大话--单例模式
定义
保证在整个软件系统中,对某个类只能存在一个对象实例,并且该类只提供一个取得其对象实例的方法(静态方法)。
优点
1、在内存里只有一个实例,减少了内存的开销,尤其是频繁的创建和销毁实例。
2、避免对资源的多重占用(比如写文件操作)。
缺点
没有接口,扩展困难。
使用场景
需要频繁的进行创建和销毁的对象、创建对象时耗时过多或耗费资源过多,但又经常用到的对象、工具类对象、频繁访问数据库或文件的对象(比如数据源、session工厂等)。
tips
- 1、单例类只能有一个实例。
- 2、单例类必须自己创建自己的唯一实例。
- 3、单例类必须给所有其他对象提供这一实例。
关键代码
构造器一定是私有的
类图
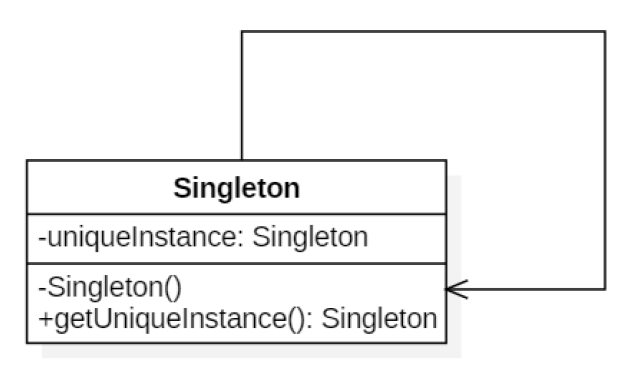
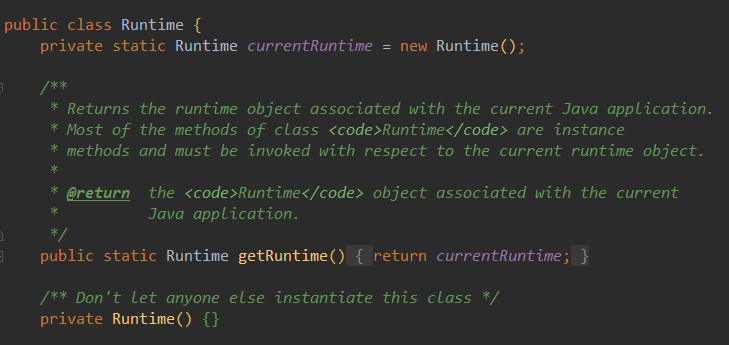
使用单例模式的源码
java.lang.Runtime就使用了饿汉式的单例模式,因为Runtime一定会被使用,所以不会造成资源浪费。
具体实现
1.饿汉式(静态常量)

1 package Singleton.Singletontest1; 2 3 /** 4 * @title: Singleton1 5 * @Author yzhengy 6 * @Date: 2020/7/30 20:22 7 * @Question: 饿汉式(静态常量) 8 */ 9 10 /* 11 * @Date: 2020/7/30 20:23 12 * 1.构造器私有化(防止new对象) 13 * 2.类的内部创建对象 14 * 3.向外暴露一个静态的公共方法(getInstance) 15 * 优点:类装载时就完成了实例化,避免了多线程同步问题。 16 * 缺点:没有达到懒加载效果,如果一直不使用这个实例,会造成内存的浪费。 17 */ 18 public class Singleton1 { 19 public static void main(String[] args) { 20 Singleton instance = Singleton.getInstance(); 21 Singleton instance2 = Singleton.getInstance(); 22 System.out.println(instance == instance2);//true 23 System.out.println(instance.hashCode()==instance2.hashCode());//true 24 } 25 } 26 27 28 class Singleton{ 29 private Singleton(){} 30 31 private final static Singleton instance = new Singleton(); 32 33 public static Singleton getInstance(){ 34 return instance; 35 } 36 }
2.饿汉式(静态代码块)

1 package Singleton.Singletontest2; 2 3 /** 4 * @title: Singleton2 5 * @Author yzhengy 6 * @Date: 2020/7/30 20:34 7 * @Question: 饿汉式(静态代码块) 8 */ 9 10 /* 11 * @Date: 2020/7/30 20:23 12 * 1.构造器私有化(防止new对象) 13 * 2.类的内部创建对象实例 14 * 3.在静态代码块中创建单例对象 15 * 4.向外暴露一个静态的公共方法(getInstance) 16 * 优缺点:与饿汉式(静态常量)的优缺点相同 17 */ 18 public class Singleton2 { 19 public static void main(String[] args) { 20 Singleton instance = Singleton.getInstance(); 21 Singleton instance2 = Singleton.getInstance(); 22 System.out.println(instance == instance2);//true 23 System.out.println(instance.hashCode()==instance2.hashCode());//true 24 } 25 } 26 27 28 class Singleton{ 29 private Singleton(){} 30 31 private static Singleton instance; 32 33 static{ 34 instance = new Singleton(); 35 } 36 37 public static Singleton getInstance(){ 38 return instance; 39 } 40 }
3.懒汉式(线程不安全)

1 package Singleton.Singletontest3; 2 3 /** 4 * @title: Singleton3 5 * @Author yzhengy 6 * @Date: 2020/7/31 8:35 7 * @Question: 懒汉式(线程不安全) 8 */ 9 10 /* 11 * @Date: 2020/7/31 8:41 12 * 起到了懒加载的效果,但是只能在单线程时使用。 13 * 如果在多线程时使用,一个线程进入了if(instance==null)判断语句块,还未来得及往下执行, 14 * 另一个线程也通过了这个判断语句,这时就会产生多个实例。就会破坏单例模式。 15 */ 16 public class Singleton3 { 17 18 public static void main(String[] args) { 19 System.out.println("我是线程不安全的懒汉式!!!"); 20 Singleton instance = Singleton.getInstance(); 21 Singleton instance2 = Singleton.getInstance(); 22 System.out.println(instance == instance2);//true 23 System.out.println(instance.hashCode()==instance2.hashCode());//true 24 } 25 26 } 27 28 class Singleton{ 29 private Singleton(){} 30 31 private static Singleton instance; 32 33 //提供一个静态公有方法,当时用到该方法时,才会创建instance。(懒汉式的核心) 34 public static Singleton getInstance(){ 35 if (instance == null) 36 instance = new Singleton(); 37 return instance; 38 } 39 }
4.懒汉式(线程安全,同步方法)

1 package Singleton.Singletontest4; 2 3 /** 4 * @title: Singleton4 5 * @Author yzhengy 6 * @Date: 2020/7/31 8:47 7 * @Question: 懒汉式(线程安全,同步方法) 8 */ 9 10 /* 11 * @Date: 2020/7/31 8:47 12 * 在线程不安全的懒汉式的基础上,直接加一个Synchronized锁,保证线程安全。 13 * 缺点:每个线程想获取类的实例时,执行getInstance()方法都要进行同步,方法同步效率太低。 14 * 其实这个方法执行一次实例化代码就可以了,后面想获取该类实例直接return就可以了。 15 */ 16 public class Singleton4 { 17 18 public static void main(String[] args) { 19 System.out.println("我是线程安全的懒汉式!!!"); 20 Singleton instance = Singleton.getInstance(); 21 Singleton instance2 = Singleton.getInstance(); 22 System.out.println(instance == instance2);//true 23 System.out.println(instance.hashCode()==instance2.hashCode());//true 24 } 25 26 } 27 28 class Singleton{ 29 private Singleton(){} 30 31 private static Singleton instance; 32 33 //提供一个静态公有方法,当时用到该方法时,才会创建instance。(懒汉式的核心) 34 public static synchronized Singleton getInstance(){ 35 if (instance == null) 36 instance = new Singleton(); 37 return instance; 38 } 39 }
5.懒汉式(线程不安全,同步代码块)

1 package Singleton.Singletontest5; 2 3 /** 4 * @title: Singleton5 5 * @Author yzhengy 6 * @Date: 2020/7/31 8:52 7 * @Question: 懒汉式(线程不安全,同步代码块) 8 */ 9 10 /* 11 * @Date: 2020/7/31 8:55 12 * 与懒汉式线程不安全会有同样的问题,可能在多线程环境下创建多个实例。 13 */ 14 public class Singleton5 { 15 16 public static void main(String[] args) { 17 System.out.println("我是线程不安全的懒汉式2!!!"); 18 Singleton instance = Singleton.getInstance(); 19 Singleton instance2 = Singleton.getInstance(); 20 System.out.println(instance == instance2);//true 21 System.out.println(instance.hashCode()==instance2.hashCode());//true 22 } 23 24 } 25 26 class Singleton{ 27 private Singleton(){} 28 29 private static Singleton instance; 30 31 //提供一个静态公有方法,当时用到该方法时,才会创建instance。(懒汉式的核心) 32 public static Singleton getInstance(){ 33 if (instance == null) 34 35 synchronized (Singleton.class){ 36 instance = new Singleton();} 37 38 return instance; 39 } 40 }
6.双重检查

1 package Singleton.Singletontest6; 2 3 /** 4 * @title: Singleton6 5 * @Author yzhengy 6 * @Date: 2020/7/31 9:09 7 * @Question: 双重检查--推荐使用 8 */ 9 public class Singleton6 { 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 System.out.println("我是双重检查"); 12 Singleton instance = Singleton.getInstance(); 13 Singleton instance2 = Singleton.getInstance(); 14 System.out.println(instance == instance2);//true 15 System.out.println(instance.hashCode()==instance2.hashCode());//true 16 } 17 } 18 19 /* 20 * @Date: 2020/7/31 9:16 21 * 线程安全;延迟加载;效率较高; 22 */ 23 class Singleton{ 24 private Singleton(){} 25 26 private static volatile Singleton instance; 27 28 public static Singleton getInstance(){ 29 if (instance == null){ 30 synchronized (Singleton.class){ 31 if (instance == null) 32 instance = new Singleton(); 33 } 34 } 35 return instance; 36 } 37 }
7.静态内部类

1 package Singleton.Singletontest7; 2 3 /** 4 * @title: Singleton7 5 * @Author yzhengy 6 * @Date: 2020/7/31 9:18 7 * @Question: 静态内部类--推荐使用 8 */ 9 public class Singleton7 { 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 System.out.println("我是静态内部类"); 12 Singleton instance = Singleton.getInstance(); 13 Singleton instance2 = Singleton.getInstance(); 14 System.out.println(instance == instance2);//true 15 System.out.println(instance.hashCode()==instance2.hashCode());//true 16 } 17 } 18 /* 19 * @Date: 2020/7/31 9:20 20 * 外部类被装载时,静态内部类并不会被装载。 21 * 当调用getInstance时才会使静态内部类被装载,而且只会装载一次,装载时线程安全。 22 * 优点:线程安全,利用静态内部类特点实现延迟加载,效率高。 23 */ 24 class Singleton{ 25 private Singleton(){} 26 27 //静态内部类,该类中有一个静态属性Singleton 28 private static class SingletonInstance{ 29 private final static Singleton INSTANCE = new Singleton(); 30 } 31 32 //提供一个静态的公有方法,直接返回SingletonInstance.INSTANCE 33 public static Singleton getInstance(){ 34 return SingletonInstance.INSTANCE; 35 } 36 }
8.枚举

1 package Singleton.Singletontest8; 2 3 /** 4 * @title: Singleton8 5 * @Author yzhengy 6 * @Date: 2020/7/31 9:30 7 * @Question: 枚举--推荐使用 8 */ 9 public class Singleton8 { 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 System.out.println("我是枚举"); 12 Singleton instance = Singleton.INSTANCE; 13 Singleton instance2 = Singleton.INSTANCE; 14 System.out.println(instance == instance2);//true 15 System.out.println(instance.hashCode()==instance2.hashCode());//true 16 17 instance.sayOK(); 18 } 19 } 20 /* 21 * @Date: 2020/7/31 9:34 22 * 使用枚举可以实现单例 23 * 不仅可以避免多线程同步问题,还能防止反序列化重新创建新的对象。(其他方法则需要使用transient关键字) 24 * 可以防止反射攻击。 25 */ 26 enum Singleton{ 27 INSTANCE; 28 public void sayOK(){ 29 System.out.println("ok"); 30 } 31 }
Stay hungry,Stay foolish



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号