实验2
实验任务1
程序源代码如下:
T.h
1 #pragma once 2 #include <string> 3 4 class T{ 5 public: 6 T(int x = 0,int y = 0); 7 T(const T &t); 8 T(T &&t); 9 ~T(); 10 11 void adjust(int radio); 12 void display() const; 13 14 private: 15 int m1,m2; 16 17 public: 18 static int get_cnt(); 19 20 public: 21 static const std::string doc; 22 static const int max_cnt; 23 24 private: 25 static int cnt; 26 27 friend void func(); 28 }; 29 30 void func();
T.cpp
1 #include "T.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <string> 4 5 const std::string T::doc{"a simple class sample"}; 6 const int T::max_cnt = 999; 7 int T::cnt = 0; 8 9 int T::get_cnt(){ 10 return cnt; 11 } 12 13 T::T(int x,int y):m1{x},m2{y}{ 14 ++cnt; 15 std::cout<<"T constructor called.\n"; 16 } 17 18 T::T(const T &t):m1{t.m1},m2{t.m2}{ 19 ++cnt; 20 std::cout<<"T copy constructor called.\n"; 21 } 22 23 T::T(T &&t):m1{t.m1},m2{t.m2}{ 24 ++cnt; 25 std::cout<<"T move constructor called.\n"; 26 } 27 28 T::~T(){ 29 --cnt; 30 std::cout<<"T destructor called.\n"; 31 } 32 33 void T::adjust(int ratio){ 34 m1*=ratio; 35 m2*=ratio; 36 } 37 38 void T::display() const{ 39 std::cout<<"("<<m1<<","<<m2<<")"; 40 } 41 42 void func(){ 43 T t5(42); 44 t5.m2 = 2049; 45 std::cout<<"t5 = "; 46 t5.display(); 47 std::cout<<'\n'; 48 std::cout<<"func: T objects'current count: "<<T::cnt; 49 std::cout<<'\n'; 50 }
test1.cpp
1 #include "T.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 4 void test_T(); 5 6 int main() { 7 std::cout << "test Class T: \n"; 8 test_T(); 9 10 std::cout << "\ntest friend func: \n"; 11 func(); 12 } 13 14 void test_T() { 15 std::cout << "T info: " << T::doc << std::endl; 16 std::cout << "T objects'max count: " << T::max_cnt << std::endl; 17 std::cout << "T objects'current count: " << T::get_cnt() << std::endl << std::endl; 18 19 T t1; 20 std::cout << "t1 = "; 21 t1.display(); 22 std::cout << std::endl; 23 24 T t2(3, 4); 25 std::cout << "t2 = "; 26 t2.display(); 27 std::cout << std::endl; 28 29 T t3(t2); 30 t3.adjust(2); 31 std::cout << "t3 = "; 32 t3.display(); 33 std::cout << std::endl; 34 35 T t4(std::move(t2)); 36 std::cout << "t4 = "; 37 t4.display(); 38 std::cout << std::endl; 39 40 std::cout << "test: T objects'current count: " << T::get_cnt() << std::endl; 41 }
运行截图如下:
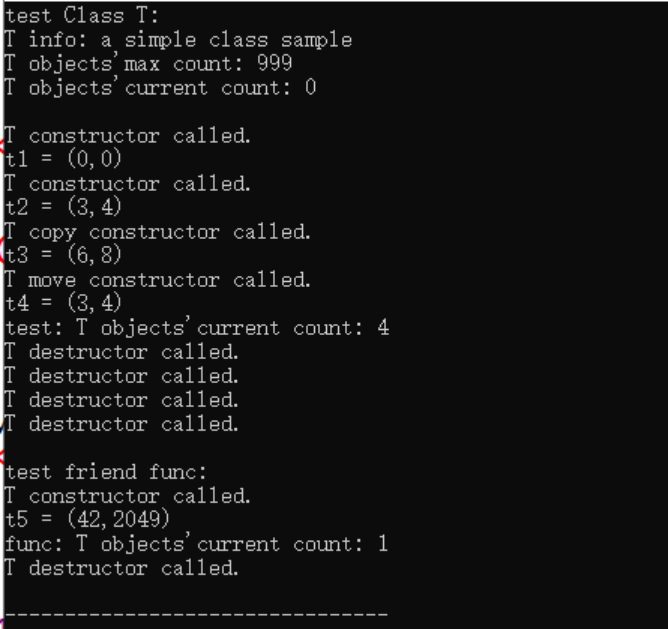
问题1:T内部已声明func是T友元函数,在类外部,去掉line36,重新编译,能否正常运行?
不能正常运行,报错信息如下:

去掉类外void func(),缺少了func函数在全局作用域的声明,在func函数被调用时找不到声明,编译器函数便会报错
问题2:总结各种构造函数、析构函数的功能、调用时机
普通构造函数通过传入参数或利用默认参数或不利用参数构造新对象,调用时机为传入参数或不传入参数构造对象时调用。
复制构造函数通过传入一个已有对象,利用已有对象的参数构造新对象,调用时机为传入已有对象来构造对象时调用。
移动构造函数通过传入一个临时对象,利用临时对象的参数构造新对象,调用时机为传入临时对象来构造对象时调用。
析构函数进行成员的资源清理工作,释放对象在构造过程中申请的内存,调用时机为对象生命周期结束时调用。
问题3:T.cpp中, line13-15,剪切到T.h的末尾,重新编译,程序能否正确编译
不能,报错信息截图如下:

T.cpp和test1.cpp都包含了头文件T.h,在头文件中进行静态成员初始化会导致静态成员被重复定义。
实验任务2
程序源代码如下:
Complex.h
1 #pragma once 2 3 #include <string> 4 5 class Complex { 6 public: 7 Complex(double x = 0.0, double y = 0.0); 8 Complex(const Complex& t); 9 10 double get_real() const; 11 double get_imag() const; 12 Complex add(const Complex& t); 13 14 private: 15 double real, imag; 16 17 public: 18 static const std::string doc; 19 20 private: 21 friend void output(const Complex& t); 22 friend double abs(const Complex& t); 23 friend Complex add(const Complex& t1, const Complex& t2); 24 friend bool is_equal(const Complex& t1, const Complex& t2); 25 friend bool is_not_equal(const Complex& t1, const Complex& t2); 26 }; 27 28 void output(const Complex& t); 29 double abs(const Complex& t); 30 Complex add(const Complex& t1, const Complex& t2); 31 bool is_equal(const Complex& t1, const Complex& t2); 32 bool is_not_equal(const Complex& t1, const Complex& t2);
Complex.cpp
1 #include "Complex.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <string> 4 #include <math.h> 5 6 const std::string Complex::doc{ "a simplified complex class" }; 7 8 Complex::Complex(double x, double y) :real{ x }, imag{ y } {}; 9 10 Complex::Complex(const Complex& t) :real{ t.real }, imag{ t.imag } {}; 11 12 double Complex::get_real() const { return real; } 13 14 double Complex::get_imag() const { return imag; } 15 16 Complex Complex::add(const Complex& t) { 17 Complex res; 18 this->real += t.real; 19 this->imag += t.imag; 20 return *this; 21 } 22 23 void output(const Complex& t) { 24 if (t.imag >= 0) { 25 std::cout << t.real << " " << "+" << " " << t.imag << "i" << std::endl; 26 } 27 else { 28 std::cout << t.real << " " << "-" << " " << -t.imag << "i" << std::endl; 29 } 30 } 31 32 double abs(const Complex& t) { return sqrt(t.imag * t.imag + t.real * t.real); } 33 34 Complex add(const Complex& t1, const Complex& t2){ 35 Complex res; 36 res.real = t1.real + t2.real; 37 res.imag = t1.imag + t2.imag; 38 return res; 39 } 40 41 bool is_equal(const Complex& t1, const Complex& t2) { 42 if ((t1.imag == t2.imag) && (t1.real == t2.real)) { 43 return true; 44 } 45 else { 46 return false; 47 } 48 } 49 50 bool is_not_equal(const Complex& t1, const Complex& t2) { return (!is_equal(t1,t2)); }
task2.cpp
1 #include "Complex.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <iomanip> 4 #include <complex> 5 6 void test_Complex(); 7 void test_std_complex(); 8 9 int main() { 10 std::cout << "*******测试1: 自定义类Complex*******\n"; 11 test_Complex(); 12 13 std::cout << "\n*******测试2: 标准库模板类complex*******\n"; 14 test_std_complex(); 15 } 16 17 void test_Complex() { 18 using std::cout; 19 using std::endl; 20 using std::boolalpha; 21 22 cout << "类成员测试: " << endl; 23 cout << Complex::doc << endl << endl; 24 25 cout << "Complex对象测试: " << endl; 26 Complex c1; 27 Complex c2(3, -4); 28 Complex c3(c2); 29 Complex c4 = c2; 30 const Complex c5(3.5); 31 32 cout << "c1 = "; output(c1); cout << endl; 33 cout << "c2 = "; output(c2); cout << endl; 34 cout << "c3 = "; output(c3); cout << endl; 35 cout << "c4 = "; output(c4); cout << endl; 36 cout << "c5.real = " << c5.get_real() 37 << ", c5.imag = " << c5.get_imag() << endl << endl; 38 39 cout << "复数运算测试: " << endl; 40 cout << "abs(c2) = " << abs(c2) << endl; 41 c1.add(c2); 42 cout << "c1 += c2, c1 = "; output(c1); cout << endl; 43 cout << boolalpha; 44 cout << "c1 == c2 : " << is_equal(c1, c2) << endl; 45 cout << "c1 != c2 : " << is_not_equal(c1, c2) << endl; 46 c4 = add(c2, c3); 47 cout << "c4 = c2 + c3, c4 = "; output(c4); cout << endl; 48 } 49 50 void test_std_complex() { 51 using std::cout; 52 using std::endl; 53 using std::boolalpha; 54 55 cout << "std::complex<double>对象测试: " << endl; 56 std::complex<double> c1; 57 std::complex<double> c2(3, -4); 58 std::complex<double> c3(c2); 59 std::complex<double> c4 = c2; 60 const std::complex<double> c5(3.5); 61 62 cout << "c1 = " << c1 << endl; 63 cout << "c2 = " << c2 << endl; 64 cout << "c3 = " << c3 << endl; 65 cout << "c4 = " << c4 << endl; 66 67 cout << "c5.real = " << c5.real() 68 << ", c5.imag = " << c5.imag() << endl << endl; 69 70 cout << "复数运算测试: " << endl; 71 cout << "abs(c2) = " << abs(c2) << endl; 72 c1 += c2; 73 cout << "c1 += c2, c1 = " << c1 << endl; 74 cout << boolalpha; 75 cout << "c1 == c2 : " << (c1 == c2) << endl; 76 cout << "c1 != c2 : " << (c1 != c2) << endl; 77 c4 = c2 + c3; 78 cout << "c4 = c2 + c3, c4 = " << c4 << endl; 79 }
运行结果截图如下:
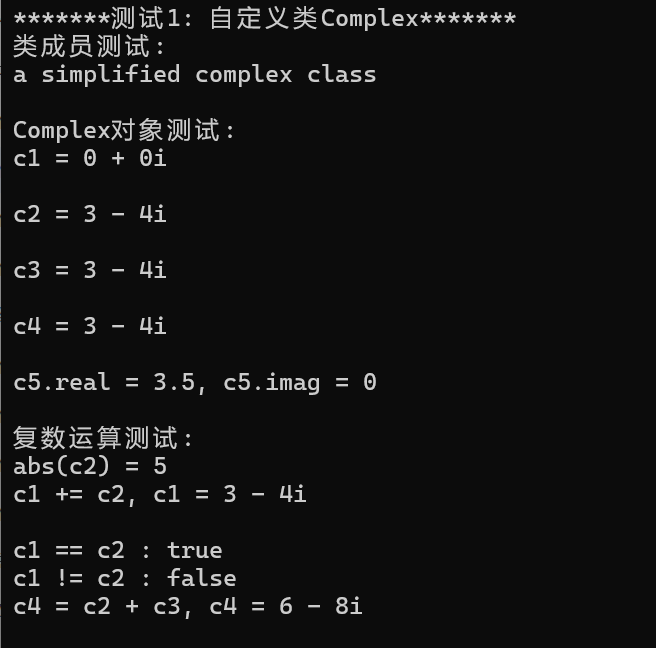

问题1:比较自定义类 Complex 和标准库模板类 complex 的用法,在使用形式上,哪一种更简洁?函数和运算内在有关联吗?
标准库模板类complex更为简洁,标准库中用法跟我们日常的书写习惯一致,更容易理解
函数和运算内在是有关联的,都可以实现复数的加减,赋值,比较大小等操作。
问题2-1:自定义 Complex 中, output/abs/add/ 等均设为友元,它们真的需要访问私有数据吗?
不一定需要访问私有数据,也可以通过get_real(),get_imag()接口获得私有数据,但设为友元之后访问起来更方便。
问题2-2:标准库 std::complex 是否把 abs 设为友元?
没有,abs是全局函数,通过接口访问私有数据
问题2-3:什么时候才考虑使用 friend?
当我们需要频繁访问类中的私有成员时再考虑使用友元,否则可以通过接口访问私有数据。
问题3:如果构造对象时禁用=形式,即遇到 Complex c4 = c2; 编译报错,类Complex的设计应如何调整?
用explicit修饰赋值构造函数,禁止构造函数被用于隐式转换或隐式初始化
实验任务3
程序源代码如下:
PlayerControl.h
1 #pragma once 2 #include <string> 3 4 enum class ControlType { Play, Pause, Next, Prev, Stop, Unknown }; 5 6 class PlayerControl { 7 public: 8 PlayerControl(); 9 10 ControlType parse(const std::string& control_str); 11 void execute(ControlType cmd) const; 12 13 static int get_cnt(); 14 15 private: 16 static int total_cnt; 17 };
PlayerControl.cpp
1 #include "PlayerControl.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 5 int PlayerControl::total_cnt = 0; 6 7 PlayerControl::PlayerControl() {} 8 9 ControlType PlayerControl::parse(const std::string& control_str) { 10 std::string input; 11 for (int i = 0; i < control_str.size(); i++) { 12 input += tolower(control_str[i]); 13 } 14 if (input == "play") { 15 total_cnt++; 16 return ControlType::Play; 17 } 18 else if (input == "pause") { 19 total_cnt++; 20 return ControlType::Pause; 21 } 22 else if (input == "next") { 23 total_cnt++; 24 return ControlType::Next; 25 } 26 else if (input == "prev") { 27 total_cnt++; 28 return ControlType::Prev; 29 } 30 else if (input == "stop") { 31 total_cnt++; 32 return ControlType::Stop; 33 } 34 else return ControlType::Unknown; 35 } 36 37 void PlayerControl::execute(ControlType cmd) const { 38 switch (cmd) { 39 case ControlType::Play: std::cout << "[play] Playing music...\n"; break; 40 case ControlType::Pause: std::cout << "[Pause] Music paused\n"; break; 41 case ControlType::Next: std::cout << "[Next] Skipping to next track\n"; break; 42 case ControlType::Prev: std::cout << "[Prev] Back to previous track\n"; break; 43 case ControlType::Stop: std::cout << "[Stop] Music stopped\n"; break; 44 default: std::cout << "[Error] unknown control\n"; break; 45 } 46 } 47 48 int PlayerControl::get_cnt() { 49 return total_cnt; 50 }
task3.cpp
1 #include "PlayerControl.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 4 void test() { 5 PlayerControl controller; 6 std::string control_str; 7 std::cout << "Enter Control: (play/pause/next/prev/stop/quit):\n"; 8 9 while (std::cin >> control_str) { 10 if (control_str == "quit") 11 break; 12 13 ControlType cmd = controller.parse(control_str); 14 controller.execute(cmd); 15 std::cout << "Current Player control: " << PlayerControl::get_cnt() << "\n\n"; 16 } 17 } 18 19 int main() { 20 test(); 21 }
运行结果截图如下:

选做:
修改task3.cpp,并在设置中添加/utf-8选项
1 #include "PlayerControl.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <Windows.h> 4 5 void test() { 6 PlayerControl controller; 7 std::string control_str; 8 std::cout << "Enter Control: (play/pause/next/prev/stop/quit):\n"; 9 10 while (std::cin >> control_str) { 11 if (control_str == "quit") 12 break; 13 14 ControlType cmd = controller.parse(control_str); 15 controller.execute(cmd); 16 std::cout << "Current Player control: " << PlayerControl::get_cnt() << "\n\n"; 17 } 18 } 19 20 int main() { 21 SetConsoleOutputCP(CP_UTF8); 22 SetConsoleCP(CP_UTF8); 23 test(); 24 }
运行结果截图:

实验任务4
程序源代码如下:
Fraction.h
1 #pragma once 2 #include <string> 3 4 class Fraction { 5 public: 6 Fraction(); 7 Fraction(int x, int y = 1); 8 Fraction(const Fraction& f); 9 10 int get_up() const; 11 int get_down() const; 12 Fraction negative(); 13 14 private: 15 int up, down; 16 17 public: 18 static const std::string doc; 19 20 private: 21 friend Fraction simplify(const Fraction &f); 22 friend void output(const Fraction &f); 23 friend Fraction normalize(const Fraction& f); 24 friend Fraction add(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2); 25 friend Fraction sub(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2); 26 friend Fraction mul(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2); 27 friend Fraction div(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2); 28 }; 29 30 Fraction simplify(const Fraction &f); 31 void output(const Fraction& f); 32 Fraction add(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2); 33 Fraction sub(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2); 34 Fraction mul(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2); 35 Fraction div(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2);
Fraction.cpp
1 #include "Fraction.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <string> 4 #include <math.h> 5 6 const std::string Fraction::doc{ "目前仅支持分数对象构造、输出、加/减/乘/除运算" }; 7 8 Fraction::Fraction() :down{ 1 } {}; 9 10 Fraction::Fraction(int x, int y) :up{ x }, down{ y } {}; 11 12 Fraction::Fraction(const Fraction &f) :up{ f.up }, down{ f.down } {}; 13 14 int Fraction::get_up() const { 15 if (down == 0) return 0; 16 else { 17 int a = abs(up); 18 int b = abs(down); 19 while (b) { 20 int temp = a % b; 21 a = b; 22 b = temp; 23 } 24 25 return up / a; 26 } 27 } 28 29 int Fraction::get_down() const { 30 if (down == 0) return 0; 31 else{ 32 int a = abs(up); 33 int b = abs(down); 34 while (b) { 35 int temp = a % b; 36 a = b; 37 b = temp; 38 } 39 return down / a; 40 } 41 } 42 43 Fraction Fraction::negative() { return Fraction(-up,down); } 44 45 Fraction simplify(const Fraction& f) { 46 int up = abs(f.up); 47 int down = abs(f.down); 48 while (down) { 49 int temp = up % down; 50 up = down; 51 down = temp; 52 } 53 54 return Fraction(f.up / up, f.down / up); 55 } 56 57 void output(const Fraction& f) { 58 Fraction res; 59 60 if (f.down == 0) std::cout << "分母不能为0" << std::endl; 61 else if (f.up == 0 && f.down != 0) std::cout << '0' << std::endl; 62 else if ((f.up > 0 && f.down > 0) || (f.up < 0 && f.down < 0)) { 63 if (f.down == 1) std::cout << f.up << std::endl; 64 else { 65 res = simplify(f); 66 std::cout << res.up << '/' << res.down << std::endl; 67 } 68 } 69 else { 70 if (f.down == 1||f.down == -1) std::cout << -f.up << std::endl; 71 else { 72 res = simplify(f); 73 std::cout << -abs(res.up) << '/' << abs(res.down) << std::endl; 74 } 75 } 76 } 77 78 Fraction normalize(const Fraction& f) { 79 if ((f.up > 0 && f.down > 0) || (f.up < 0 && f.down < 0)) return Fraction(abs(f.up), abs(f.down)); 80 else return Fraction(-abs(f.up), abs(f.down)); 81 } 82 83 Fraction add(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2) { 84 Fraction res,newf1,newf2; 85 newf1 = normalize(f1); 86 newf2 = normalize(f2); 87 88 if (newf1.down == newf2.down) { 89 res.down = newf1.down; 90 res.up = newf1.up + newf2.up; 91 res = simplify(res); 92 return res; 93 } 94 else { 95 res.down = newf1.down * newf2.down; 96 res.up = newf1.up * newf2.down + newf2.up * newf1.down; 97 res = simplify(res); 98 return res; 99 } 100 } 101 102 Fraction sub(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2) { 103 Fraction res, newf1, newf2; 104 newf1 = normalize(f1); 105 newf2 = normalize(f2); 106 107 if (newf1.down == newf2.down) { 108 res.down = newf1.down; 109 res.up = newf1.up - newf2.up; 110 res = simplify(res); 111 return res; 112 } 113 else { 114 res.down = newf1.down * newf2.down; 115 res.up = newf1.up * newf2.down - newf2.up * newf1.down; 116 res = simplify(res); 117 return res; 118 } 119 } 120 121 Fraction mul(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2) { 122 Fraction res, newf1, newf2; 123 newf1 = normalize(f1); 124 newf2 = normalize(f2); 125 126 res.up = newf1.up * newf2.up; 127 res.down = newf1.down * newf2.down; 128 res = simplify(res); 129 return res; 130 } 131 132 Fraction div(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2) { 133 Fraction res, newf1, newf2; 134 newf1 = normalize(f1); 135 newf2 = normalize(f2); 136 137 res.up = newf1.up * newf2.down; 138 res.down = newf1.down * newf2.up; 139 res = simplify(res); 140 res = normalize(res); 141 return res; 142 }
task4.cpp
1 #include "Fraction.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 4 void test1(); 5 void test2(); 6 7 int main() { 8 std::cout << "测试1: Fraction类基础功能测试\n"; 9 test1(); 10 11 std::cout << "\n测试2: 分母为0测试: \n"; 12 test2(); 13 } 14 15 void test1() { 16 using std::cout; 17 using std::endl; 18 19 cout << "Fraction类测试: " << endl; 20 cout << Fraction::doc << endl << endl; 21 22 Fraction f1(5); 23 Fraction f2(3, -4), f3(-18, 12); 24 Fraction f4(f3); 25 cout << "f1 = "; output(f1); cout << endl; 26 cout << "f2 = "; output(f2); cout << endl; 27 cout << "f3 = "; output(f3); cout << endl; 28 cout << "f4 = "; output(f4); cout << endl; 29 30 const Fraction f5(f4.negative()); 31 cout << "f5 = "; output(f5); cout << endl; 32 cout << "f5.get_up() = " << f5.get_up() 33 << ", f5.get_down() = " << f5.get_down() << endl; 34 35 cout << "f1 + f2 = "; output(add(f1, f2)); cout << endl; 36 cout << "f1 - f2 = "; output(sub(f1, f2)); cout << endl; 37 cout << "f1 * f2 = "; output(mul(f1, f2)); cout << endl; 38 cout << "f1 / f2 = "; output(div(f1, f2)); cout << endl; 39 cout << "f4 + f5 = "; output(add(f4, f5)); cout << endl; 40 } 41 void test2() { 42 using std::cout; 43 using std::endl; 44 45 Fraction f6(42, 55), f7(0, 3); 46 cout << "f6 = "; output(f6); cout << endl; 47 cout << "f7 = "; output(f7); cout << endl; 48 cout << "f6 / f7 = "; output(div(f6, f7)); cout << endl; 49 }
运行结果截图如下:
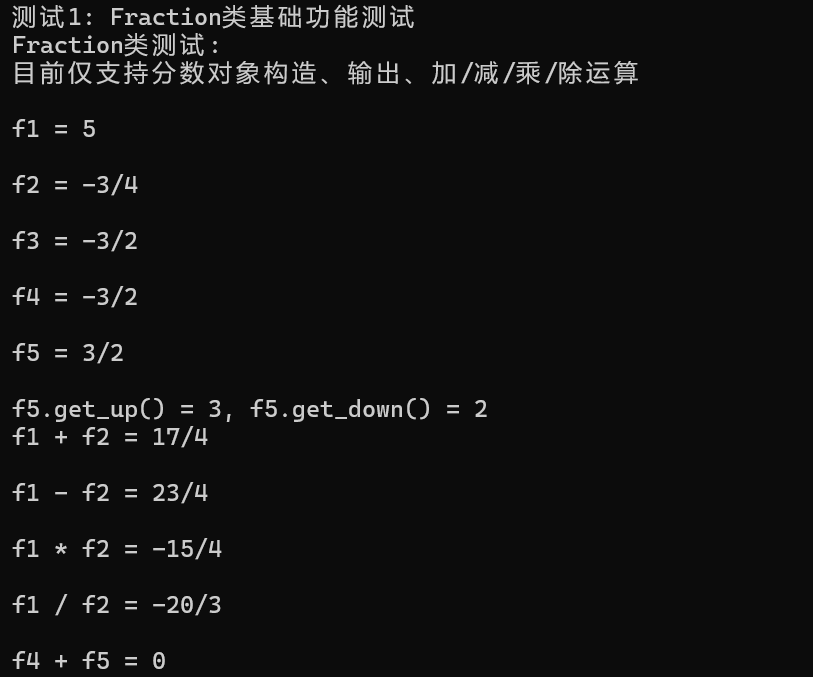

我采取的是友元+自由函数的设计方案。首先鉴于先前的实验1用了此方案,我受其启发继续沿用。其次友元+自由函数可直接访问类内私有成员,此方案要访问私有成员数量很多,采取此方案更方便
实验总结
通过此次实验我收获颇深,首先对于频繁访问类内私有成员的场景可以用友元,其次static const类型成员初始化时要注意位置和初始化方式,最后在设计类中方法时要充分在一个方法中调用另一个方法,可以使代码更精简。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号