实验6 文件IO与异常处理
实验任务1
代码组织:
contestant.hpp 结构体Contestant定义及其重载运算符函数>>和<<实现
utils.hpp 工具函数实现(排序函数、数据读/写)
task1.cpp 应用代码 + main
contestant.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
struct Contestant {
long id; // 学号
std::string name; // 姓名
std::string major; // 专业
int solved; // 解题数
int penalty; // 总罚时
};
// 重载<<
// 要求:姓名/专业里不含空白符
inline std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& out, const Contestant& c) {
out << std::left;
out << std::setw(15) << c.id
<< std::setw(15) << c.name
<< std::setw(15) << c.major
<< std::setw(10) << c.solved
<< std::setw(10) << c.penalty;
return out;
}
// 重载>>
inline std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& in, Contestant& c) {
in >> c.id >> c.name >> c.major >> c.solved >> c.penalty;
return in;
}
utils.hpp
#pragma once
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include "contestant.hpp"
// ACM 排序规则:先按解题数降序,再按罚时升序
inline bool cmp_by_solve(const Contestant& a, const Contestant& b) {
if(a.solved != b.solved)
return a.solved > b.solved;
return a.penalty < b.penalty;
}
// 将结果写至任意输出流
inline void write(std::ostream& os, const std::vector<Contestant>& v) {
for (const auto& x : v)
os << x << '\n';
}
// 将结果打印到屏幕
inline void print(const std::vector<Contestant>& v) {
write(std::cout, v);
}
// 将结果保存到文件
inline void save(const std::string& filename, const std::vector<Contestant>& v) {
std::ofstream os(filename);
if (!os)
throw std::runtime_error("fail to open " + filename);
write(os, v);
}
// 从文件读取信息(跳过标题行)
inline std::vector<Contestant> load(const std::string& filename) {
std::ifstream is(filename);
if (!is)
throw std::runtime_error("fail to open " + filename);
std::string line;
std::getline(is, line); // 跳过标题
std::vector<Contestant> v;
Contestant t;
int seq;
while (is >> seq >> t)
v.push_back(t);
return v;
}
task1.cpp
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <vector>
#include "contestant.hpp"
#include "utils.hpp"
const std::string in_file = "./data.txt";
const std::string out_file = "./ans.txt";
void app() {
std::vector<Contestant> contestants;
try {
contestants = load(in_file);
std::sort(contestants.begin(), contestants.end(), cmp_by_solve);
print(contestants);
save(out_file, contestants);
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
std::cerr << e.what() << '\n';
return;
}
}
int main() {
app();
}
运行测试结果如下:

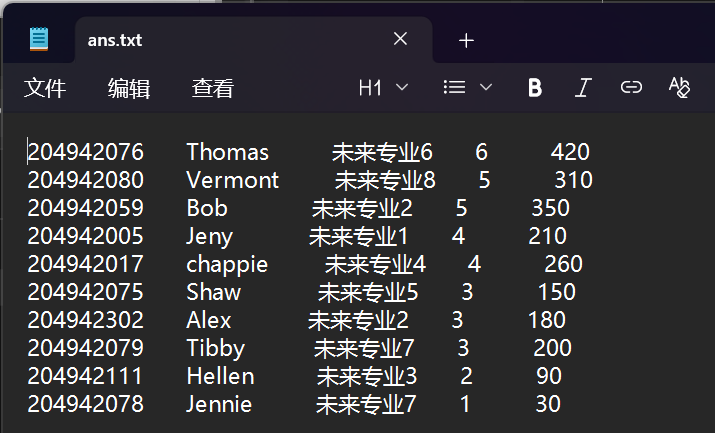
ans.txt:
问题1(1):参数类型std::ostream&传递的是标准库输出流类对象的引用,对象std::cout本身就是标准库输出流类对象,而std::ofstream类是std::ofstream类的派生类,将派生类对象赋给基类引用不会导致数据异常问题,因此,对于std::ostream&类的形参,std::cout和std::fostream类对象都可以作为实参传入
(2):不需要改动,设备提供syd::ostream接口,标准库输出流类对象会自动处理标准输出流与设备硬件的匹配,不需要额外代码控制
问题2:(1)在文件操作函数save()和load()中打开文件失败时会throw抛出异常(2)异常被功能函数app()捕获,捕获后在标准错误流中输出异常的信息
问题3:从代码上看,所给的lambda表达式和cmp_by_solve()函数逻辑一致,功能相同,if语句和? :运算符优化后性能几乎一致,虽然cmp_by_solve()是外部定义的函数,但使用了内联,所以传递的开销也下降了,两种方案性能方面应该没有明显区别
问题4:运行测试结果如下:
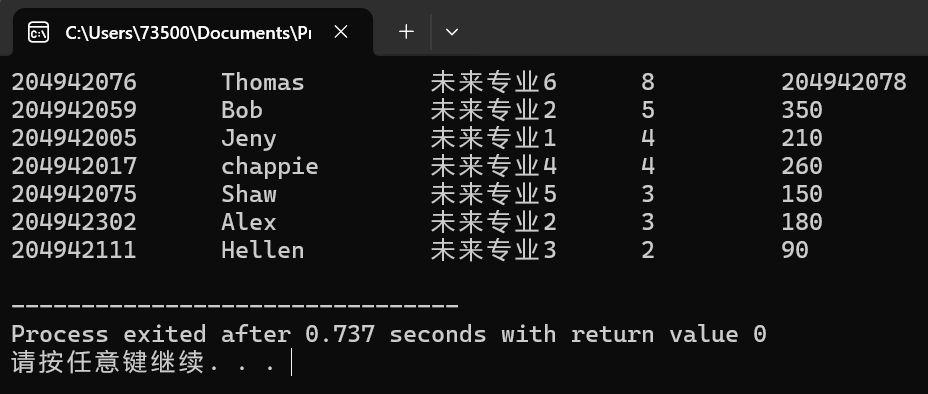
由于空白字段的干扰,语句while(is >> seq >> t)流类对象is在读入变量seq 时由于读取了字符串导致了意外的停止,同时导致数据错位,干扰了排序工作。
修改:
// 从文件读取信息(跳过标题行)
inline std::vector<Contestant> load(const std::string& filename) {
std::ifstream is(filename);
if (!is)
throw std::runtime_error("fail to open " + filename);
std::string line;
std::getline(is, line); // 跳过标题
std::vector<Contestant> v;
Contestant t;
int seq, cnt = 0;
std::string temp;
while (getline(is, temp)) {
try {
++cnt;
t.clear();
if (temp.empty()) {
throw std::invalid_argument("第" + std::to_string(cnt) + "行是空行");
}
std::stringstream ss(temp);
ss >> seq >> t;
if (!t.common()) {
throw std::runtime_error("第" + std::to_string(cnt) + "行数据异常");
}
v.push_back(t);
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
std::cerr << "[warning] " << e.what() << std::endl;
}
}
return v;
}
//Contestant类附加功能实现
void Contestant::clear() {
this->id = -1;
this->name = "\0";
this->major = "\0";
this->solved = -1;
this->penalty = -1;
}
bool Contestant::common() {
return this->id != -1 &&
this->name != "\0" &&
this->major != "\0" &&
this->solved != -1 &&
this->penalty != -1;
}
运行测试结果如下:
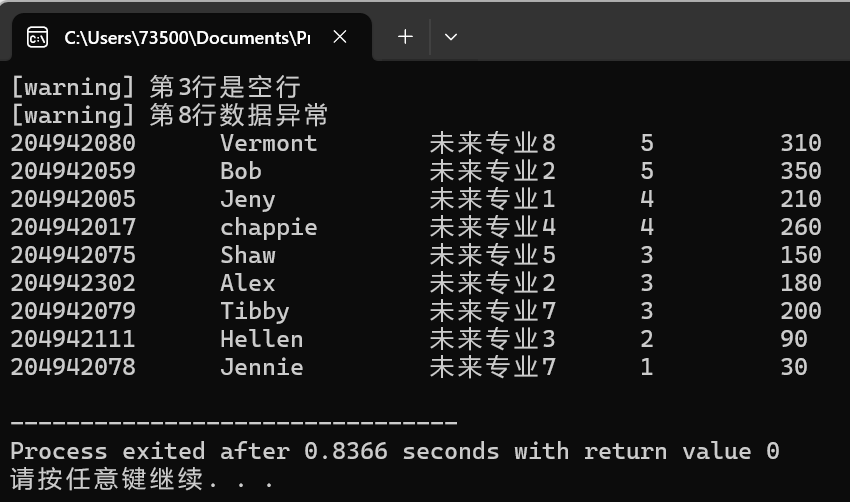
实验任务2
代码组织
student.hpp 学员类Student及其重载运算符函数声明
student.cpp 学员类Student及其重载运算符函数实现 (待实现)
stumgr.hpp 学员成绩管理类StuMgr声明
stumgr.cpp 学员成绩管理类StuMgr实现 (待实现)
task2.cpp 应用代码
student.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
class Student {
public:
Student() = default;
~Student() = default;
const std::string get_major() const;
int get_grade() const;
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const Student& s);
friend std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& is, Student& s);
private:
int id;
std::string name;
std::string major;
int grade; // 0-100
};
student.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include "student.hpp"
const std::string Student::get_major() const {
return major;
}
int Student::get_grade() const {
return grade;
}
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const Student& s) {
return os << std::left << std::setw(8) << s.id << std::setw(10) << s.name << std::setw(10) << s.major << s.grade;
}
std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& is, Student& s) {
return is >> s.id >> s.name >> s.major >> s.grade;
}
stumgr.hpp
#pragma once
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include "student.hpp"
class StuMgr {
public:
void load(const std::string& file); // 加载数据文件(空格分隔)
void sort(); // 排序: 按专业字典序升序、同专业分数降序
void print() const; // 打印到屏幕
void save(const std::string& file) const; // 保存到文件
private:
void write(std::ostream &os) const; // 把数据写到任意输出流
private:
std::vector<Student> students;
};
stumgr.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <algorithm>
#include "stumgr.hpp"
void StuMgr::load(const std::string& file) {
std::ifstream is(file);
if (!is)
throw std::runtime_error("fail to open " + file);
std::string line;
std::getline(is, line); // 跳过标题
Student t;
while (is >> t)
students.push_back(t);
}
void StuMgr::sort() {
std::sort(students.begin(), students.end(), [](const Student& s1, const Student& s2){return s1.get_major() != s2.get_major() ? s1.get_major() < s2.get_major() : s1.get_grade() > s2.get_grade();});
}
void StuMgr::print() const {
write(std::cout);
}
void StuMgr::save(const std::string& file) const {
std::ofstream os(file);
if (!os)
throw std::runtime_error("fail to open " + file);
write(os);
}
inline void StuMgr::write(std::ostream &os) const {
for (const auto& x : students)
os << x << '\n';
}
task2.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <limits>
#include <string>
#include "stumgr.hpp"
const std::string in_file = "./data.txt";
const std::string out_file = "./ans.txt";
void menu() {
std::cout << "\n**********简易应用**********\n"
"1. 加载文件\n"
"2. 排序\n"
"3. 打印到屏幕\n"
"4. 保存到文件\n"
"5. 退出\n"
"请选择:";
}
void app() {
StuMgr mgr;
while(true) {
menu();
int choice;
std::cin >> choice;
try {
switch (choice) {
case 1: mgr.load(in_file);
std::cout << "加载成功\n"; break;
case 2: mgr.sort();
std::cout << "排序已完成\n"; break;
case 3: mgr.print();
std::cout << "打印已完成\n"; break;
case 4: mgr.save(out_file);
std::cout << "导出成功\n"; break;
case 5: return;
default: std::cout << "不合法输入\n";
}
}
catch (const std::exception& e) {
std::cout << "Error: " << e.what() << '\n';
}
}
}
int main() {
app();
}
运行测试结果如下:

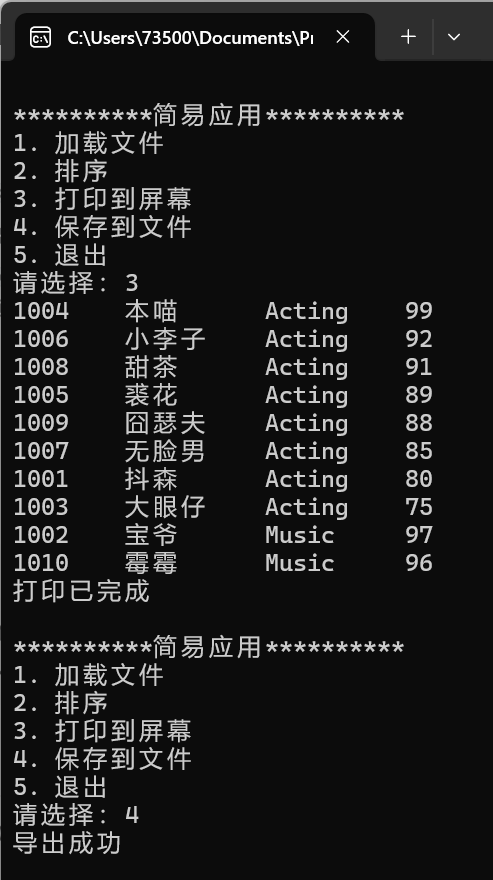
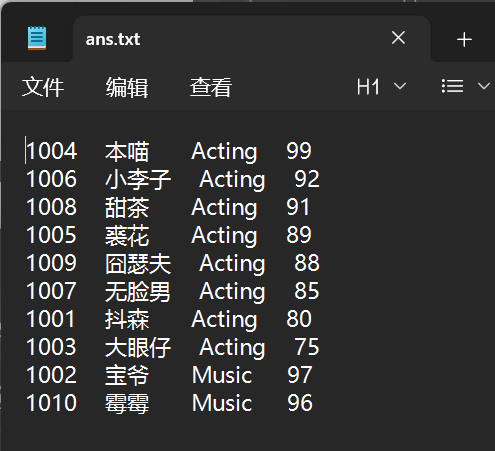
ans.txt:
为了处理data_bad.txt文件中的错误数据, 做出以下修改:
//student.hpp
//Student类中附加声明
void clear();
bool common() const;
//student.cpp
//附加成员函数实现
void Student::clear() {
this->id = -1;
this->name = "\0";
this->major = "\0";
this->grade = -1;
}
bool Student::common() const {
return this->id != -1 &&
this->name != "\0" &&
this->major != "\0" &&
this->grade != -1;
}
//stumgr.cpp
//修改功能函数load()的实现
void StuMgr::load(const std::string& file) {
std::ifstream is(file);
if (!is)
throw std::runtime_error("fail to open " + file);
std::string line;
std::getline(is, line); // 跳过标题
Student t;
int cnt = 0;
while (getline(is, line)) {
try {
++cnt;
t.clear();
std::stringstream ss(line);
ss >> t;
if (!t.common()) {
throw std::runtime_error("line " + std::to_string(cnt) + " format error");
} else if (t.get_grade() < 0 || t.get_grade() > 100) {
throw std::invalid_argument("line " + std::to_string(cnt) + " grade invalid");
} else {
students.push_back(t);
}
} catch (std::exception& e) {
std::cerr << "[warning] " << e.what() << ", skipped: " << line << std::endl;
}
}
}
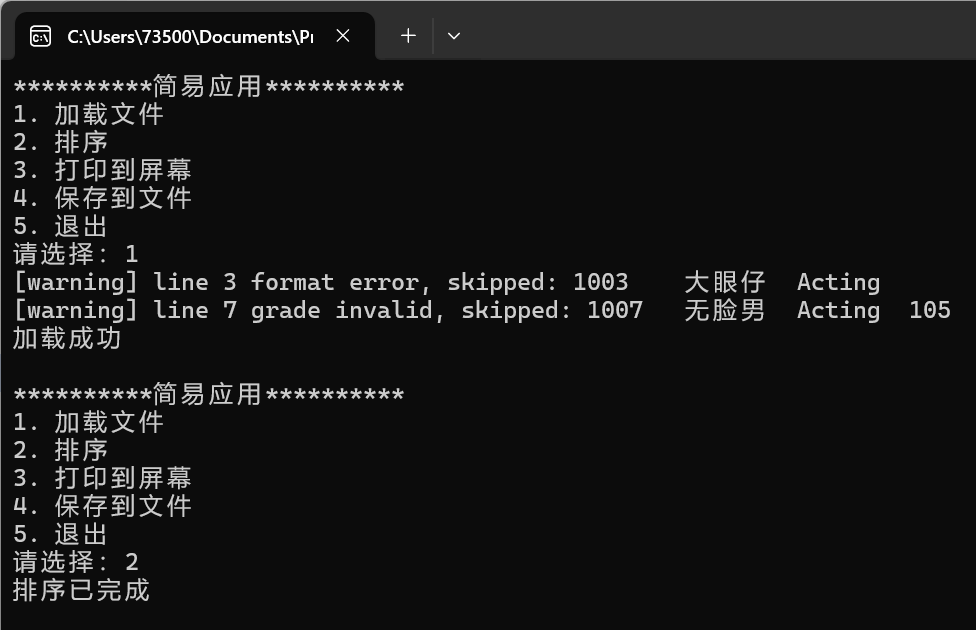
运行测试结果如下:
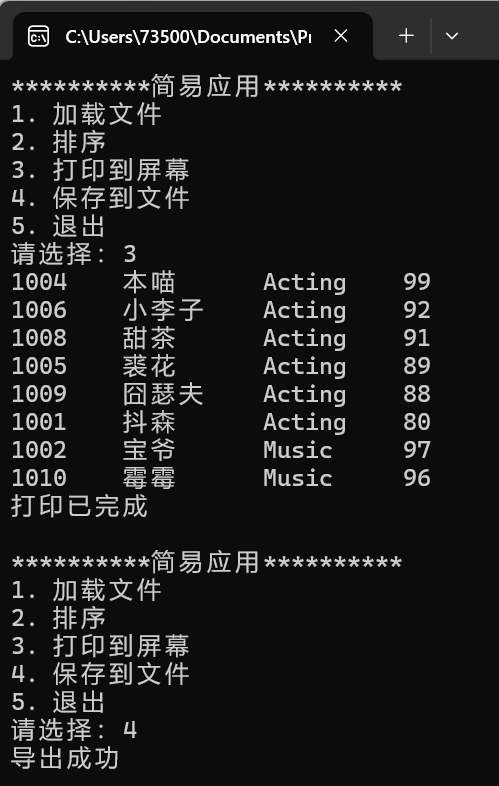
ans.txt:
实验总结
在命令行中的输入输出,归根结底就是对字符串流的格式控制,c++中提供了标准库流类的实现来自动控制输入输出功能,同时用户也可以自主重载<<和>>运算符来控制自定义类的输入输出。文件输入输出也是如此,通过封装的fstream来自动控制文件的生命周期,结束时自动关闭文件,无需手动控制,同时文件流操作也可以使用标准输入输出流的操作。
c++提供的异常处理方案try-throw-catch代码块和标准库定义的exception异常类大大增加了异常处理的灵活性,异常类的存在使得c++中的运行时异常可以返回丰富的信息,而不是像C语言一样只有一个的状态码或使用if卫语句直接退出,c++的异常处理方案可以在出现异常时恢复,增加了程序的健壮性,同时用户还可以派生异常类,以此传递更多与异常有关的信息。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号