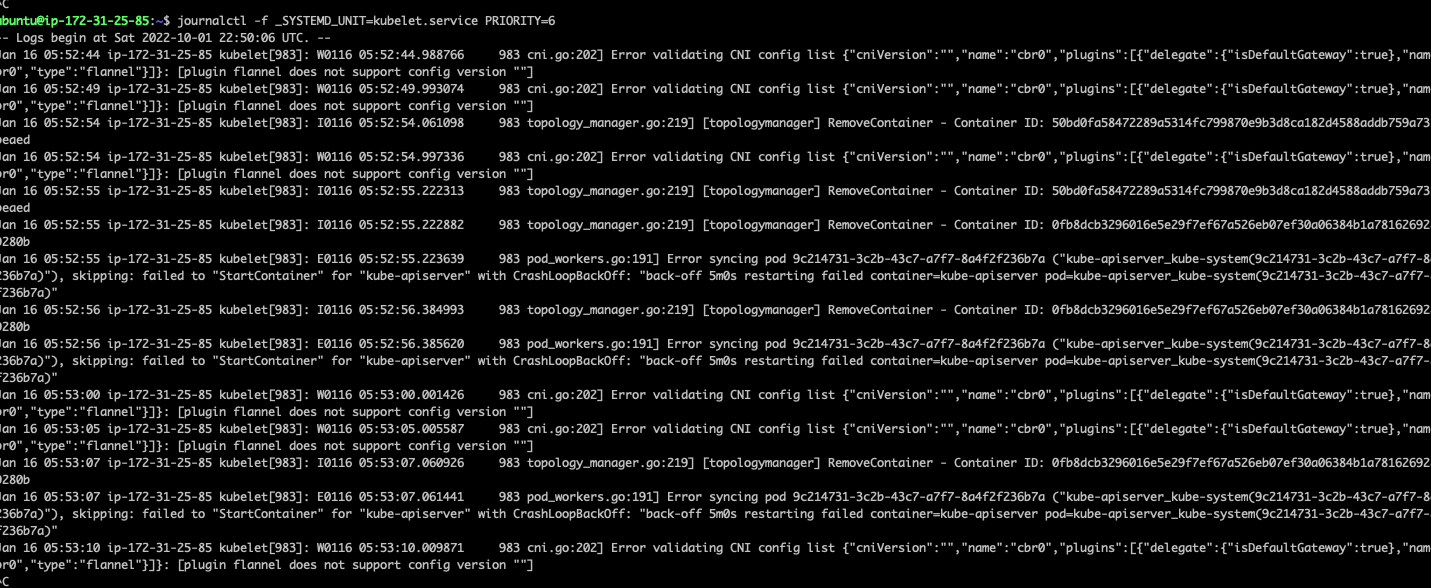
3.3. fellow输出某个服务info以上的系统日志
journalctl -f _SYSTEMD_UNIT=kubelet.service PRIORITY=6
priority等级:
0: emerg
1: alert
2: crit
3: err
4: warning
5: notice
6: info
7: debug
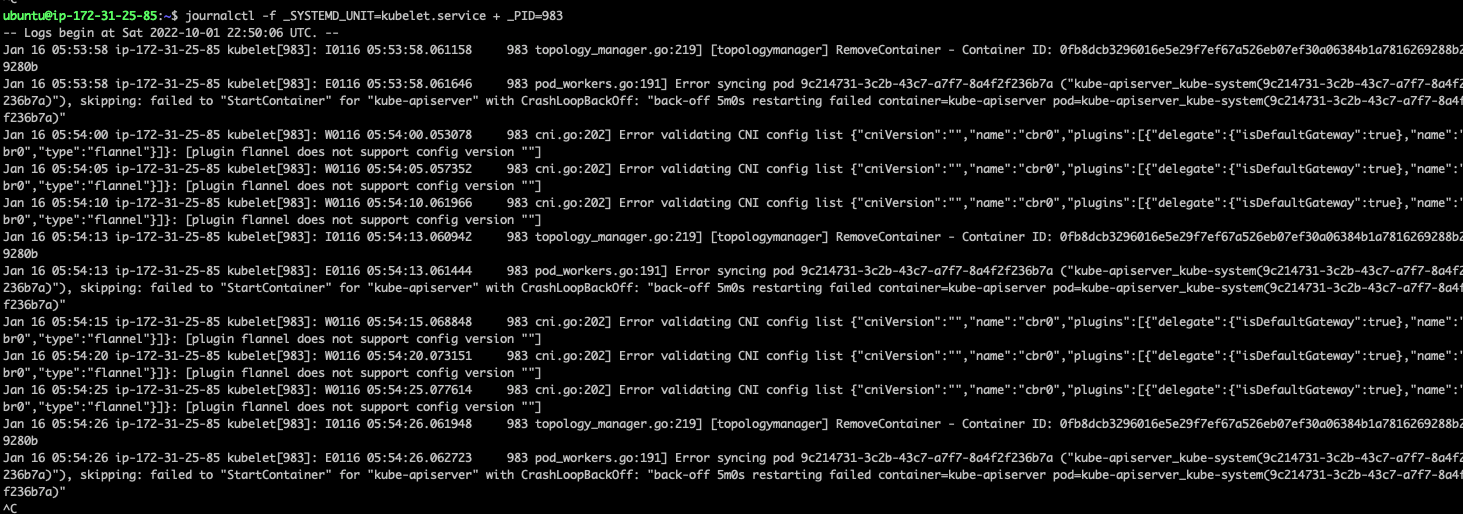
3.4. fellow输出某个服务以及某个pid的日志
journalctl -f _SYSTEMD_UNIT=kubelet.service + _PID=983
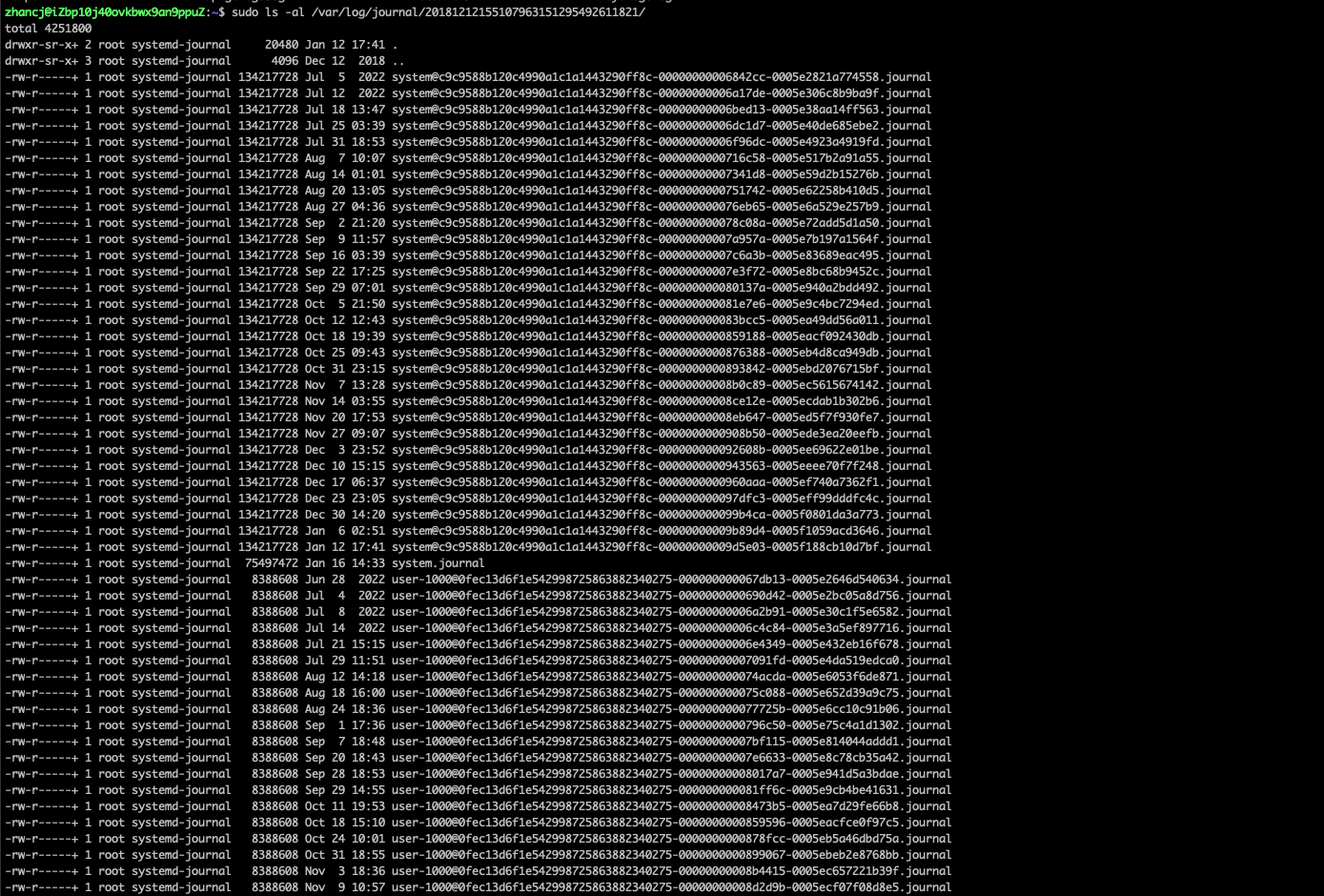
3.5. 查看所有的日志文件:
3.6. 同时应用 match 和时间过滤条件:
实际的使用中更常见的用例是同时应用 match 和时间条件,比如要过滤出某个时间段中 cron 服务的日志记录:
$ sudo journalctl _SYSTEMD_UNIT=cron.service --since "2018-03-27" --until "2018-03-27 01:00"
4. 日志管理
4.1. 查看日志占据的硬盘
ubuntu@ip-172-31-25-85:~$ sudo journalctl --disk-usage
Archived and active journals take up 4.0G in the file system.
ubuntu@ip-172-31-25-85:~$4.2. 使用 –vacuum-size 选项,则可硬性指定日志的总体体积
意味着其会不断删除旧有记录直到所占容量符合要求:
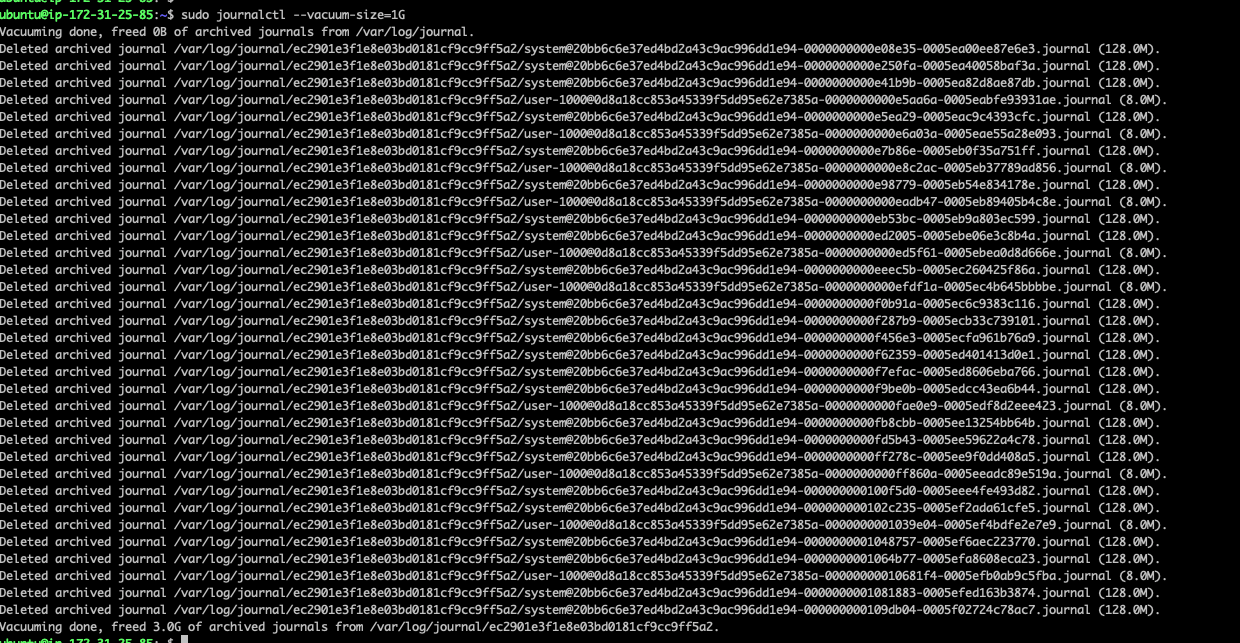
可以看到释放了3G硬盘。
只保留500MB的日志:journalctl --vacuum-size=500M
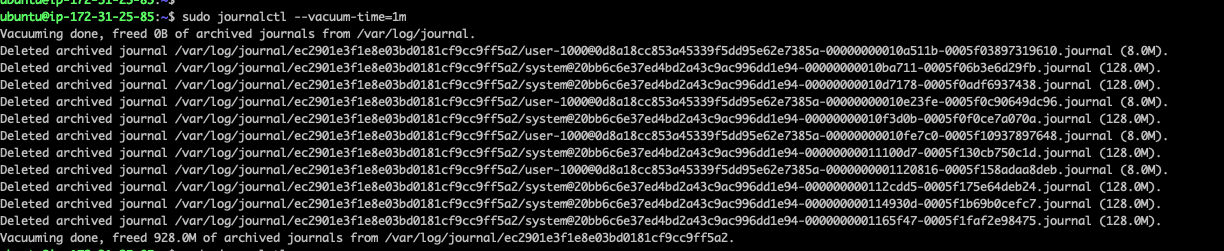
4.3. 使用 –vacuum-time 选项。任何早于这一时间点的条目都将被删除
设置为一个月清空一次




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号