[每日一题] [力扣430] 扁平化多级双向链表 2021.9.24
题目描述
多级双向链表中,除了指向下一个节点和前一个节点指针之外,它还有一个子链表指针,可能指向单独的双向链表。这些子列表也可能会有一个或多个自己的子项,依此类推,生成多级数据结构,如下面的示例所示。
给你位于列表第一级的头节点,请你扁平化列表,使所有结点出现在单级双链表中。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5,6,null,null,null,7,8,9,10,null,null,11,12]
输出:[1,2,3,7,8,11,12,9,10,4,5,6]
解释:
输入的多级列表如下图所示:
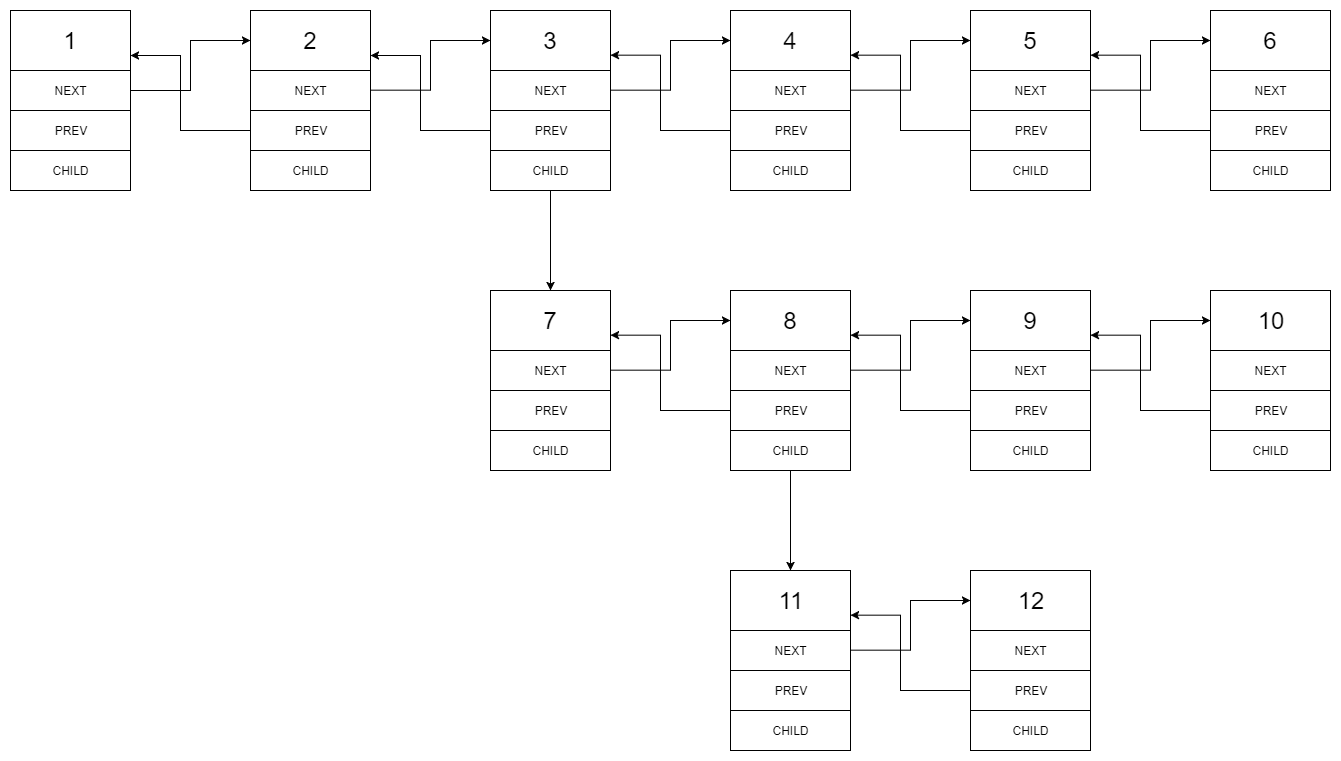
扁平化的链表如下图

来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/flatten-a-multilevel-doubly-linked-list
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
思路
dfs 把child保存在stack中,如果遍历完child的链表到空。再把stack弹栈把child的链表尾续到原来压栈的地方。
如图

代码
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* prev;
Node* next;
Node* child;
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* flatten(Node* head) {
auto root = head;
std::stack<Node *> stack;
do {
// while head 之后一定可以找到这一层的最后的节点。
Node *head_previous = head;
//printf("Go Down Through !\n");
while (head) {
head_previous = head;
if (head->child) {
// stack中保存head的指针
stack.push(head);
//printf("Push Head -> %d\n",head->val);
head = head->child;
continue;
}
//printf("Go Next Head -> %d\n",head->val);
head = head->next;
}
if(!stack.empty()) {
// 获取栈顶的head元素
Node* top = stack.top();
// 弹出
stack.pop();
// 把child置空 并把子结点保留
Node* head_child = top->child;
top->child = nullptr;
Node* head_next = top->next;
// 节点12的next置为9
head_previous->next = head_next;
if(head_next) {
//9的prev置为12
head_next->prev = head_previous;
}
// head->next = child;
top->next = head_child;
if(head_child) {
head_child->prev = top;
}
head = head_previous;
}
} while (!stack.empty() || head);
return root;
}
};


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号