浅谈委托
1. 委托 和 事件在 .Net Framework中的应用非常广泛,然而,较好地理解委托和事件对很多接触C#时间不长的人来说并不容易。委托是一个类,它定义了方法的类型,使得可以将方法当作另一个方法的参数来进行传递,这种将方法动态地赋给参数的做法,可以避免在程序中大量使用If-Else(Switch)语句,同时使得程序具有更好的可扩展性。我们知道委托是一个引用类型,所以它具有引用类型所具有的通性。它保存的不是实际值,而是保存对存储在托管堆(managed heap)中的对象的引用。那它保存的是对什么的引用呢?委托保存的是对函数(function)的引用。对学过C/C++的人,是不是觉得跟函数指针很像呢!委托可以引用实例和静态(在 Visual Basic 中为 Shared)方法,而函数指针只能引用静态方法。 其实它们是有区别的,在非托管C/C++中,函数的地址就是一个内存地址。该地址不会携带任何额外的信息,例如函数期望的参数个数、参数类型、函数的返回值类型及函数的调用约定。总之,非托管C/C++中函数指针是非类型安全的。而.NET中的委托是类型安全的,委托会检测它所保存的函数引用是否和声明的委托匹配。
2. 委托与事件的区别。
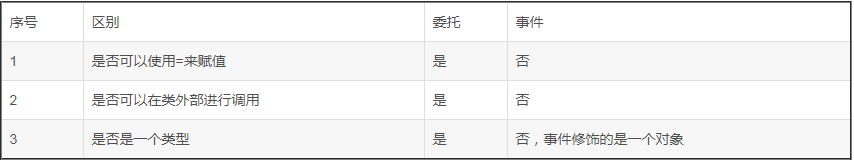
3.
定义
public class Heater
{
private int _temperature;
public int Temperature
{
get
{
return _temperature;
}
set
{
if (_temperature != value)
{
_temperature = value;
PropertyEvent("Temperature");
}
}
}
private int _volume;
public int Volume
{
get
{
return _volume;
}
set
{
if (_volume != value)
{
_volume = value;
PropertyEvent("Volume");
}
}
}
public delegate void BoilHandler(int param); //声明委托
public event BoilHandler BoilEvent; //声明事件
public delegate void PropertyHandler(string propertyName); //声明委托
public event PropertyHandler PropertyEvent; //声明事件
public void Boil()
{
for(int i = 0; i < 101; i++)
{
Temperature = i;
if(Temperature == 100)
{
BoilEvent?.Invoke(Temperature);
}
}
}
}
使用
Heater t = new Heater();
t.BoilEvent += x=> { Console.WriteLine(x); };
t.BoilEvent += x => { Console.WriteLine("告警"); };
t.PropertyEvent += x => { Console.WriteLine(x); };
t.Volume = 10;
t.Boil();
4.常用委托
a.Delegate
Delegate至少0个参数,至多32个参数,可以无返回值,也可以指定返回值类型。
public delegate int MethodtDelegate(int x, int y);表示有两个参数,并返回int型。
b.Action
Action至少0个参数,至多16个参数,无返回值。
例:Action<int,string,bool> 表示有传入参数int,string,bool无返回值的委托。
c.Func
Func<T1,T2,,T3,int> 表示传入参数为T1,T2,,T3(泛型)返回值为int的委托。
Func至少0个参数,至多16个参数,根据返回值泛型返回。必须有返回值,不可void。
d.Predicate
Predicate有且只有一个参数,返回值固定为bool。
例:public delegate bool Predicate<T> (T obj)。
5.委托的高级使用
在System.Linq下实现了对很多类型的扩展,比如数组的OrderBy,现在我们自己写一个扩展重载OrderBy,并扩展一个新方法Filter。
定义:
public static class MyExt
{
public static T1[] OrderBy2<T1,T2>(this T1[] array, Func<T1, T2> func)
{
for (int i = 0; i < array.Length - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < array.Length - 1 - i; j++)
{
IComparer<T2> @default = Comparer<T2>.Default;
int ret = @default.Compare(func(array[j + 1]), func(array[j])) ;
if (ret == 1)
{
T1 tmp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = tmp;
}
}
}
return array;
}
public static T1[] Filter<T1>(this T1[] array, Predicate<T1> pre)
{
List<T1> tmp = new List<T1>();
for(int i = 0;i < array.Length; i++)
{
if(pre(array[i]))
{
tmp.Add(array[i]);
}
}
return tmp.ToArray();
}
}
使用:
int[] a = new int[] {2,10,3,4,5 };
a = a.Filter(x => x > 3).OrderBy2(x=>x);




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号