codeforces错题本
B. Berland Crossword(1400)
Berland crossword is a puzzle that is solved on a square grid with nn rows and nn columns. Initially all the cells are white.
To solve the puzzle one has to color some cells on the border of the grid black in such a way that:
- exactly UU cells in the top row are black;
- exactly RR cells in the rightmost column are black;
- exactly DD cells in the bottom row are black;
- exactly LL cells in the leftmost column are black.
Note that you can color zero cells black and leave every cell white.
Your task is to check if there exists a solution to the given puzzle.
The first line contains a single integer tt (1≤t≤10001≤t≤1000) — the number of testcases.
Then the descriptions of tt testcases follow.
The only line of each testcase contains 55 integers n,U,R,D,Ln,U,R,D,L (2≤n≤1002≤n≤100; 0≤U,R,D,L≤n0≤U,R,D,L≤n).
For each testcase print "YES" if the solution exists and "NO" otherwise.
You may print every letter in any case you want (so, for example, the strings yEs, yes, Yes and YES are all recognized as positive answer).
4 5 2 5 3 1 3 0 0 0 0 4 4 1 4 0 2 1 1 1 1
YES YES NO YES
Here are possible solutions to testcases 11, 22 and 44:
题目总结:本题看起来复杂,其实思路找对题目变得很简单,本题关键在于看出边角格子的影响,可以设置四个变量ui=0,ri=0,di=0,li=0记录边角格子对相邻两边的影响,如:示例一右边要求五个涂黑
则上边受影响ui++,下边同样di++。最后判断ui<=u,如果四个变量都满足即可输出yes。另外需要特判当两边涂黑数一样,则每一条边相应变量分别加1,不能只给一边加。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<algorithm>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const ll nl=1e5+5;
#define speed_up ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int main(){
speed_up;
ll t;
cin>>t;
ll i,j;
while(t--){
ll n;
cin>>n;
ll u,r,d,l;
cin>>u>>r>>d>>l;
ll ui=0,ri=0,di=0,li=0,f=0,fl=0;
if(u>n-2){
if(u==n){
ri+=1;
li+=1;
}else if(u==n-1){
if(r>l){
ri++;
}else if(r==l){
ri++;
f=0;
}else{
li++;
}
}
}
if(r>n-2){
if(r==n){
ui+=1;
di+=1;
}else if(r==n-1){
if(u>d){
ui++;
}else if(u==d){
ui++;
fl=0;
}else{
di++;
}
}
}
if(d>n-2){
if(d==n){
ri+=1;
li+=1;
}else if(d==n-1){
if(r>l){
ri++;
}else if(r==l){
li++;
}else{
li++;
}
}
}
if(l>n-2){
if(l==n){
ui+=1;
di+=1;
}else if(l==n-1){
if(u>d){
ui++;
}else if(u==d){
di++;
}else{
di++;
}
}
}
//cout<<ui<<" "<<ri<<" "<<di<<" "<<li<<endl;
if(ui<=u&&ri<=r&&di<=d&&li<=l){
cout<<"YES"<<endl;
}else{
cout<<"NO"<<endl;
}
}
}
B. Planet Lapituletti(1300)
The time on the planet Lapituletti goes the same way it goes on Earth but a day lasts hh hours and each hour lasts mm minutes. The inhabitants of that planet use digital clocks similar to earth ones. Clocks display time in a format HH:MM (the number of hours in decimal is displayed first, then (after the colon) follows the number of minutes in decimal; the number of minutes and hours is written with leading zeros if needed to form a two-digit number). Hours are numbered from 00 to h−1h−1 and minutes are numbered from 00 to m−1m−1.
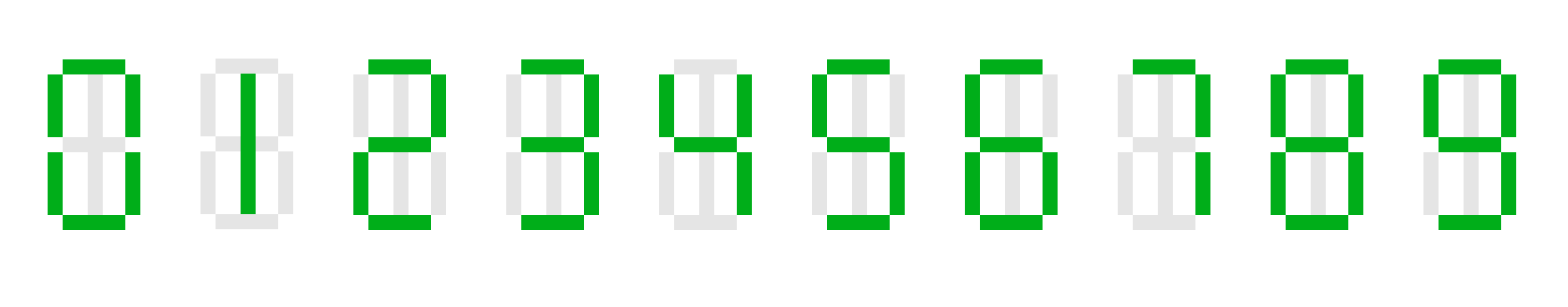
That's how the digits are displayed on the clock. Please note that digit 11 is placed in the middle of its position.
A standard mirror is in use on the planet Lapituletti. Inhabitants often look at the reflection of the digital clocks in the mirror and feel happy when what you see on the reflected clocks is a valid time (that means that you see valid digits in the reflection and this time can be seen on the normal clocks at some moment of a day).
The image of the clocks in the mirror is reflected against a vertical axis.
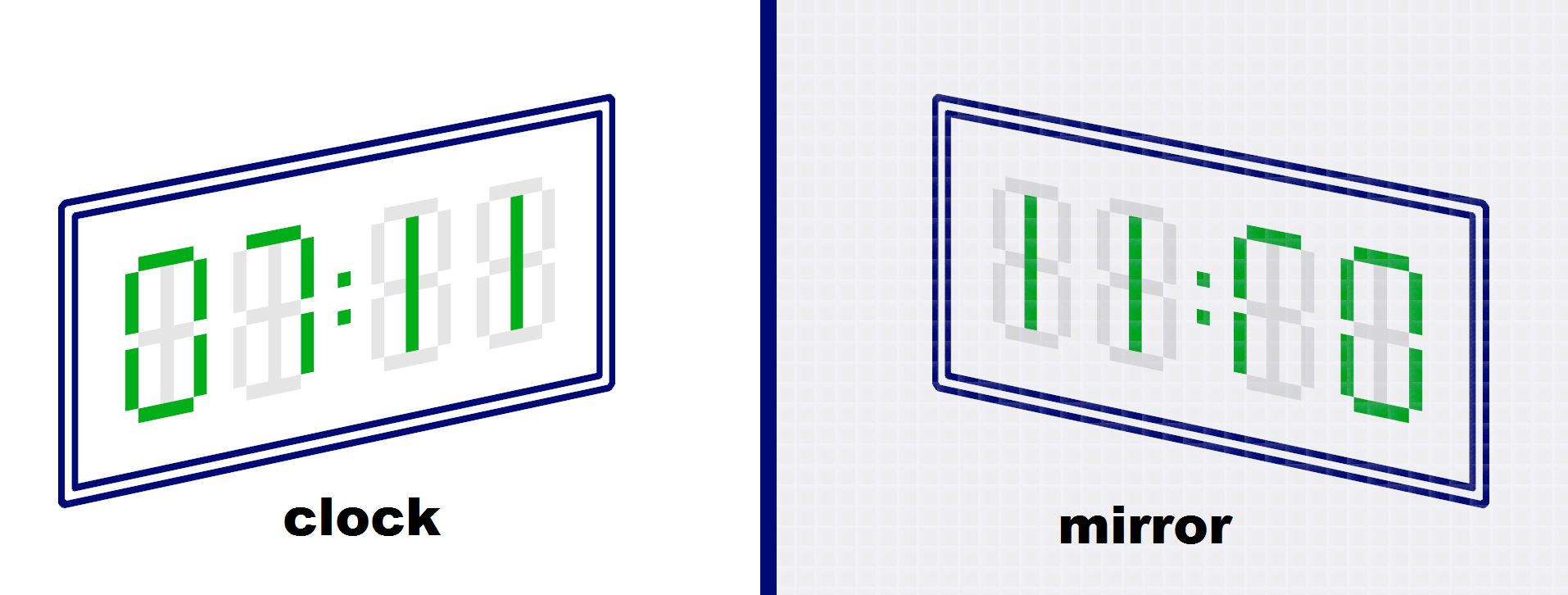
The reflection is not a valid time.
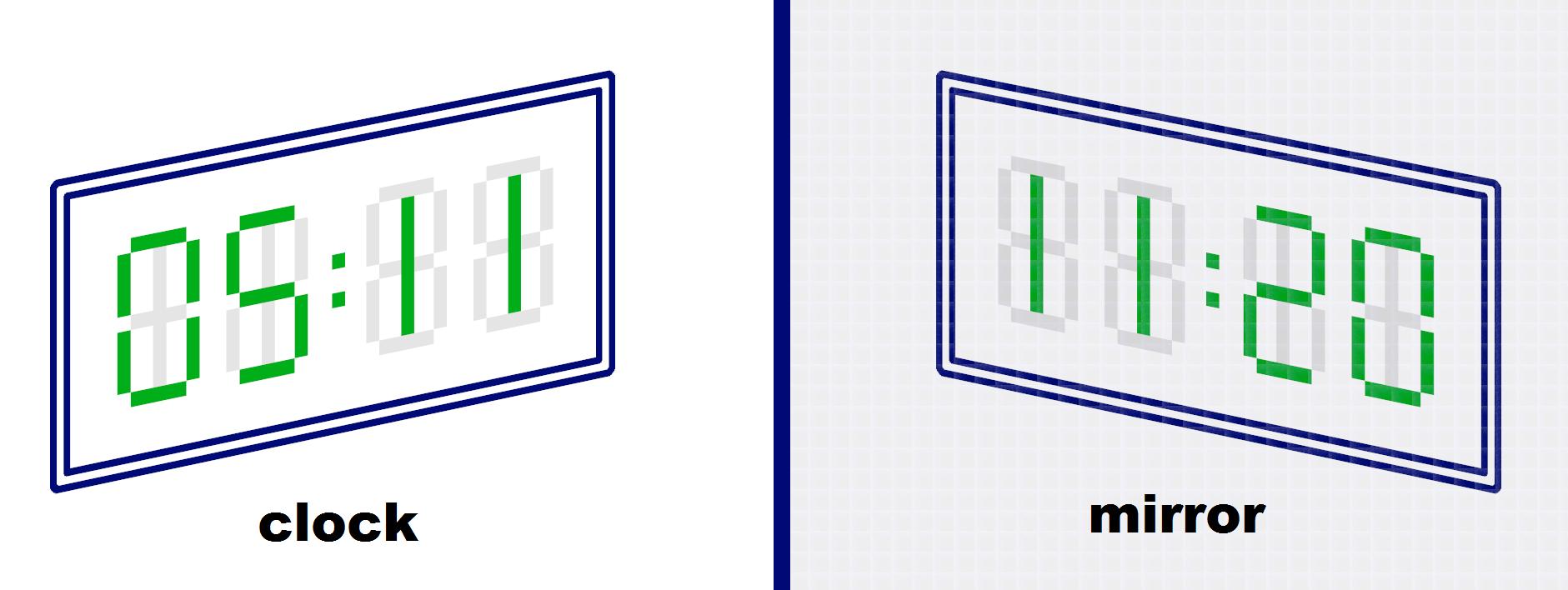
The reflection is a valid time with h=24h=24, m=60m=60. However, for example, if h=10h=10, m=60m=60, then the reflection is not a valid time.
An inhabitant of the planet Lapituletti begins to look at a mirrored image of the clocks at some time moment ss and wants to know the nearest future time moment (which can possibly happen on the next day), when the reflected clock time is valid.
It can be shown that with any hh, mm, ss such a moment exists. If the reflected time is correct at the moment the inhabitant began to look at the clock, that moment is considered the nearest.
You are asked to solve the problem for several test cases.
The first line contains a single integer TT (1≤T≤1001≤T≤100) — the number of test cases.
The next 2⋅T2⋅T lines contain the description of test cases. The description of each test case consists of two lines.
The first line of a test case contains two integers hh, mm (1≤h,m≤1001≤h,m≤100).
The second line contains the start time ss in the described format HH:MM.
For each test case output in a separate line the nearest moment in format HH:MM when the reflected time is correct.
5 24 60 12:21 24 60 23:59 90 80 52:26 1 100 00:01 10 10 04:04
12:21 00:00 52:28 00:00 00:00
In the second test case it is not hard to show that the reflection of 23:59 is incorrect, while the reflection of the moment 00:00 on the next day is correct.
本题字数很多,但是不难理解,不要被它的字数吓到。题目要求如果输出满足要求的最近的时刻。要求:1.倒过来(镜面反射)不能超过题目所给范围,还有不能包含3,4,6,7,9这五个数字,因为倒过来不能识别,还有注意5倒过来是2倒过来是5。本题wa的次数蛮多的,原因是没搞清楚题目细节,我的思路是直接暴力,直接四层for循环,然后跟上判断,注意当出现2和5时要特判。
- #include<bits/stdc++.h>
- #include<algorithm>
- #define ll long long
- using namespace std;
- const ll nl=1e5+5;
- ll z[101]={0};
- #define speed_up ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
- int main(){
- speed_up;
- ll t;
- cin>>t;
- ll i,j;
- z[3]=1,z[4]=1,z[6]=1,z[7]=1,z[9]=1,z[2]=2,z[5]=2;
- while(t--){
- ll h,m;
- cin>>h>>m;
- string n;
- cin>>n;
- ll ai=0,bi=0,ci=0,di=0;
- ai=n[0]-'0';
- bi=n[1]-'0';
- ci=n[3]-'0';
- di=n[4]-'0';
- ll a,b,c,d;
- ll f=0;
- for(a=ai;a<=h/10;a++){
- for(b=0;b<10;b++){
- for(c=0;c<10;c++){
- for(d=0;d<10;d++){
- if(z[a]!=1&&z[b]!=1&&z[c]!=1&&z[d]!=1){
- if(a*10+b<h&&c*10+d<m){
- if(z[a]!=2&&z[b]!=2&&z[c]!=2&&z[d]!=2){
- if(d*10+c<h&&b*10+a<m){
- if(a>ai){
- f=1;
- }else if(a==ai){
- if((b==bi&&(c*10+d>=ci*10+di))||(b>bi)){
- f=1;
- }
- }
- }
- }else{
- ll aii,bii,cii,dii;
- aii=a;
- bii=b;
- cii=c;
- dii=d;
- if(z[a]==2){
- if(aii==2){
- aii=5;
- }else{
- aii=2;
- }
- }
- if(z[b]==2){
- if(bii==2){
- bii=5;
- }else{
- bii=2;
- }
- }
- if(z[c]==2){
- if(cii==2){
- cii=5;
- }else{
- cii=2;
- }
- }
- if(z[d]==2){
- if(dii==2){
- dii=5;
- }else{
- dii=2;
- }
- }
- if(dii*10+cii<h&&bii*10+aii<m){
- if(a>ai){
- f=1;
- }else if(a==ai){
- if((b==bi&&(c*10+d>=ci*10+di))||(b>bi)){
- f=1;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- if(f==1){
- break;
- }
- }
- if(f==1){
- break;
- }
- }
- if(f==1){
- break;
- }
- }
- if(f==1){
- break;
- }
- }
- if(f==1){
- cout<<a<<b<<":"<<c<<d<<endl;
- }else{
- cout<<"00:00"<<endl;
- }
- }
- }
L1-017 到底有多二 (15 分)
输出%,printf需要连续敲两个%;
L1-018 大笨钟 (10 分)
题目过不了。可以换一下scanf printf;
You are given an array a1,a2,…,ana1,a2,…,an consisting of nn positive integers and a positive integer mm.
You should divide elements of this array into some arrays. You can order the elements in the new arrays as you want.
Let's call an array mm-divisible if for each two adjacent numbers in the array (two numbers on the positions ii and i+1i+1 are called adjacent for each ii) their sum is divisible by mm. An array of one element is mm-divisible.
Find the smallest number of mm-divisible arrays that a1,a2,…,ana1,a2,…,an is possible to divide into.
The first line contains a single integer tt (1≤t≤1000)(1≤t≤1000) — the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains two integers nn, mm (1≤n≤105,1≤m≤105)(1≤n≤105,1≤m≤105).
The second line of each test case contains nn integers a1,a2,…,ana1,a2,…,an (1≤ai≤109)(1≤ai≤109).
It is guaranteed that the sum of nn and the sum of mm over all test cases do not exceed 105105.
For each test case print the answer to the problem.
4 6 4 2 2 8 6 9 4 10 8 1 1 1 5 2 4 4 8 6 7 1 1 666 2 2 2 4
3 6 1 1
In the first test case we can divide the elements as follows:
- [4,8][4,8]. It is a 44-divisible array because 4+84+8 is divisible by 44.
- [2,6,2][2,6,2]. It is a 44-divisible array because 2+62+6 and 6+26+2 are divisible by 44.
- [9][9]. It is a 44-divisible array because it consists of one element
题解:当时看的时候没有任何思路,其实取余即可,余数相加等于m的即可放到一组中。注意余数为零时余数相等时的情况。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
const ll nl=1e5+5;
ll a[nl]={0};
ll b[nl]={0};
int main(){
ll t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
ll n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
ll i,j;
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>a[i];
b[a[i]%m]++;
}
for(i=0;i<=m/2;i++){
if(i==0){//余数为零的情况
if(b[i]>1){
n-=b[i]-1;
}
}else{
if(b[i]>0&&b[m-i]>0){
if(i==m-i){//余数相等的情况
n-=b[i]-1;
}else{
if(b[i]==b[m-i]){
n-=b[i]*2-1;
}else{
n-=min(b[i],b[m-i])*2;
}
}
}
}
}
cout<<n<<endl;
for(i=0;i<m;i++){
b[i]=0;
}
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号