基于本地的ComfyUI的API调用指南
基于本地的ComfyUI API调用指南
ComfyUI作为文生图、文生视频、图生图、图生视频的各类模型的工作流都非常好用,可组合各种模型和Lora。但是想要通过API调用相对比较复杂,且无完善的文档。
本文阐述了ComfyUI API调用完整指南,涵盖工作流导出、API调用流程、参数说明及Python代码实现。
零、代码
不想看太多字,直接下载Demo查看示例即可
https://github.com/zer0Black/ComfyUI-Api-Demo
一、概述
ComfyUI提供了强大的API接口,允许开发者通过编程方式调用ComfyUI工作流,实现AI图像生成的自动化。通过API调用,可以批量生成图像、集成到现有系统中,大幅提升工作效率。
二、准备工作
2.1 搭建工作流
在ComfyUI WebUI中按照需求搭建工作流:
- 打开ComfyUI界面,拖拽所需的节点
- 连接节点之间的数据流
- 配置节点参数(模型、提示词、采样器等)
- 点击"Queue Prompt"测试工作流是否能正常生成图像
- 确认工作流运行无误后,准备导出
2.2 导出API格式的JSON文件
导出步骤:
- 在ComfyUI界面点击顶部菜单栏的工作流 (Workflow)
- 选择导出(API) (Export API)
- 浏览器会自动下载一个JSON文件,通常命名为
workflow_api.json
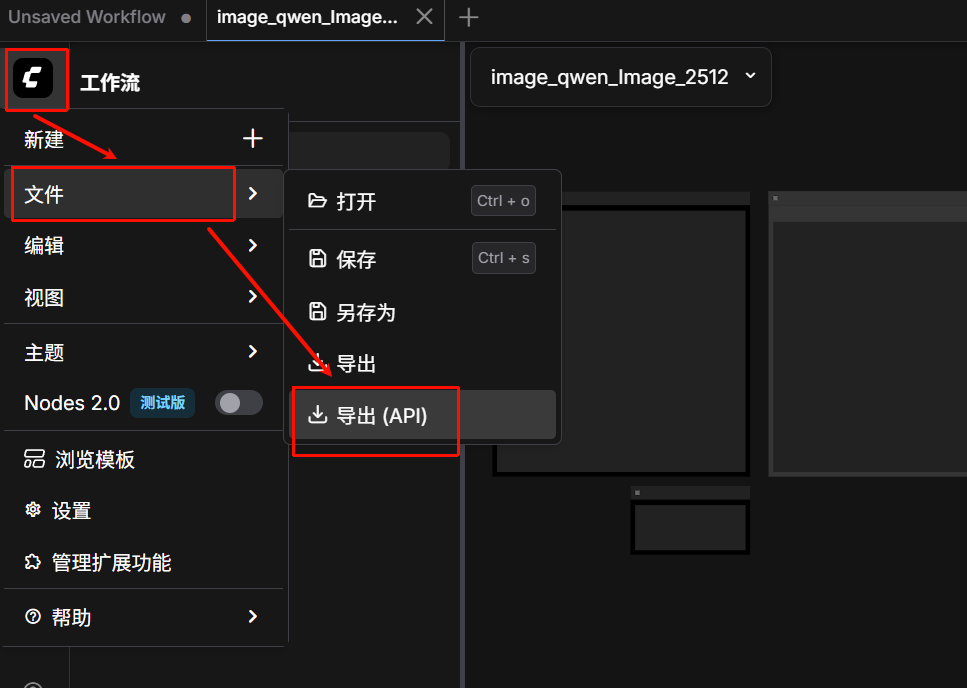
重要提示: 导出的JSON文件包含了工作流的完整配置,包括所有节点的ID、参数和连接关系。这个文件是API调用的核心输入。
三、JSON文件详解
3.1 JSON文件结构
导出的workflow_api.json文件是一个字典,键为节点ID,值为节点配置:
{
"60": {
"inputs": {
"filename_prefix": "Qwen-Image-2512",
"images": [
"86:8",
0
]
},
"class_type": "SaveImage",
"_meta": {
"title": "保存图像"
}
},
"91": {
"inputs": {
"value": "提示词写在这"
},
"class_type": "PrimitiveStringMultiline",
"_meta": {
"title": "Prompt"
}
},
"86:39": {
"inputs": {
"vae_name": "qwen_image_vae.safetensors"
},
"class_type": "VAELoader",
"_meta": {
"title": "加载VAE"
}
},
"86:38": {
"inputs": {
"clip_name": "qwen_2.5_vl_7b_fp8_scaled.safetensors",
"type": "qwen_image",
"device": "default"
},
"class_type": "CLIPLoader",
"_meta": {
"title": "加载CLIP"
}
},
"86:37": {
"inputs": {
"unet_name": "qwen_image_2512_fp8_e4m3fn.safetensors",
"weight_dtype": "default"
},
"class_type": "UNETLoader",
"_meta": {
"title": "UNet加载器"
}
},
"86:3": {
"inputs": {
"seed": 4,
"steps": 50,
"cfg": 4,
"sampler_name": "euler",
"scheduler": "simple",
"denoise": 1,
"model": [
"86:66",
0
],
"positive": [
"86:81",
0
],
"negative": [
"86:7",
0
],
"latent_image": [
"86:58",
0
]
},
"class_type": "KSampler",
"_meta": {
"title": "K采样器"
}
},
"86:58": {
"inputs": {
"width": 1664,
"height": 928,
"batch_size": 1
},
"class_type": "EmptySD3LatentImage",
"_meta": {
"title": "空Latent图像(SD3)"
}
},
"86:81": {
"inputs": {
"text": [
"91",
0
],
"clip": [
"86:38",
0
]
},
"class_type": "CLIPTextEncode",
"_meta": {
"title": "CLIP Text Encode (Positive Prompt)"
}
},
"86:8": {
"inputs": {
"samples": [
"86:3",
0
],
"vae": [
"86:39",
0
]
},
"class_type": "VAEDecode",
"_meta": {
"title": "VAE解码"
}
},
"86:66": {
"inputs": {
"shift": 3.1000000000000005,
"model": [
"86:37",
0
]
},
"class_type": "ModelSamplingAuraFlow",
"_meta": {
"title": "采样算法(AuraFlow)"
}
},
"86:7": {
"inputs": {
"text": "低分辨率,低画质,肢体畸形,手指畸形,画面过饱和,蜡像感,人脸无细节,过度光滑,画面具有AI感。构图混乱。文字模糊,扭曲",
"clip": [
"86:38",
0
]
},
"class_type": "CLIPTextEncode",
"_meta": {
"title": "CLIP Text Encode (Negative Prompt)"
}
}
}
3.2 JSON文件的来源
JSON文件是通过ComfyUI WebUI的"工作流 > 导出(API)"功能自动生成的,它准确反映了当前可视化工作流的状态。
3.3 需要修改的参数
通常情况下,你需要修改以下参数来实现动态调用:
| 节点类型 | 参数名称 | 说明 | 修改建议 |
|---|---|---|---|
| KSampler | seed |
随机种子 | 设置为-1可自动生成随机数,或每次请求指定不同的值 |
| KSampler | steps |
采样步数 | 根据质量需求调整,通常20-50 |
| KSampler | cfg |
提示词相关性 | 通常7-12,数值越高越遵循提示词 |
| CLIPTextEncode | text |
提示词 | 修改为你要生成的图像描述 |
| EmptyLatentImage | width |
图像宽度 | 根据需求调整(如512, 768, 1024) |
| EmptyLatentImage | height |
图像高度 | 根据需求调整 |
| CheckpointLoaderSimple | ckpt_name |
模型文件名 | 切换不同的基础模型 |
修改示例:
由于每个工作流配置出的节点名称不一样,需要根据到处的json格式进行修改
# 加载原始JSON
with open("workflow_api.json", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
workflow = json.load(f)
# 修改提示词
workflow["91"]["inputs"]["text"] = "一只可爱的猫咪在花园里玩耍,高清摄影,8K"
# 修改图像尺寸
workflow["86:58"]["inputs"]["width"] = 1024
workflow["86:58"]["inputs"]["height"] = 1024
# 随机种子
workflow["86:3"]["inputs"]["seed"] = -1
四、API调用流程
4.1 调用流程图
1. 搭建ComfyUI工作流
↓
2. 在WebUI中测试并确认工作正常
↓
3. 导出API格式JSON文件
↓
4. 在代码中加载JSON
↓
5. 修改需要动态调整的参数
↓
6. 发送POST请求到ComfyUI服务器
↓
7. 等待并接收生成结果
↓
8. 处理返回的图像数据
4.2 获取ComfyUI服务器地址
- 本地部署: 通常为
http://127.0.0.1:8188/api - 云服务器: 替换为你的公网IP或域名
五、Python代码实现
5.1 基础同步调用
最简单的调用方式,直接等待结果返回:
import requests
import json
# ComfyUI服务器地址
COMFYUI_ADDRESS = "http://127.0.0.1:8188/api"
def generate_image_sync(prompt_text, width=512, height=512):
"""
同步调用ComfyUI API生成图像
"""
# 1. 加载工作流JSON
with open("workflow_api.json", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
workflow = json.load(f)
# 2. 修改参数
workflow["91"]["inputs"]["text"] = prompt_text # 修改提示词
workflow["86:58"]["inputs"]["width"] = width
workflow["86:58"]["inputs"]["height"] = height
workflow["86:3"]["inputs"]["seed"] = -1 # 随机种子
# 3. 发送POST请求
endpoint = f"{COMFYUI_ADDRESS}/prompt"
response = requests.post(
endpoint,
json={"prompt": workflow},
headers={"Content-Type": "application/json"}
)
# 4. 获取prompt_id
result = response.json()
prompt_id = result["prompt_id"]
print(f"任务已提交,prompt_id: {prompt_id}")
# 5. 等待生成完成
history_endpoint = f"{COMFYUI_ADDRESS}/history/{prompt_id}"
import time
while True:
history_response = requests.get(history_endpoint)
history_data = history_response.json()
if prompt_id in history_data:
# 获取生成的图像
outputs = history_data[prompt_id]["outputs"]
for node_id, output_data in outputs.items():
if "images" in output_data:
for img in output_data["images"]:
image_filename = img["filename"]
print(f"图像已生成: {image_filename}")
return {
"prompt_id": prompt_id,
"filename": image_filename,
"full_path": f"{COMFYUI_ADDRESS}/view?filename={image_filename}"
}
break
time.sleep(1)
return None
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
result = generate_image_sync(
prompt_text="一只可爱的猫咪在花园里玩耍,高清摄影,8K,细节丰富",
width=768,
height=768
)
print(result)
5.2 使用WebSocket实时监听
获取实时进度,适合需要显示生成过程的场景:
import websocket
import json
import uuid
import requests
import time
class ComfyUIWebSocketClient:
def __init__(self, server_address="127.0.0.1:8188"):
self.server_address = server_address
self.client_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
self.ws = None
self.result = None
def send_prompt(self, workflow):
"""
通过WebSocket发送工作流
"""
# 连接WebSocket
ws_url = f"ws://{self.server_address}/ws?clientId={self.client_id}"
self.ws = websocket.create_connection(ws_url)
# 发送POST请求
prompt_endpoint = f"http://{self.server_address}/api/prompt"
payload = {
"prompt": workflow,
"client_id": self.client_id
}
response = requests.post(
prompt_endpoint,
json=payload,
headers={"Content-Type": "application/json"}
)
return response.json()
def listen_progress(self, prompt_id):
"""
监听生成进度
"""
try:
while True:
message = self.ws.recv()
data = json.loads(message)
# 处理不同类型的消息
if data["type"] == "status":
print(f"状态更新: {data['data']}")
elif data["type"] == "executing":
node_id = data["data"].get("node")
print(f"正在执行节点: {node_id}")
elif data["type"] == "progress":
value = data["data"]["value"]
max_value = data["data"]["max"]
print(f"进度: {value}/{max_value}")
elif data["type"] == "execution_start":
print("开始执行")
elif data["type"] == "execution_success":
print("执行成功!")
self.result = data
break
elif data["type"] == "execution_cached":
print("使用了缓存")
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("监听中断")
finally:
self.ws.close()
def generate_image_with_websocket(prompt_text):
"""
使用WebSocket方式生成图像
"""
client = ComfyUIWebSocketClient()
# 加载并修改工作流
with open("workflow_api.json", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
workflow = json.load(f)
workflow["91"]["inputs"]["text"] = prompt_text # 修改提示词
workflow["86:3"]["inputs"]["seed"] = -1 # 随机种子
# 发送工作流
result = client.send_prompt(workflow)
prompt_id = result["prompt_id"]
print(f"Prompt ID: {prompt_id}")
# 监听进度
client.listen_progress(prompt_id)
return client.result
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
result = generate_image_with_websocket("日落时分的海边风光,金黄色的阳光洒在沙滩上")
print(f"生成完成: {result}")
5.3 批量生成图像
自动化批量生成多个图像:
import requests
import json
import time
import concurrent.futures
COMFYUI_ADDRESS = "http://127.0.0.1:8188"
def generate_single_image(prompt_text, seed=None, width=512, height=512):
"""
生成单张图像
"""
with open("workflow_api.json", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
workflow = json.load(f)
workflow["91"]["inputs"]["text"] = prompt_text # 修改提示词
workflow["86:58"]["inputs"]["width"] = width
workflow["86:58"]["inputs"]["height"] = height
workflow["86:3"]["inputs"]["seed"] = -1 # 随机种子
if seed is None:
workflow["86:3"]["inputs"]["seed"] = -1 # 随机种子
else:
workflow["86:3"]["inputs"]["seed"] = seed
endpoint = f"{COMFYUI_ADDRESS}/prompt"
response = requests.post(
endpoint,
json={"prompt": workflow},
headers={"Content-Type": "application/json"}
)
result = response.json()
prompt_id = result["prompt_id"]
# 等待完成
while True:
history_response = requests.get(f"{COMFYUI_ADDRESS}/history/{prompt_id}")
history_data = history_response.json()
if prompt_id in history_data:
outputs = history_data[prompt_id]["outputs"]
for node_id, output_data in outputs.items():
if "images" in output_data:
filename = output_data["images"][0]["filename"]
return {
"prompt": prompt_text,
"seed": workflow["86:3"]["inputs"]["seed"],
"filename": filename,
"url": f"{COMFYUI_ADDRESS}/view?filename={filename}"
}
time.sleep(0.5)
def batch_generate(prompts, max_workers=2):
"""
批量生成图像(并发)
"""
results = []
with concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=max_workers) as executor:
future_to_prompt = {
executor.submit(generate_single_image, prompt): prompt
for prompt in prompts
}
for future in concurrent.futures.as_completed(future_to_prompt):
prompt = future_to_prompt[future]
try:
result = future.result()
results.append(result)
print(f"✓ 完成: {prompt}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"✗ 失败: {prompt}, 错误: {e}")
return results
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
prompts = [
"一只可爱的猫咪在花园里玩耍",
"美丽的日落风景,金色阳光",
"高山湖泊,倒影清晰",
"城市夜景,霓虹闪烁",
"森林小径,阳光斑驳"
]
print("开始批量生成...")
results = batch_generate(prompts, max_workers=2)
print(f"\n生成完成,共 {len(results)} 张图像:")
for i, result in enumerate(results, 1):
print(f"{i}. {result['prompt']}")
print(f" 文件: {result['filename']}")
print(f" 链接: {result['url']}\n")
5.4 下载生成的图像
将生成的图像保存到本地:
import requests
import os
def download_image(image_url, save_path, filename=None):
"""
下载生成的图像到本地
"""
try:
response = requests.get(image_url)
response.raise_for_status()
if filename is None:
filename = image_url.split("filename=")[-1]
full_path = os.path.join(save_path, filename)
os.makedirs(save_path, exist_ok=True)
with open(full_path, "wb") as f:
f.write(response.content)
print(f"图像已保存: {full_path}")
return full_path
except Exception as e:
print(f"下载失败: {e}")
return None
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
image_url = "http://127.0.0.1:8188/view?filename=ComfyUI_00001.png"
save_path = "./generated_images"
download_image(image_url, save_path)
六、传参要求详解
6.1 请求参数
| 参数 | 类型 | 必填 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
prompt |
object | 是 | 工作流JSON对象 |
client_id |
string | 否 | 客户端标识符,用于区分不同请求 |
6.2 响应参数
| 参数 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
prompt_id |
string | 任务的唯一标识符 |
number |
number | 队列中排队的任务数 |
node_errors |
object | 节点错误信息 |
6.3 常见HTTP状态码
| 状态码 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 200 | 请求成功 |
| 400 | 请求参数错误 |
| 500 | 服务器内部错误 |
七、常见问题
Q1: 提示词不生效怎么办?
检查节点ID是否正确。导出的JSON中,CLIPTextEncode节点的ID可能与你的不同,需要根据实际JSON调整。
Q2: 如何获取生成的图像文件?
方法1: 通过/view端点直接访问
image_url = f"{COMFYUI_ADDRESS}/view?filename={filename}"
方法2: 从ComfyUI的output目录直接复制文件
Q3: 批量生成速度慢怎么办?
- 使用多线程并发请求
- 优化工作流,减少不必要的节点
- 使用更强大的GPU
- 考虑使用云平台的Serverless API,支持多实例并发
Q4: API调用返回错误?
检查:
- ComfyUI服务器是否正常运行
- 工作流JSON格式是否正确
- 节点连接关系是否完整
- 模型文件是否存在
八、进阶技巧
8.1 动态替换模型
def change_model(workflow, model_name):
"""
切换模型
"""
# 假设节点4是CheckpointLoaderSimple
workflow["4"]["inputs"]["ckpt_name"] = model_name
return workflow
# 使用
workflow = change_model(workflow, "sd_xl_base_1.0.safetensors")
8.2 添加ControlNet
导出的JSON如果包含ControlNet,需要确保ControlNet模型已加载:
# ControlNet预处理器节点通常需要额外的参数
workflow["controlnet_node"]["inputs"]["image"] = ["load_image_node", 0]
8.3 Lora调用
# 在KSampler之前添加Lora加载节点
# 修改model的连接,从CheckpointLoader改为LoraLoader
workflow["3"]["inputs"]["model"] = ["lora_loader_node", 0]
九、总结
通过ComfyUI API,我们可以实现:
- ✓ 工作流自动化执行
- ✓ 批量图像生成
- ✓ 集成到现有系统
- ✓ 实时进度监控
- ✓ 云端部署和扩展
关键步骤:
- 在ComfyUI WebUI中搭建并测试工作流
- 导出API格式JSON文件
- 在代码中加载JSON并修改参数
- 通过HTTP/WebSocket发送请求
- 处理返回结果



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号