Java8 Stream API 的使用示例及解析
本文章使用jdk8测试 ,并结合使用lambda测试
测试前准备一些测试数据:

class ObjectDemo { private Integer id; private String name; private Integer classNo; public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getClassNo() { return classNo; } public void setClassNo(Integer classNo) { this.classNo = classNo; } @Override public String toString() { return "ObjectDemo{" + "id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", classNo=" + classNo + '}'; } } class ObjectDemoList { List<ObjectDemo> getSomeDemo() { //手动简历一些测试对象,加入到list中,模拟为从数据库取出来的数据 List<ObjectDemo> objectDemoList = new ArrayList<ObjectDemo>(); ObjectDemo objectDemo1 = new ObjectDemo(); ObjectDemo objectDemo2 = new ObjectDemo(); ObjectDemo objectDemo3 = new ObjectDemo(); ObjectDemo objectDemo4 = new ObjectDemo(); ObjectDemo objectDemo5 = new ObjectDemo(); ObjectDemo objectDemo6 = new ObjectDemo(); ObjectDemo objectDemo7 = new ObjectDemo(); ObjectDemo objectDemo8 = new ObjectDemo(); ObjectDemo objectDemo9 = new ObjectDemo(); ObjectDemo objectDemo10 = new ObjectDemo(); //手动赋值 objectDemo1.setId(1); objectDemo1.setClassNo(1); objectDemo1.setName("object01"); objectDemo2.setId(2); objectDemo2.setClassNo(1); objectDemo2.setName("object02"); objectDemo3.setId(3); objectDemo3.setClassNo(1); objectDemo3.setName("object03"); objectDemo4.setId(5); objectDemo4.setClassNo(2); objectDemo4.setName("object05"); objectDemo5.setId(6); objectDemo5.setClassNo(3); objectDemo5.setName("object06"); objectDemo6.setId(7); objectDemo6.setClassNo(3); objectDemo6.setName("object07"); objectDemo7.setId(8); objectDemo7.setClassNo(3); objectDemo7.setName("object08"); objectDemo8.setId(9); objectDemo8.setClassNo(3); objectDemo8.setName("object09"); objectDemo9.setId(10); objectDemo9.setClassNo(4); objectDemo9.setName("object10"); objectDemo10.setId(4); objectDemo10.setClassNo(4); objectDemo10.setName("object04"); objectDemoList.add(objectDemo1); objectDemoList.add(objectDemo2); objectDemoList.add(objectDemo3); objectDemoList.add(objectDemo4); objectDemoList.add(objectDemo5); objectDemoList.add(objectDemo6); objectDemoList.add(objectDemo7); objectDemoList.add(objectDemo8); objectDemoList.add(objectDemo9); objectDemoList.add(objectDemo10); return objectDemoList; } }
1:collection.stream().forEach() → collection.forEach()
此方法作用为对colleaction流进行遍历--->
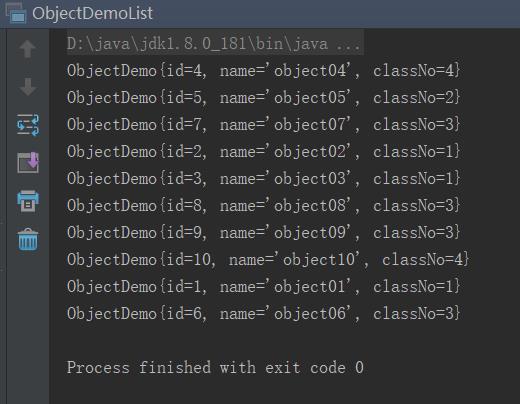
List<ObjectDemo> objectDemoList = new ObjectDemoList().getSomeDemo();
//foreach test objectDemoList.forEach(item -> { System.out.println(item.toString()); });
控制台数据:

2:collection.stream().collect(toList/toSet/toCollection()) → new CollectionType<>(collection)
此方法作用为对colleaction流进行类型转换,当前为list,转化为set示例--->
List<ObjectDemo> objectDemoList = new ObjectDemoList().getSomeDemo(); //type change test of jdk8 Set<ObjectDemo> objectDemoSet = new HashSet<>(objectDemoList); objectDemoSet.forEach(item -> { System.out.println(item.toString()); }); //type change test of jdk7 Set<ObjectDemo> objectDemoSet3 = objectDemoList.stream().collect(Collectors.toSet());
控制台数据:
3:collection.stream().toArray() → collection.toArray()
此方法作用为对colleaction流进行类型转换为array--->
此处不做控制台演示
//cast as array test Object[] test = objectDemoList.toArray(); Arrays.stream(test).forEach(item -> {
System.out.println(item.toString()); });
4:Arrays.asList().stream() → Arrays.stream() or Stream.of()
此方法作用为将array转换为stream流--->
//test of jdk7 Arrays.asList(test).stream(); //test of jdk8 Arrays.stream(test); Stream.of(test);
Stream.of()底部还是由Arrays.stream()实现的,因此我们正式使用时用Arrays.stream()就行了
public static<T> Stream<T> of(T... values) { return Arrays.stream(values); }
5:IntStream.range(0, array.length).mapToObj(idx -> array[idx]) → Arrays.stream(array)
同上,不做多余介绍,但是看看kdk7的写法吧
1 IntStream.range(0, test.length).mapToObj(id -> test[id]) 2 .forEach(item -> { 3 System.out.println(item.toString()); 4 });
6:IntStream.range(0, list.size()).mapToObj(idx -> list.get(idx)) → list.stream()
list转化为stram流,同上,不做多余介绍
7:Collections.singleton().stream() → Stream.of()
与topic4相同,但介绍一下jdk7的写法
Collections.singleton(objectDemoList).stream();
8:Collections.emptyList().stream() → Stream.empty()
源码部分:
public static<T> Stream<T> empty() { return StreamSupport.stream(Spliterators.<T>emptySpliterator(), false); }
作用:返回一个空stream
9:stream.filter().findFirst().isPresent() → stream.anyMatch()
判断此stream种是否存在符合条件的elem:
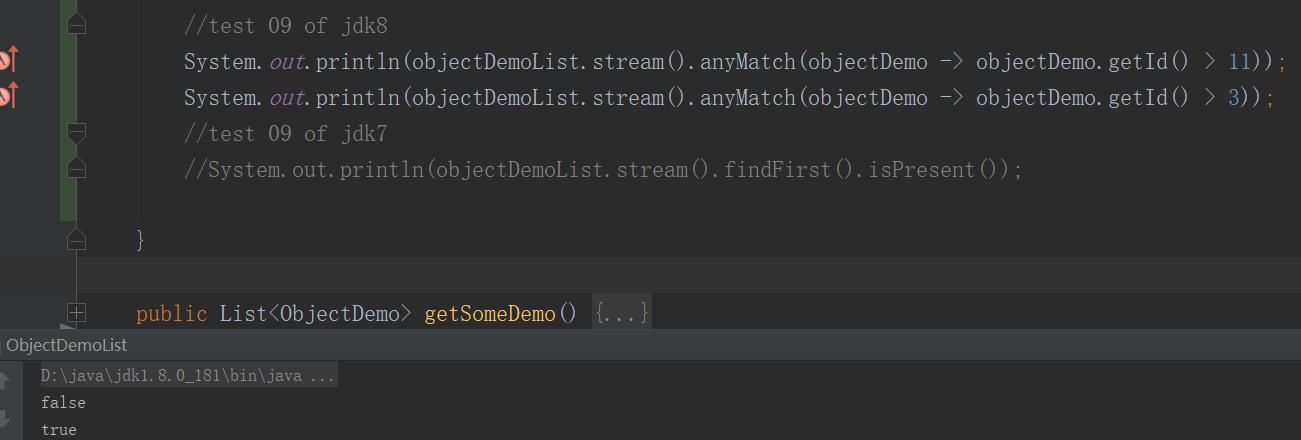
//test 09 of jdk8 System.out.println(objectDemoList.stream().anyMatch(objectDemo -> objectDemo.getId() > 11)); //test 09 of jdk7 System.out.println(objectDemoList.stream().findFirst().isPresent());
stream.anyMatch()源码:
boolean anyMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate);
Predicate.test():
boolean test(T t);
作用:只要符合test,就会返回一个新的predicate;
而我在jdk8中筛选的是 objectDemo.getId() > 11 的objectDemo对象,因此不会有满足条件的objectDemo对象,验证为false;
而条件为 objectDemo.getId() > 3 时 objectDemoLis 中有满足条件 的objectDemo对象,因此不会有满足条件的objectDemo对象,验证为true;
控制台输出:
10:stream.collect(Collectors.counting()) → stream.count()
作用:计算stream内的elem数量(大小)
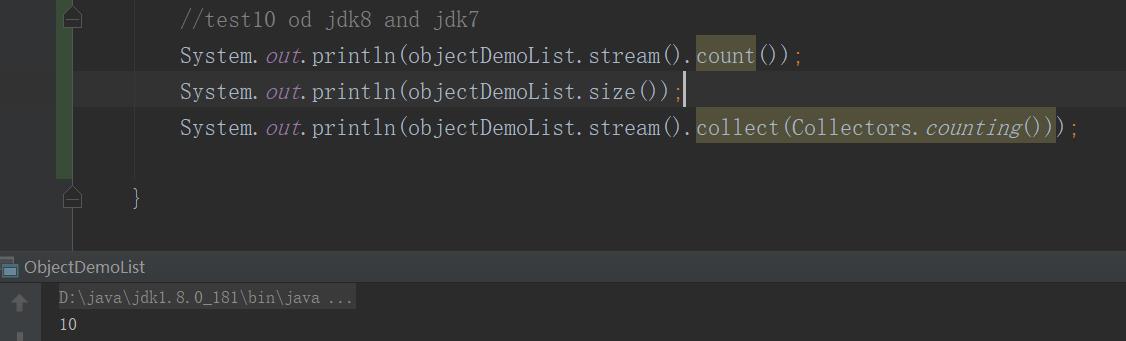
//test10 od jdk8 and jdk7 System.out.println(objectDemoList.stream().count()); System.out.println(objectDemoList.size()); System.out.println(objectDemoList.stream().collect(Collectors.counting()));
11:stream.collect(Collectors.maxBy()) → stream.max()
作用:返回该stream中的最大elem,前提是根据哪个属性排序,我这里使用id排序
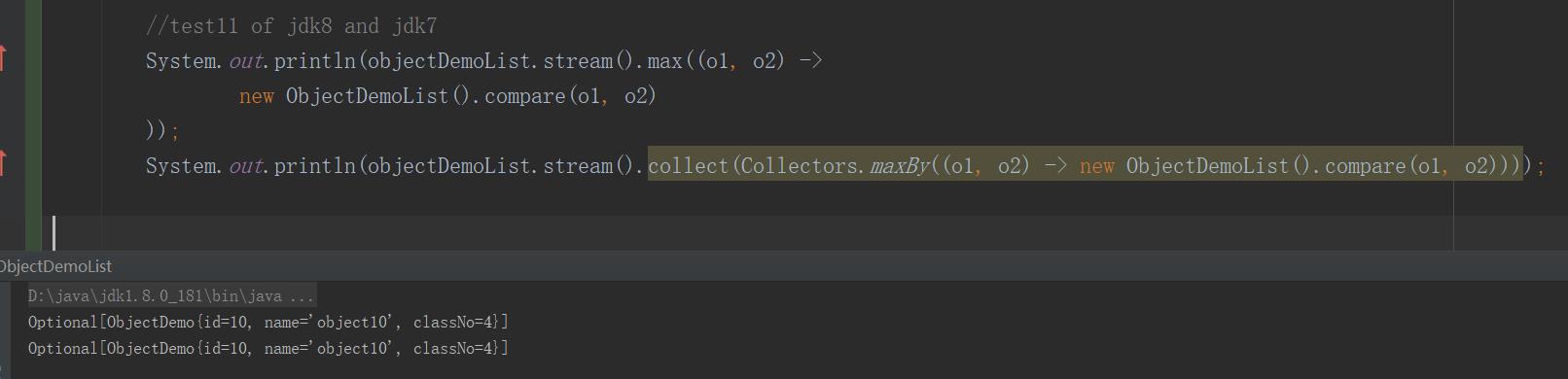
//test11 of jdk8 and jdk7 System.out.println(objectDemoList.stream().max((o1, o2) -> new ObjectDemoList().compare(o1, o2) )); private Integer compare(ObjectDemo objectDemo, ObjectDemo objectDemo2) { if (objectDemo.getId() < objectDemo2.getId()) { return -1; } if (objectDemo.getId().equals(objectDemo2.getId())) { return 0; } if (objectDemo.getId() > objectDemo2.getId()) { return 1; } return -1;
}
stream.max()源码:
Optional<T> max(Comparator<? super T> comparator);
Comparator.compare()源码:
* Compares its two arguments for order. Returns a negative integer, * zero, or a positive integer as the first argument is less than, equal * to, or greater than the second.<p>
int compare(T o1, T o2);
compare接口方法当o1>o2时,返回负整数,o1.equal(o2)时返回0,o1>02时返回正整数;
因此我编写了一个compare方法来返回具体结果(学而不精,若有好的意见望下方留言,感谢)
控制台输出:
12:stream.collect(Collectors.mapping()) → stream.map().collect()
先讲讲map()方法的作用:个人认为是将stream中的数据做萃取,就比如我们在数据中select * from [table] 时会出现id,name,age字段,但是若我们需要单独取 id 字段时,
就要 select [table].id from [table] ;这里的map是一样的作用,为我们做数据字段筛选提供了可行条件:

13:stream.collect(Collectors.reducing()) → stream.reduce()
唯一:将stream精简到只剩一个

14:stream.collect(Collectors.summingInt()) → stream.mapToInt().sum()
作用:为每个elem或者elem中的某个属性求总和:
类似的方法还有 stream.mapToDouble().sum() 、 stream.mapToLong().sum()
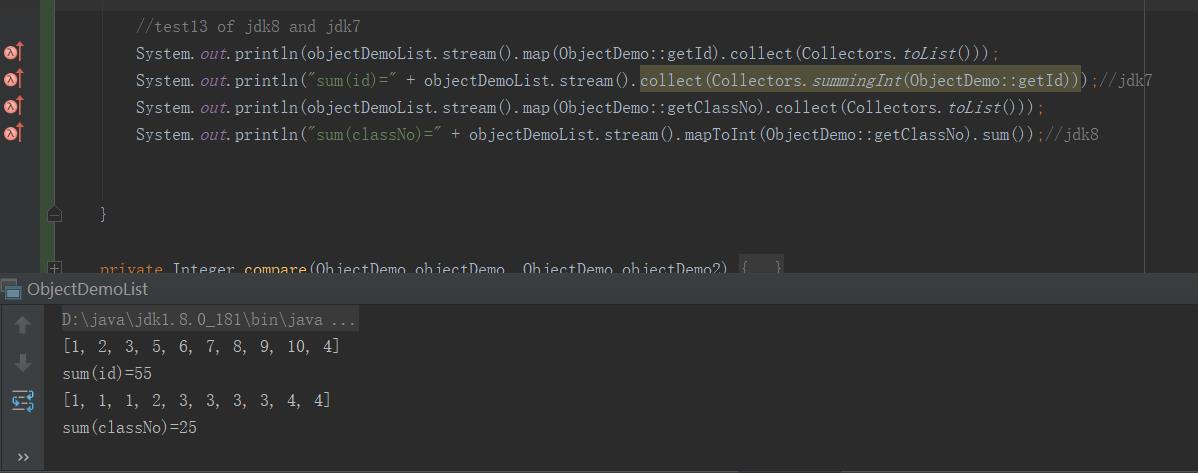
//test13 of jdk8 and jdk7 System.out.println(objectDemoList.stream().map(ObjectDemo::getId).collect(Collectors.toList())); System.out.println("sum(id)=" + objectDemoList.stream().collect(Collectors.summingInt(ObjectDemo::getId)));//jdk7 System.out.println(objectDemoList.stream().map(ObjectDemo::getClassNo).collect(Collectors.toList())); System.out.println("sum(classNo)=" + objectDemoList.stream().mapToInt(ObjectDemo::getClassNo).sum());//jdk8
控制台输出:
15:stream.distinct
作用:去重(与sql中的distinct作用一致)
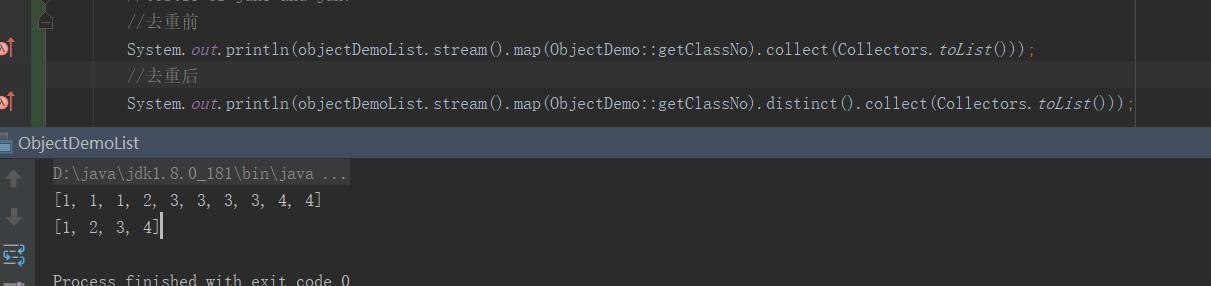
//去重前 System.out.println(objectDemoList.stream().map(ObjectDemo::getClassNo).collect(Collectors.toList())); //去重后 System.out.println(objectDemoList.stream().map(ObjectDemo::getClassNo).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList()));
控制台输出:
16:!stream.anyMatch() → stream.noneMatch()
stream.anyMatch():stream中只要含有满足条件的elem就返回true,否则false
stream.noneMatch():stream中只要没有满足条件的elem就返回true,否则false
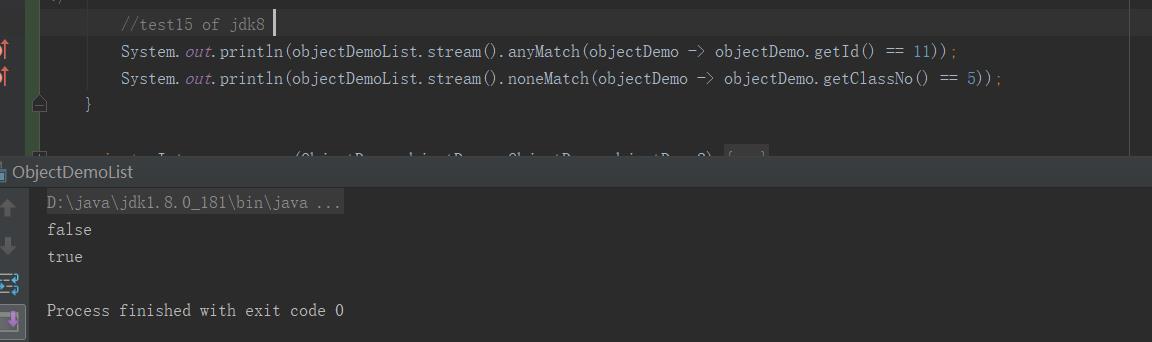
System.out.println(objectDemoList.stream().anyMatch(objectDemo -> objectDemo.getId() == 11));
System.out.println(objectDemoList.stream().noneMatch(objectDemo -> objectDemo.getClassNo() == 5));
控制台输出:
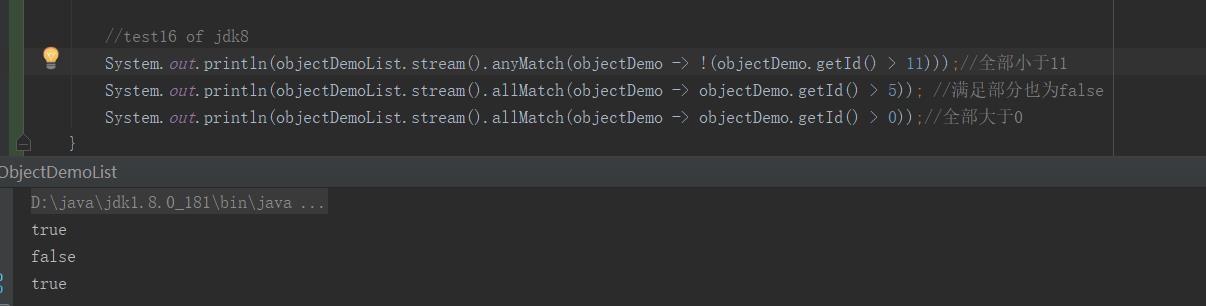
17:!stream.anyMatch(x -> !(...)) → stream.allMatch()
作用:全部符合条件才为true,否则为false
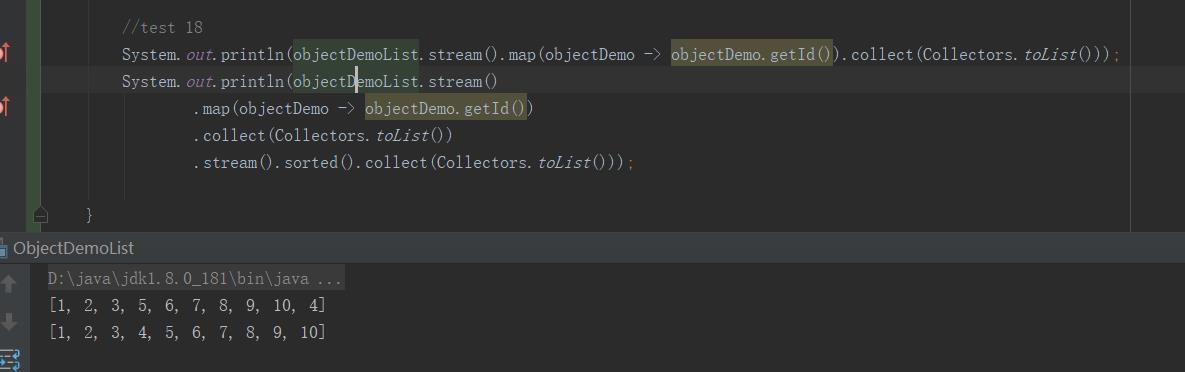
18:stream.sorted
作用:将elem根据某一属性进行排序(因为无法直接比较两个对象的大小)
源码中这么写的:传入的对象要有可比较性!!!
* Returns a stream consisting of the elements of this stream, sorted * according to natural order. If the elements of this stream are not * {@code Comparable}, a {@code java.lang.ClassCastException} may be thrown * when the terminal operation is executed.
Stream<T> sorted();
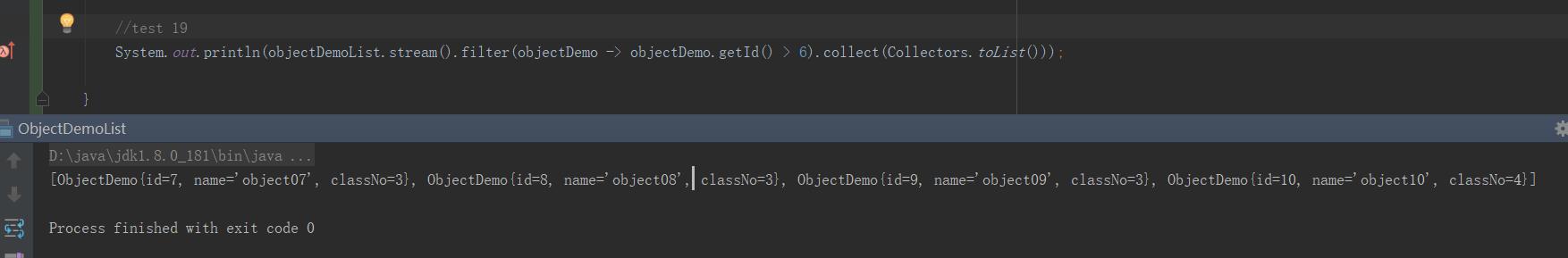
19:stream.filter()
作用:过滤掉你不需要的对象
20:stream.concat()
作用:对两个stream进行拼接并转化为一个stream
List<ObjectDemo> objectDemoList2 = new ArrayList<>(); ObjectDemo objectDemo13 = new ObjectDemo(); objectDemo13.setId(5); objectDemo13.setName("object13"); objectDemo13.setClassNo(5); objectDemoList2.add(objectDemo13); Stream streamT = Stream.concat(objectDemoList.stream(), objectDemoList2.stream()); System.out.println(streamT.collect(Collectors.toList()));
![]()
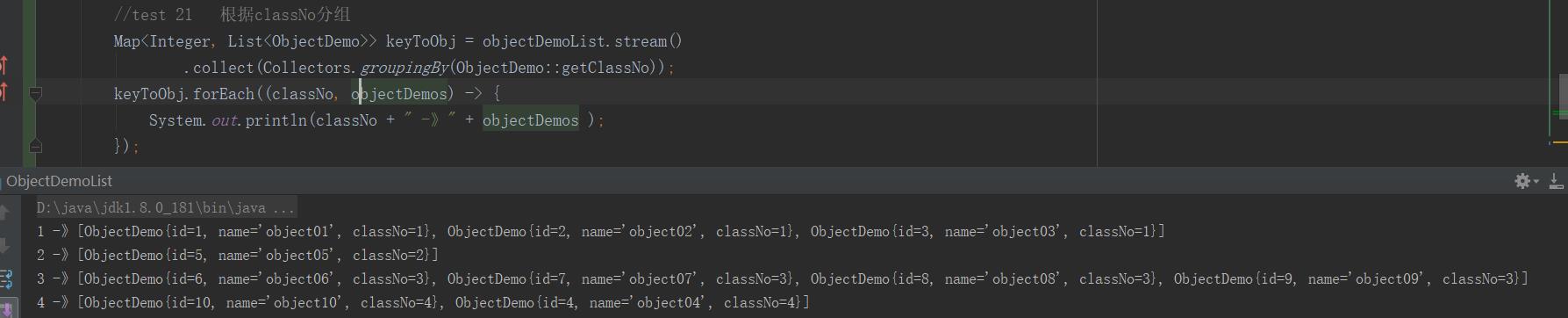
21:Collector.grouping()
与数据库中 的group by 一样的作用




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号