Logstash同步MySQL一对多关联表到Elasticsearch父子文档
2021-12-20 20:07 北桥苏 阅读(531) 评论(0) 收藏 举报前言:
目前大部分业务开发中,ElasticSearch主要还是用来做搜索。而支撑搜索功能的数据结构比较单一,不会有数据嵌套或者多种关联之类的。尽管没有,但是有些小众需求可能还会有一对多查询的场景。为了实现和MySQL的Join类似的查询方式,以下以ES的父子文档方式储存,并详细演示Logstash如何将MySQL的多张有关联的表同步到ES的父子文档。
手动演示:
以下以restful方式创建父子文档索引,并以简单的方式查询类似join的数据返回。下面所有演示的索引名称都为 "my_join_index"。
1. 创建父子关联索引
PUT my_join_index
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"my_join_field": {
"type": "join",
"relations": {
"question": "answer"
}
}
}
}
}2. 创建父文档
PUT my_join_index/_doc/1?refresh
{
"text": "This is a question",
"my_join_field": "question"
}
PUT my_join_index/_doc/2?refresh
{
"text": "This is another question",
"my_join_field": "question"
}3. 创建子文档
PUT my_join_index/_doc/3?routing=1&refresh
{
"text": "This is an answer",
"my_join_field": {
"name": "answer",
"parent": "1"
}
}
PUT my_join_index/_doc/4?routing=1&refresh
{
"text": "This is another answer2",
"my_join_field": {
"name": "answer",
"parent": "2"
}
}4. 全局检索
GET my_join_index/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"sort": ["_id"]
}5. 根据父文档查找子文档
GET my_join_index/_search
{
"query": {
"has_parent" : {
"parent_type" : "question",
"query" : {
"match" : {
"text" : "This is"
}
}
}
}
}6. 根据子文档查找父文档
GET my_join_index/_search
{
"query": {
"has_child" : {
"type" : "answer",
"query" : {
"match" : {
"text" : "This is question"
}
}
}
}
}7. Join聚合
GET my_join_index/_search
{
"query": {
"parent_id": {
"type": "answer",
"id": "1"
}
},
"aggs": {
"parents": {
"terms": {
"field": "my_join_field#question",
"size": 10
}
}
},
"script_fields": {
"parent": {
"script": {
"source": "doc['my_join_field#question']"
}
}
}
}8. 单条联合查询, 可以是一条父文档对应多个子文档
GET my_join_index/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"title": "历史圈"
}
},
{
"has_child": {
"type": "answer",
"query": {
"match": {
"text":"是的"
}
},
"inner_hits":{}
}
}
]
}
}
}
Logstash同步:
以下以文章分类表和文章表为例,二者系一对多的关系。同步文档时,文章分类作为父文档,文章作为子文档,关联字段为 “my_join_field”。
1. 创建有父子文档的索引
PUT hhyp_article
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"my_join_field": {
"type": "join",
"relations": {
"article_cate": "article"
}
}
}
}
}
2. 配置同步代码
input {
stdin {
}
jdbc {
# mysql 数据库链接,shop为数据库名
jdbc_connection_string => "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/rebuild?characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false"
# 用户名和密码
jdbc_user => "root"
jdbc_password => "root"
# 驱动
jdbc_driver_library => "E:/2setsoft/1dev/logstash-7.8.0/mysqletc/mysql-connector-java-5.1.7-bin.jar"
# 驱动类名
jdbc_driver_class => "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"
jdbc_paging_enabled => "true"
jdbc_page_size => "50000"
parameters => {"number" => "200"}
statement => "SELECT * FROM `hhyp_article` WHERE delete_time = 0"
# 是否将字段名转换为小写,默认true(如果有数据序列化、反序列化需求,建议改为false);
lowercase_column_names => false
# Value can be any of: fatal,error,warn,info,debug,默认info;
sql_log_level => warn
# 设置监听间隔 各字段含义(由左至右)分、时、天、月、年,全部为*默认含义为每分钟都更新
schedule => "* * * * *"
# 索引类型
type => "article"
}
jdbc {
# mysql 数据库链接,shop为数据库名
jdbc_connection_string => "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/rebuild?characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false"
# 用户名和密码
jdbc_user => "root"
jdbc_password => "root"
# 驱动
jdbc_driver_library => "E:/2setsoft/1dev/logstash-7.8.0/mysqletc/mysql-connector-java-5.1.7-bin.jar"
# 驱动类名
jdbc_driver_class => "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"
jdbc_paging_enabled => "true"
jdbc_page_size => "50000"
parameters => {"number" => "200"}
statement => "SELECT * FROM `hhyp_article_cate` WHERE delete_time = 0"
# 是否将字段名转换为小写,默认true(如果有数据序列化、反序列化需求,建议改为false);
lowercase_column_names => false
# Value can be any of: fatal,error,warn,info,debug,默认info;
sql_log_level => warn
# 设置监听间隔 各字段含义(由左至右)分、时、天、月、年,全部为*默认含义为每分钟都更新
schedule => "* * * * *"
# 索引类型
type => "article_cate"
}
}
filter {
if [type]=="article_cate" {
mutate {
add_field => { "my_join_field" => "article_cate" }
}
}
if [type]=="article" {
mutate {
add_field => {"[my_join_field][name]" => "article"}
#catalog_id 子表的父id
add_field => {"[my_join_field][parent]" => "%{cid}"}
}
}
}
output {
if[type] == "article_cate" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => "localhost:9200"
index => "hhyp_article"
document_type => "_doc"
document_id => "%{id}"
}
}
if[type] == "article" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => "localhost:9200"
index => "hhyp_article"
document_type => "_doc"
document_id => "%{id}"
routing => "%{cid}"
}
}
stdout {
codec => json_lines
}
}
3. 运行命令开始同步
bin\logstash -f mysql\mysql.conf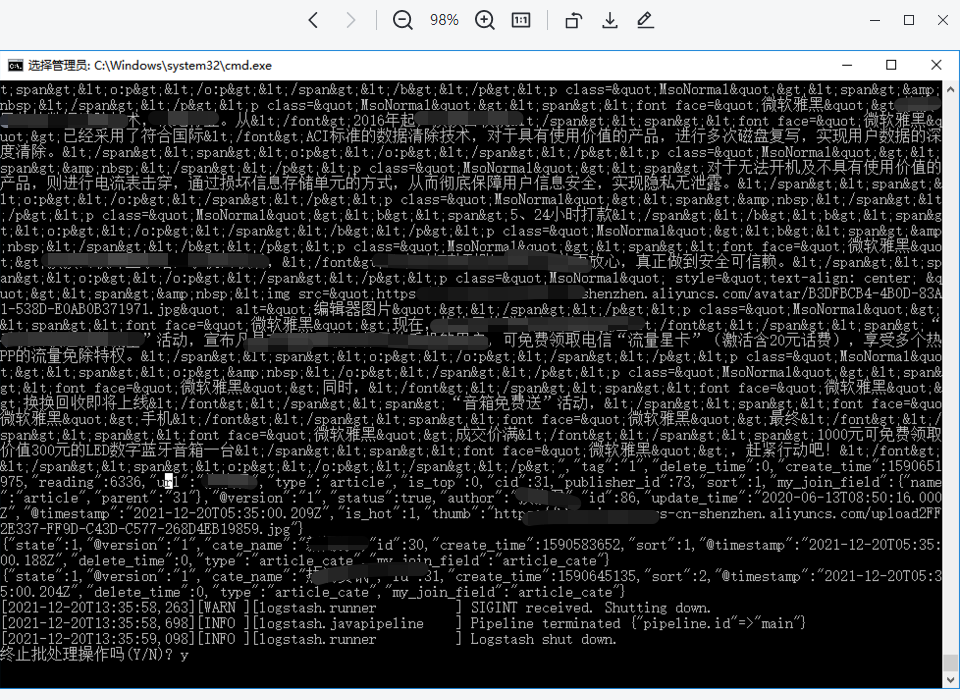
4. 通过搜索父文档标题查询子文档数据

交流学习

个人网站:www.zerofc.cn
公众号:ZEROFC_DEV
QQ交流群:515937120
QQ:2652364582
头条号:1637769351151619
B站:286666708
大鱼号:北桥苏

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号