ping源码解析
ping的源码解析
1、下载Ubuntu的ping源码
-
查看ping的源码在哪个包下
![]()
-
下载源码包:apt-get source iputils-ping
- 如果出现了"You must put some 'source' URIs in your sources.list"错误,需要先在系统设置->Software&Updates里把Source code选项打开
- 下载的源代码在当前的文件夹下
2、编译/执行ping
-
在源码文件夹iputils-20121221下执行make ping
如果出现了"fatal error: sys/capability.h: No such file or directory
compilation terminated"错误,则执行"apt-get install libcap-dev" -
得到编译好的ping.o和ping的可执行文件。测试是否能用。
3、源码分析
- 查看makefile可以看到,ping主要是由ping_common.h、ping_common.c、ping.c编译得来的。
- 查看ping.c里包含的头文件,包括netinet/ip.h、netinet/ip_icmp.h、ifaddrs.h。在/usr/include下把这些头文件也给找到。
- find指令:find /usr/include -name ip.h
- 整体结构图
![]()
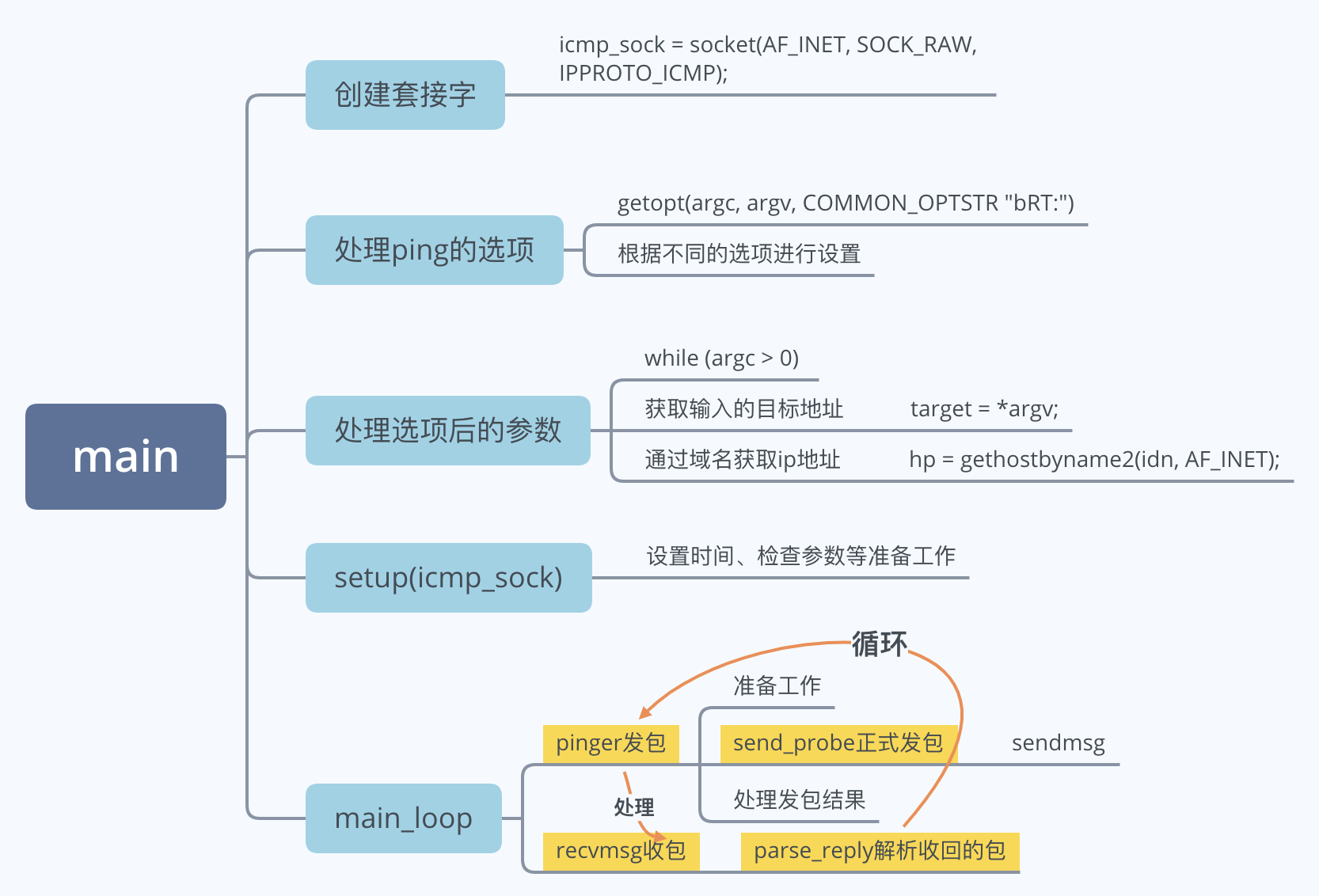
4、main函数
先从最顶层开始看,且由于ping的选项很多,关注顶层时不要死抓住各种选项的设置不放,先通过研究ping的最基本用法【ping 地址】来理清主要框架。
// 全局变量和结构声明
struct sockaddr_in whereto; /* who to ping */
int optlen = 0;
int settos = 0; /* Set TOS, Precendence or other QOS options */
int icmp_sock; /* socket file descriptor */
u_char outpack[0x10000];
int maxpacket = sizeof(outpack);
struct sockaddr_in source;
// sockaddr_in定义在<netinet/in.h>中,这里把它拿过来
struct sockaddr_in {
sa_family_t sin_family; //地址族
uint16_t sin_port; // 16位TCP/UDP端口号
struct in_addr sin_addr; //32位IP地址
char sin_zero[8]; //不使用
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
struct hostent *hp;
int ch, hold, packlen;
int socket_errno;
u_char *packet;
char *target;
//把预编译的东西折叠不看
#ifdef USE_IDN...
#else...
#endif
char rspace[3 + 4 * NROUTES + 1]; /* record route space */
limit_capabilities();
#ifdef USE_IDN...
#endif
enable_capability_raw();
//创建icmp套接字
icmp_sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_ICMP);
socket_errno = errno;
disable_capability_raw();
source.sin_family = AF_INET;
preload = 1;
//根据ping的选项来设置
while ((ch = getopt(argc, argv, COMMON_OPTSTR "bRT:")) != EOF) {
switch(ch) {
case 'b':...
case 'Q':...
case 'R':...
case 'T':...
case 'I':...
case 'M':...
case 'V':
printf("ping utility, iputils-%s\n", SNAPSHOT);
exit(0);
//如果是一般选项,则交给common_option函数处理
COMMON_OPTIONS
common_options(ch);
break;
default:
usage();
}
}
argc -= optind; //处理完选项参数,参数个数减少
argv += optind; //为获取下个参数,参数指针增加
//如果后面没参数了,打印用法(usage)
if (argc == 0)
usage();
//参数个数大于1,根据选项进行设置,跳过
if (argc > 1) {...
}
// 定义目标
while (argc > 0) {
//获取输入的目标地址
target = *argv;
memset((char *)&whereto, 0, sizeof(whereto));
whereto.sin_family = AF_INET;
if (inet_aton(target, &whereto.sin_addr) == 1) {
hostname = target;
if (argc == 1)
options |= F_NUMERIC;
} else {
char *idn;
//通过域名获取ip地址
hp = gethostbyname2(idn, AF_INET);
if (!hp) {
fprintf(stderr, "ping: unknown host %s\n", target);
exit(2);
}
hostname = hnamebuf;
}
if (argc > 1)
route[nroute++] = whereto.sin_addr.s_addr;
argc--;
argv++;
}
// 判断是否是广播地址,并对目标IP尝试连接
if (source.sin_addr.s_addr == 0) {
socklen_t alen;
struct sockaddr_in dst = whereto;
int probe_fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
if (probe_fd < 0) {
perror("socket");
exit(2);
}
close(probe_fd);
} while (0);
// 如果目标ip地址为0,则赋值为127.0.0.1,本地回环地址
if (whereto.sin_addr.s_addr == 0)
whereto.sin_addr.s_addr = source.sin_addr.s_addr;
// icmp套接字创建失败
if (icmp_sock < 0) {
errno = socket_errno;
perror("ping: icmp open socket");
exit(2);
}
// -I选择的设置,跳过
if (device) {....
}
// -b选项的设置,跳过
if (broadcast_pings || IN_MULTICAST(ntohl(whereto.sin_addr.s_addr))) {...
}
// -M选项的设置,跳过
if (pmtudisc >= 0) {...
}
// -I选项的设置,跳过
if ((options&F_STRICTSOURCE) && bind(icmp_sock, (struct sockaddr*)&source, sizeof(source)) == -1) {
}
// 其他一些选项的设置,跳过
...
// 设置套接字接受和发送缓冲区的大小
hold = datalen + 8;
hold += ((hold+511)/512)*(optlen + 20 + 16 + 64 + 160);
sock_setbufs(icmp_sock, hold);
// 以下就是ping的过程中我们能看到的打印信息了
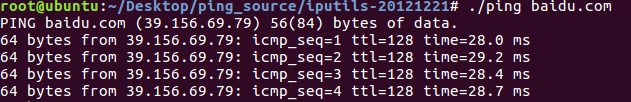
// 如 PING baidu.com (39.156.69.79)
printf("PING %s (%s) ", hostname, inet_ntoa(whereto.sin_addr));
if (device || (options&F_STRICTSOURCE))
printf("from %s %s: ", inet_ntoa(source.sin_addr), device ?: "");
// 56(84) bytes of data.
// datalen默认是(64-8)= 56
printf("%d(%d) bytes of data.\n", datalen, datalen+8+optlen+20);
// 重点1
setup(icmp_sock);
// 重点2
main_loop(icmp_sock, packet, packlen);
}
5、setup函数
void setup(int icmp_sock)
{
....
//以上为选项设置 跳过
//获取进程ID,识别包要用
ident = htons(getpid() & 0xFFFF);
set_signal(SIGINT, sigexit);
set_signal(SIGALRM, sigexit);
set_signal(SIGQUIT, sigstatus);
sigemptyset(&sset);
sigprocmask(SIG_SETMASK, &sset, NULL);
gettimeofday(&start_time, NULL);
if (deadline) {
struct itimerval it;
it.it_interval.tv_sec = 0;
it.it_interval.tv_usec = 0;
it.it_value.tv_sec = deadline;
it.it_value.tv_usec = 0;
setitimer(ITIMER_REAL, &it, NULL);
}
if (isatty(STDOUT_FILENO)) {
struct winsize w;
if (ioctl(STDOUT_FILENO, TIOCGWINSZ, &w) != -1) {
if (w.ws_col > 0)
screen_width = w.ws_col;
}
}
}
6、main_loop函数
main_loop里面是个死循环,根据时间间隔发包->收包->解析包->发包...
void main_loop(int icmp_sock, __u8 *packet, int packlen)
{
char addrbuf[128];
char ans_data[4096];
struct iovec iov;
struct msghdr msg;
struct cmsghdr *c;
int cc;
int next;
int polling;
iov.iov_base = (char *)packet;
for (;;) {
/* 检查退出情况 */
if (exiting)
break;
if (npackets && nreceived + nerrors >= npackets)
break;
if (deadline && nerrors)
break;
/* 检查状态并作出回应。status_snapshot在setup时被修改过
* 丢包、拒收或超时等情况 */
if (status_snapshot)
status();
/* 发包 */
do {
next = pinger();
next = schedule_exit(next);
} while (next <= 0);
/* "next"如果为正,则为发下个probe的时间
* 如果 next<=0 则表示现在尽快发出 */
/* Technical part. Looks wicked. Could be dropped,
* if everyone used the newest kernel. :-)
* Its purpose is:
* 1. Provide intervals less than resolution of scheduler.
* Solution: spinning.
* 2. Avoid use of poll(), when recvmsg() can provide
* timed waiting (SO_RCVTIMEO). */
polling = 0;
// 控制发送时间间隔
if ((options & (F_ADAPTIVE|F_FLOOD_POLL)) || next<SCHINT(interval)) {
int recv_expected = in_flight();
/* If we are here, recvmsg() is unable to wait for
* required timeout. */
if (1000 % HZ == 0 ? next <= 1000 / HZ : (next < INT_MAX / HZ && next * HZ <= 1000)) {
/* Very short timeout... So, if we wait for
* something, we sleep for MININTERVAL.
* Otherwise, spin! */
if (recv_expected) {
next = MININTERVAL;
} else {
next = 0;
/* When spinning, no reasons to poll.
* Use nonblocking recvmsg() instead. */
polling = MSG_DONTWAIT;
/* But yield yet. */
sched_yield();
}
}
if (!polling &&
((options & (F_ADAPTIVE|F_FLOOD_POLL)) || interval)) {
struct pollfd pset;
pset.fd = icmp_sock;
pset.events = POLLIN|POLLERR;
pset.revents = 0;
if (poll(&pset, 1, next) < 1 ||
!(pset.revents&(POLLIN|POLLERR)))
continue;
polling = MSG_DONTWAIT;
}
}
// 接收ICMP回应包
for (;;) {
struct timeval *recv_timep = NULL;
struct timeval recv_time;
int not_ours = 0; /* Raw socket can receive messages
* destined to other running pings. */
iov.iov_len = packlen;
memset(&msg, 0, sizeof(msg));
// msg是msghdr类型全局变量,msghdr结构的定义见后
msg.msg_name = addrbuf;
msg.msg_namelen = sizeof(addrbuf);
msg.msg_iov = &iov;
msg.msg_iovlen = 1;
msg.msg_control = ans_data;
msg.msg_controllen = sizeof(ans_data);
cc = recvmsg(icmp_sock, &msg, polling); //收包
polling = MSG_DONTWAIT;
// 如果接收失败
if (cc < 0) {
if (errno == EAGAIN || errno == EINTR)
break;
if (!receive_error_msg()) {
if (errno) {
perror("ping: recvmsg");
break;
}
not_ours = 1;
}
} else {
#ifdef SO_TIMESTAMP
for (c = CMSG_FIRSTHDR(&msg); c; c = CMSG_NXTHDR(&msg, c)) {
if (c->cmsg_level != SOL_SOCKET ||
c->cmsg_type != SO_TIMESTAMP)
continue;
if (c->cmsg_len < CMSG_LEN(sizeof(struct timeval)))
continue;
recv_timep = (struct timeval*)CMSG_DATA(c);
}
#endif
if ((options&F_LATENCY) || recv_timep == NULL) {
if ((options&F_LATENCY) ||
ioctl(icmp_sock, SIOCGSTAMP, &recv_time))
gettimeofday(&recv_time, NULL);
recv_timep = &recv_time;
}
// 解析收到的包
not_ours = parse_reply(&msg, cc, addrbuf, recv_timep);
}
/* See? ... someone runs another ping on this host. */
if (not_ours)
install_filter();
/* If nothing is in flight, "break" returns us to pinger. */
if (in_flight() == 0)
break;
/* Otherwise, try to recvmsg() again. recvmsg()
* is nonblocking after the first iteration, so that
* if nothing is queued, it will receive EAGAIN
* and return to pinger. */
}
}
finish();
}
6、pinger函数
组成并传送一个ICMP ECHO请求包。
ID是UNIX进程的ID,sequence number是一个递增的整数。
data段的头8个字节装UNIX的时间戳,用来计算往返时间。
具体装包发包是由send_probe函数实现的。
int pinger(void)
{
static int oom_count;
static int tokens;
int i;
/* 如果发够了就随机返回一个正数 */
if (exiting || (npackets && ntransmitted >= npackets && !deadline))
return 1000;
/* Check that packets < rate*time + preload */
if (cur_time.tv_sec == 0) {
gettimeofday(&cur_time, NULL);
tokens = interval*(preload-1);
} else {
long ntokens;
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
ntokens = (tv.tv_sec - cur_time.tv_sec)*1000 +
(tv.tv_usec-cur_time.tv_usec)/1000;
if (!interval) {
/* Case of unlimited flood is special;
* if we see no reply, they are limited to 100pps */
if (ntokens < MININTERVAL && in_flight() >= preload)
return MININTERVAL-ntokens;
}
ntokens += tokens;
if (ntokens > interval*preload)
ntokens = interval*preload;
if (ntokens < interval)
return interval - ntokens;
cur_time = tv;
tokens = ntokens - interval;
}
if (options & F_OUTSTANDING) {
if (ntransmitted > 0 && !rcvd_test(ntransmitted)) {
print_timestamp();
printf("no answer yet for icmp_seq=%lu\n", (ntransmitted % MAX_DUP_CHK));
fflush(stdout);
}
}
resend:
i = send_probe(); // 处理工作做完,发包
// 发送成功
if (i == 0) {
oom_count = 0;
advance_ntransmitted();
if (!(options & F_QUIET) && (options & F_FLOOD)) {
/* Very silly, but without this output with
* high preload or pipe size is very confusing. */
if ((preload < screen_width && pipesize < screen_width) ||
in_flight() < screen_width)
write_stdout(".", 1);
}
return interval - tokens;
}
/* 发送失败,处理各种错误 */
if (i > 0) {
/* Apparently, it is some fatal bug. */
abort();
} else if (errno == ENOBUFS || errno == ENOMEM) {
int nores_interval;
/* Device queue overflow or OOM. Packet is not sent. */
tokens = 0;
/* Slowdown. This works only in adaptive mode (option -A) */
rtt_addend += (rtt < 8*50000 ? rtt/8 : 50000);
if (options&F_ADAPTIVE)
update_interval();
nores_interval = SCHINT(interval/2);
if (nores_interval > 500)
nores_interval = 500;
oom_count++;
if (oom_count*nores_interval < lingertime)
return nores_interval;
i = 0;
/* Fall to hard error. It is to avoid complete deadlock
* on stuck output device even when dealine was not requested.
* Expected timings are screwed up in any case, but we will
* exit some day. :-) */
} else if (errno == EAGAIN) {
/* Socket buffer is full. */
tokens += interval;
return MININTERVAL;
} else {
if ((i=receive_error_msg()) > 0) {
/* An ICMP error arrived. */
tokens += interval;
return MININTERVAL;
}
/* Compatibility with old linuces. */
if (i == 0 && confirm_flag && errno == EINVAL) {
confirm_flag = 0;
errno = 0;
}
if (!errno)
goto resend;
}
/* Hard local error. Pretend we sent packet. */
advance_ntransmitted();
if (i == 0 && !(options & F_QUIET)) {
if (options & F_FLOOD)
write_stdout("E", 1);
else
perror("ping: sendmsg");
}
tokens = 0;
return SCHINT(interval);
}
7、send_probe函数
int send_probe()
{
// ICMP报文头部
struct icmphdr *icp;
int cc;
int i;
icp = (struct icmphdr *)outpack;
icp->type = ICMP_ECHO; // 请求类型:request
icp->code = 0;
icp->checksum = 0; //校验和
icp->un.echo.sequence = htons(ntransmitted+1); //
icp->un.echo.id = ident; // 进程ID
rcvd_clear(ntransmitted+1);
if (timing) {
if (options&F_LATENCY) {
struct timeval tmp_tv;
gettimeofday(&tmp_tv, NULL);
memcpy(icp+1, &tmp_tv, sizeof(tmp_tv));
} else {
memset(icp+1, 0, sizeof(struct timeval));
}
}
cc = datalen + 8; /* skips ICMP portion */
/* compute ICMP checksum here */
icp->checksum = in_cksum((u_short *)icp, cc, 0);
if (timing && !(options&F_LATENCY)) {
struct timeval tmp_tv;
gettimeofday(&tmp_tv, NULL);
memcpy(icp+1, &tmp_tv, sizeof(tmp_tv));
icp->checksum = in_cksum((u_short *)&tmp_tv, sizeof(tmp_tv), ~icp->checksum);
}
// 发出去之前得把包封装成msghdr类型
do {
static struct iovec iov = {outpack, 0};
static struct msghdr m = { &whereto, sizeof(whereto),
&iov, 1, &cmsg, 0, 0 };
m.msg_controllen = cmsg_len;
iov.iov_len = cc;
i = sendmsg(icmp_sock, &m, confirm); // 在这里发包
confirm = 0;
} while (0);
return (cc == i ? 0 : i);
}
8、parse_reply函数
打印收到的ICMP包,就是一个拆包的过程
int
parse_reply(struct msghdr *msg, int cc, void *addr, struct timeval *tv)
{
struct sockaddr_in *from = addr;
__u8 *buf = msg->msg_iov->iov_base;
struct icmphdr *icp;
struct iphdr *ip;
int hlen;
int csfailed;
/* 检查IP包头部 */
ip = (struct iphdr *)buf;
hlen = ip->ihl*4; // IP包头长度
if (cc < hlen + 8 || ip->ihl < 5) {
if (options & F_VERBOSE)
fprintf(stderr, "ping: packet too short (%d bytes) from %s\n", cc,
pr_addr(from->sin_addr.s_addr));
return 1;
}
/* ICMP包部分 */
cc -= hlen;
//指针往右走hlen就是ICMP包的起始
icp = (struct icmphdr *)(buf + hlen);
//检查校验和
csfailed = in_cksum((u_short *)icp, cc, 0);
// 收到ICMP包如果是回应类型
if (icp->type == ICMP_ECHOREPLY) {
// 先对比进程ID,确定是自己要的包
if (icp->un.echo.id != ident)
return 1; /* 'Twas not our ECHO */
// 计算来回的时间
if (gather_statistics((__u8*)icp, sizeof(*icp), cc,
ntohs(icp->un.echo.sequence),
ip->ttl, 0, tv, pr_addr(from->sin_addr.s_addr),
pr_echo_reply)) {
fflush(stdout);
return 0; // 回到main_loop
}
} else {
/* 当收到一个重定向或源抑制包时进入
/* We fall here when a redirect or source quench arrived.
* Also this branch processes icmp errors, when IP_RECVERR
* is broken. */
switch (icp->type) {
case ICMP_ECHO: // 收到一个ICMP请求包
/* MUST NOT */
return 1;
case ICMP_SOURCE_QUENCH: // 源抑制
case ICMP_REDIRECT: // 重定向
case ICMP_DEST_UNREACH: // 目标不可达
case ICMP_TIME_EXCEEDED: // 超时
case ICMP_PARAMETERPROB: // 参数错误
{
struct iphdr * iph = (struct iphdr *)(&icp[1]);
struct icmphdr *icp1 = (struct icmphdr*)((unsigned char *)iph + iph->ihl*4);
int error_pkt;
if (cc < 8+sizeof(struct iphdr)+8 ||
cc < 8+iph->ihl*4+8)
return 1;
if (icp1->type != ICMP_ECHO ||
iph->daddr != whereto.sin_addr.s_addr ||
icp1->un.echo.id != ident)
return 1;
error_pkt = (icp->type != ICMP_REDIRECT &&
icp->type != ICMP_SOURCE_QUENCH);
if (error_pkt) {
acknowledge(ntohs(icp1->un.echo.sequence));
return 0;
}
nerrors+=error_pkt;
// 根据选项操作
...
}
return 0;
}
9、常用网络编程函数:
- socket函数:用来创建套接字
- 函数原型 int socket(int domain, int type, int protocol);
- domain表示套接字要使用的协议簇
- AF_UNIX(本机通信)
- AF_INET(TCP/IP – IPv4)
- AF_INET6(TCP/IP – IPv6)
- type表示套接字类型
- SOCK_STREAM(TCP流)
- SOCK_DGRAM(UDP数据报)
- SOCK_RAW(原始套接字)
- protocol用来确定协议种类,一般为0
- htons函数:将端口号由主机字节序转换为网络字节序的整数值
- 如 mysock.sin_port = htons(80)
- inet_addr函数:将一个IP字符串转化为一个网络字节序的整数值
- 如 mysock.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("192.168.1.0")
- recvmsg\ sendmsg函数
- ssize_t recvmsg ( int sockfd , struct msghdr * msg , int flags )
- ssize_t sendmsg ( int sockfd , struct msghdr * msg , int flags ) ;
- sockfd - 套接字描述符
- msg - 消息头部
- flags - 套接口设置标识
- msghdr结构体
struct msghdr {
void * msg_name ; / * 消息的协议地址 * /
socklen_t msg_namelen ; / * 地址的长度 * /
struct iovec * msg_iov ; / * 多io缓冲区的地址 * /
int msg_iovlen ; / * 缓冲区的个数 * /
void * msg_control ; / * 辅助数据的地址 * /
socklen_t msg_controllen ; / * 辅助数据的长度 * /
int msg_flags ; / * 接收消息的标识 * /
} ;
10、感想心得
- 每个命令都有很多可选参数,第一遍读源码时去深究每个参数的功能实现是很难的,很容易陷入层层递进的函数,最后放弃。应该先把实现框架搞懂。
- 主要功能的实现依靠icmp包的封装,icmp包的解析,sendmsg和recvmsg两个函数。复杂之处在于
- 各个参数的不同设置
- 发包时间间隔的设置,涉及进程信号处理
- 整理一下parse_reply即收到包的解析
- 首先解析IP包的头部,解析完指针往前走
- 读取ICMP包的type段、code段判断是否是reply包
- 检查校验和
- 比较标识符(进程ID)
- 根据时间戳计算来回时间
- 今后还需要加深对UNIX网络编程的学习。由于很多定义和函数用法不熟悉,浪费了很多时间。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号