Binary Tree Traversals
A binary tree is a finite set of vertices that is either empty or consists of a root r and two disjoint binary trees called the left and right subtrees. There are three most important ways in which the vertices of a binary tree can be systematically traversed or ordered. They are preorder, inorder and postorder. Let T be a binary tree with root r and subtrees T1,T2.
In a preorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the root r followed by visiting the vertices of T1 in preorder, then the vertices of T2 in preorder.
In an inorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in inorder, then the root r, followed by the vertices of T2 in inorder.
In a postorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in postorder, then the vertices of T2 in postorder and finally we visit r.
Now you are given the preorder sequence and inorder sequence of a certain binary tree. Try to find out its postorder sequence.
![]()
In a preorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the root r followed by visiting the vertices of T1 in preorder, then the vertices of T2 in preorder.
In an inorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in inorder, then the root r, followed by the vertices of T2 in inorder.
In a postorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in postorder, then the vertices of T2 in postorder and finally we visit r.
Now you are given the preorder sequence and inorder sequence of a certain binary tree. Try to find out its postorder sequence.
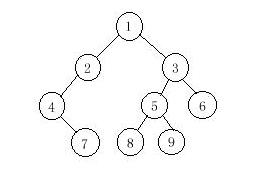
InputThe input contains several test cases. The first line of each test case contains a single integer n (1<=n<=1000), the number of vertices of the binary tree. Followed by two lines, respectively indicating the preorder sequence and inorder sequence. You can assume they are always correspond to a exclusive binary tree.
OutputFor each test case print a single line specifying the corresponding postorder sequence.
Sample Input
9 1 2 4 7 3 5 8 9 6 4 7 2 1 8 5 9 3 6
Sample Output
7 4 2 8 9 5 6 3 1
题意:给出二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历,求后序遍历。
思路:用递归的宏观思路,结合前序历遍和中序历遍,找根节点,在中序历遍中,根节点左边的全部是左子树,右边的全部是右子树,那么将这些结点慢慢划分为一个个子问题。左子树的第一个结点又可以看作一个新的根节点,它有它的左子树和右子树,同理,慢慢划分,递归的思路也就出来了。假如中序历遍中第i个点是根节点,那么划分为两个区域,0~ i-1和i+1~n-1;那么我们只需要将递归的顺序设置为左右根,输出的自然就是后序遍历。
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 const int maxn=1005; 4 int a[maxn]; 5 int b[maxn]; 6 int ans=0; 7 void fun(int *a,int *b,int n) 8 { 9 if(n==0) return; 10 int i=0; 11 for(;i<n;i++) 12 { 13 if(b[i]==*a) break; 14 } 15 fun(a+1,b,i); 16 fun(a+i+1,b+i+1,n-i-1); 17 if(ans>0) 18 cout<<" "; 19 ans++; 20 cout<<a[0]; 21 } 22 int main() 23 { 24 int n; 25 while(cin>>n) 26 { 27 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 28 { 29 cin>>a[i]; 30 } 31 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 32 { 33 cin>>b[i]; 34 } 35 fun(a,b,n); 36 cout<<endl; 37 } 38 return 0; 39 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号