- 在openEuler(推荐)或Ubuntu或Windows(不推荐)中完成下面任务
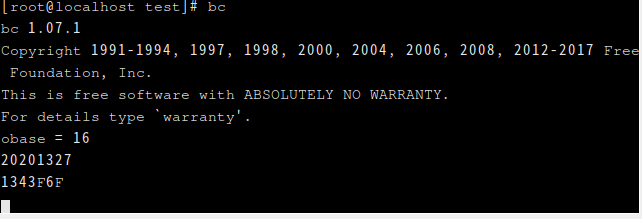
- 使用工具(如bc,计算机器等)把自己学号转化为16进制,提交转化过程和结果截图(2‘)
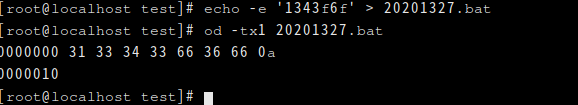
- 使用工具(如echo -e, ultraedit等)把上面转化的结果写入二进制文件“你的学号.dat”中,并用工具
od -tx1 你的学号.dat,提交命令运行(3’)
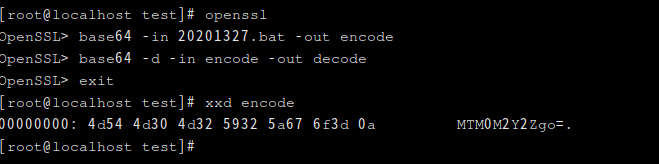
- 使用OpenSSL的base64命令对"你的学号.dat"进行编码解码,提交过程截图(5')
- 使用OpenSSL编程对"你的学号.dat"进行编码解码,提交代码和运行结果截图。(10’)
![]()
![]()
![]()
#include <openssl/evp.h>
#include <openssl/bio.h>
#include <openssl/buffer.h>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
char * base64Encode(const char *buffer, int length, bool newLine);
char * base64Decode(char *input, int length, bool newLine);
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
bool newLine = false;
string input = "Hello World!";
char * encode = base64Encode(input.c_str(), input.length(), newLine);
char * decode = base64Decode(encode, strlen(encode), newLine);
cout << "Base64 Encoded : " << encode << endl;
cout << "Base64 Decoded : " << decode << endl;
cin.get();
}
// base64 编码
char * base64Encode(const char *buffer, int length, bool newLine)
{
BIO *bmem = NULL;
BIO *b64 = NULL;
BUF_MEM *bptr;
b64 = BIO_new(BIO_f_base64());
if (!newLine) {
BIO_set_flags(b64, BIO_FLAGS_BASE64_NO_NL);
}
bmem = BIO_new(BIO_s_mem());
b64 = BIO_push(b64, bmem);
BIO_write(b64, buffer, length);
BIO_flush(b64);
BIO_get_mem_ptr(b64, &bptr);
BIO_set_close(b64, BIO_NOCLOSE);
char *buff = (char *)malloc(bptr->length + 1);
memcpy(buff, bptr->data, bptr->length);
buff[bptr->length] = 0;
BIO_free_all(b64);
return buff;
}
// base64 解码
char * base64Decode(char *input, int length, bool newLine)
{
BIO *b64 = NULL;
BIO *bmem = NULL;
char *buffer = (char *)malloc(length);
memset(buffer, 0, length);
b64 = BIO_new(BIO_f_base64());
if (!newLine) {
BIO_set_flags(b64, BIO_FLAGS_BASE64_NO_NL);
}
bmem = BIO_new_mem_buf(input, length);
bmem = BIO_push(b64, bmem);
BIO_read(bmem, buffer, length);
BIO_free_all(bmem);
return buffer;
}
![]()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号