实验五
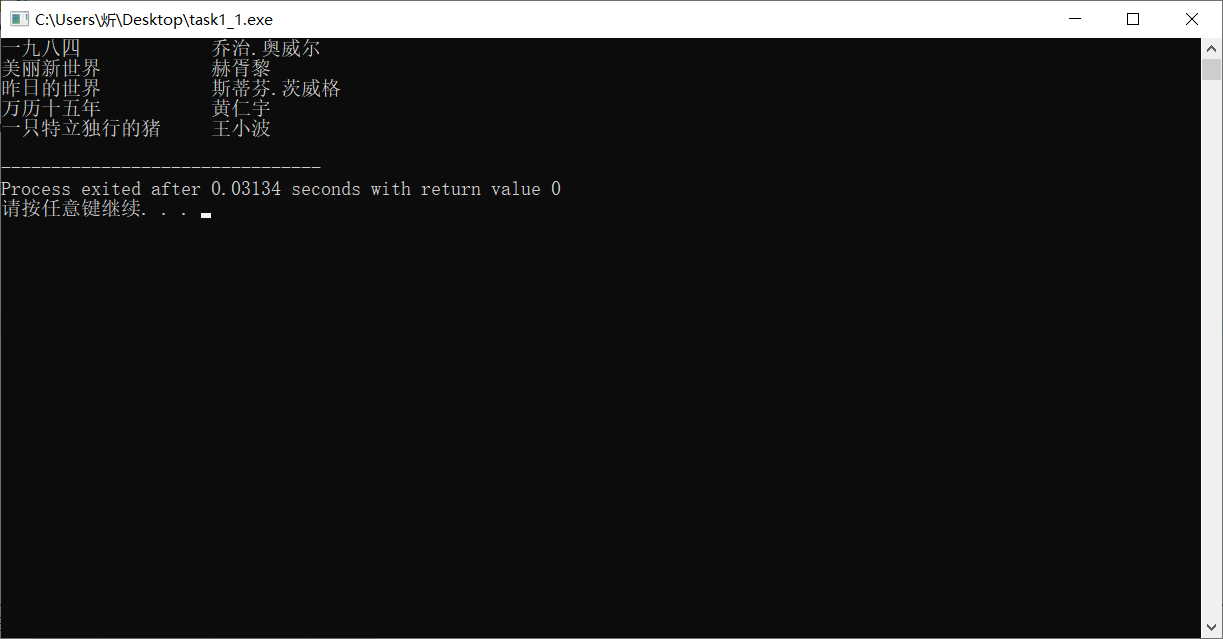
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 #define N 5 4 #define M 80 5 typedef struct { 6 char name[M]; 7 char author[M]; 8 } Book; 9 10 int main() { 11 Book x[N] = {{"一九八四", "乔治.奥威尔"}, 12 {"美丽新世界", "赫胥黎"}, 13 {"昨日的世界", "斯蒂芬.茨威格"}, 14 {"万历十五年", "黄仁宇"}, 15 {"一只特立独行的猪", "王小波"}}; 16 int i; 17 FILE *fp; 18 fp = fopen("data1.txt", "w"); 19 if (fp == NULL) { 20 printf("fail to open file\n"); 21 return 1; 22 } 23 24 for (i = 0; i < N; i++) { 25 fprintf(fp, "%-20s %-20s\n", x[i].name, x[i].author); 26 printf("%-20s %-20s\n", x[i].name, x[i].author); 27 } 28 fclose(fp); 29 return 0; 30 }
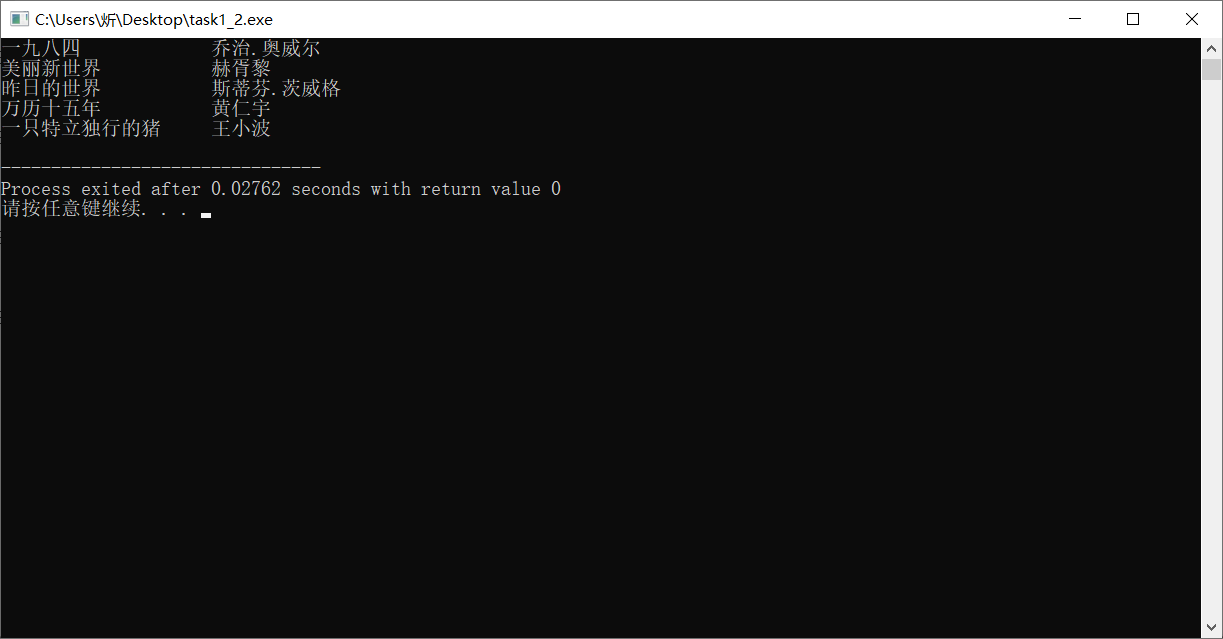
#include <stdio.h> #define N 5 #define M 80 typedef struct { char name[M]; // 书名 char author[M]; // 作者 }Book; int main() { Book x[N]; int i; FILE *fp; // 以读的方式打开文本文件data1.txt fp = fopen("data1.txt", "r"); // 如果打开文件失败,输出提示信息并返回 if(fp == NULL) { printf("fail to open file\n"); return 1; } // 从fp指向的文件data1.txt中读取信息到结构体数组x // 同时,把x的内容输出到屏幕上 for(i=0; i<N; ++i) { fscanf(fp, "%s %s\n", x[i].name, x[i].author); printf("%-20s %-20s\n", x[i].name, x[i].author); } fclose(fp); return 0; }
它本身就是地址符,所以不需要加&
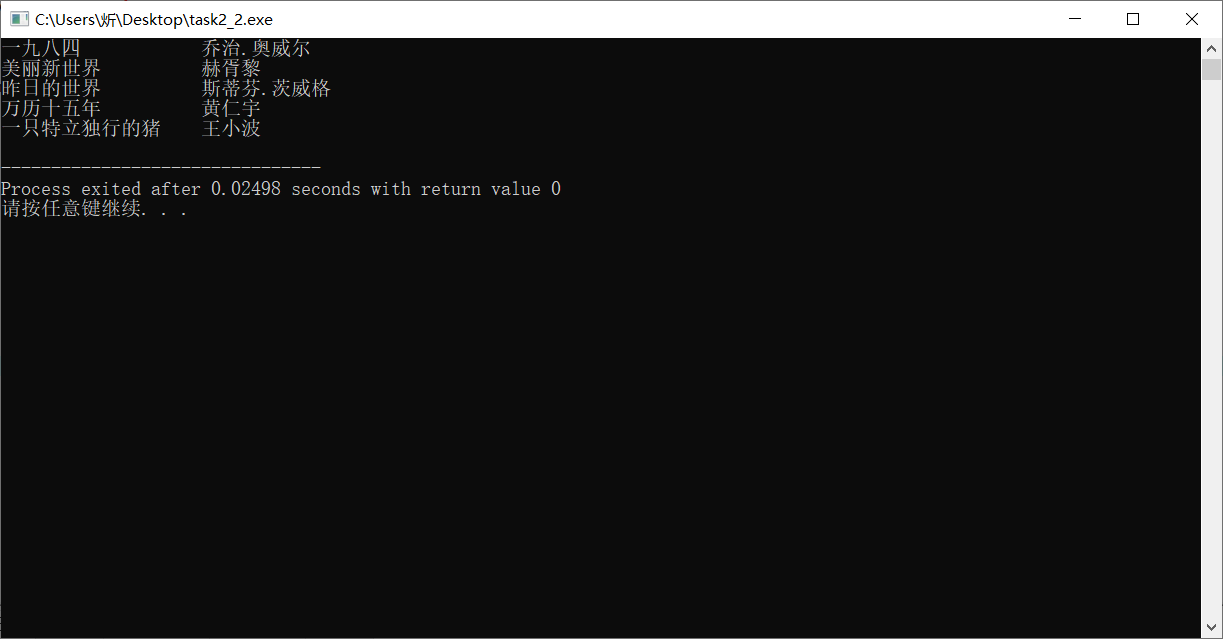
#include <stdio.h> #define N 5 #define M 80 typedef struct { char name[M]; char author[M]; } Book; int main(){ Book x[N] = {{"一九八四", "乔治.奥威尔"}, {"美丽新世界", "赫胥黎"}, {"昨日的世界", "斯蒂芬.茨威格"}, {"万历十五年", "黄仁宇"}, {"一只特立独行的猪", "王小波"}}; int i; FILE *fp; fp = fopen("data2.dat", "wb"); if (fp == NULL) { printf("fail to open file\n"); return 1; } fwrite(x,sizeof(Book),N,fp); fclose(fp); return 0; }
#include <stdio.h> #define N 5 #define M 80 typedef struct { char name[M]; char author[M]; } Book; int main(){ Book x[N]; int i; FILE *fp; fp = fopen("data2.dat","rb"); if(fp==NULL){ printf("fail to open file\n"); return 1; } fread(x,sizeof(Book),N,fp); for(i=0;i<N;i++) printf("%-20s%-20s\n", x[i].name, x[i].author); fclose(fp); return 0; }
可以
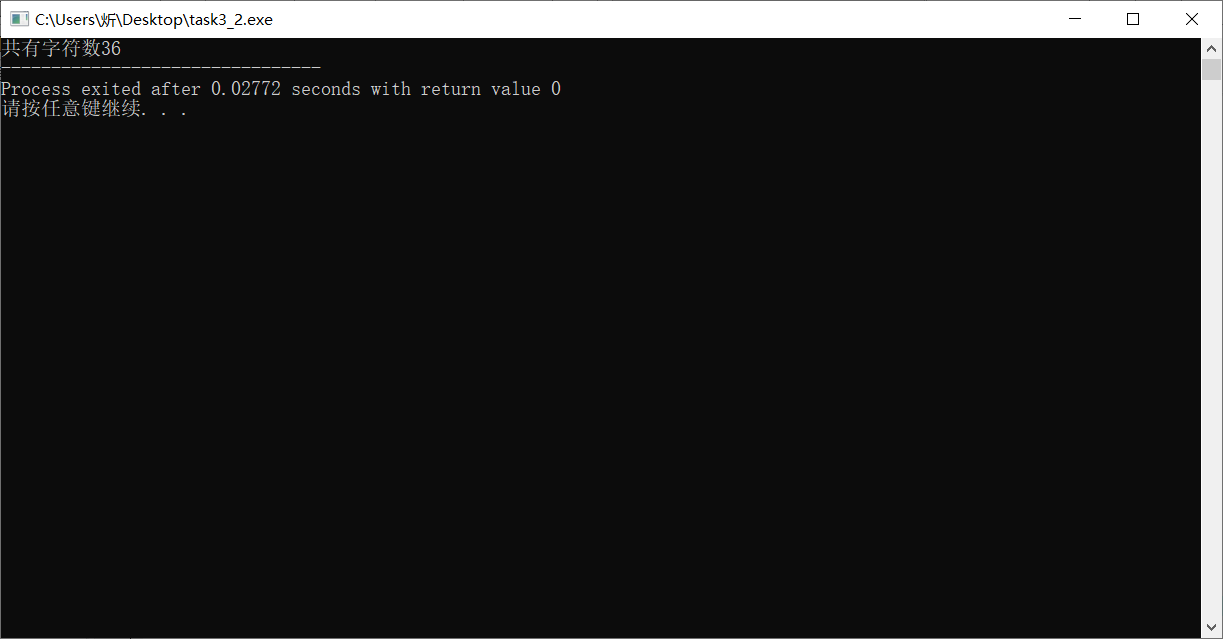
#include <stdio.h> int main(){ FILE *fin,*fout; char ch; int i=0; fin =fopen("data3_1.txt","r"); if(fin==NULL){ printf("fail to open file data3_1.txt\n"); return 1; } fout =fopen("data3_2.txt","w"); if(fout==NULL){ printf("fail to open file data3_2.txt\n"); return 1; } while(!feof(fin)){ ch =fgetc(fin); if(ch>='a'&&ch<='z') ch-=32; if(ch>=33&&ch<=126) i+=1; fputc(ch,fout); } fclose(fin); fclose(fout); printf("共有字符数%d",i); return 0; }
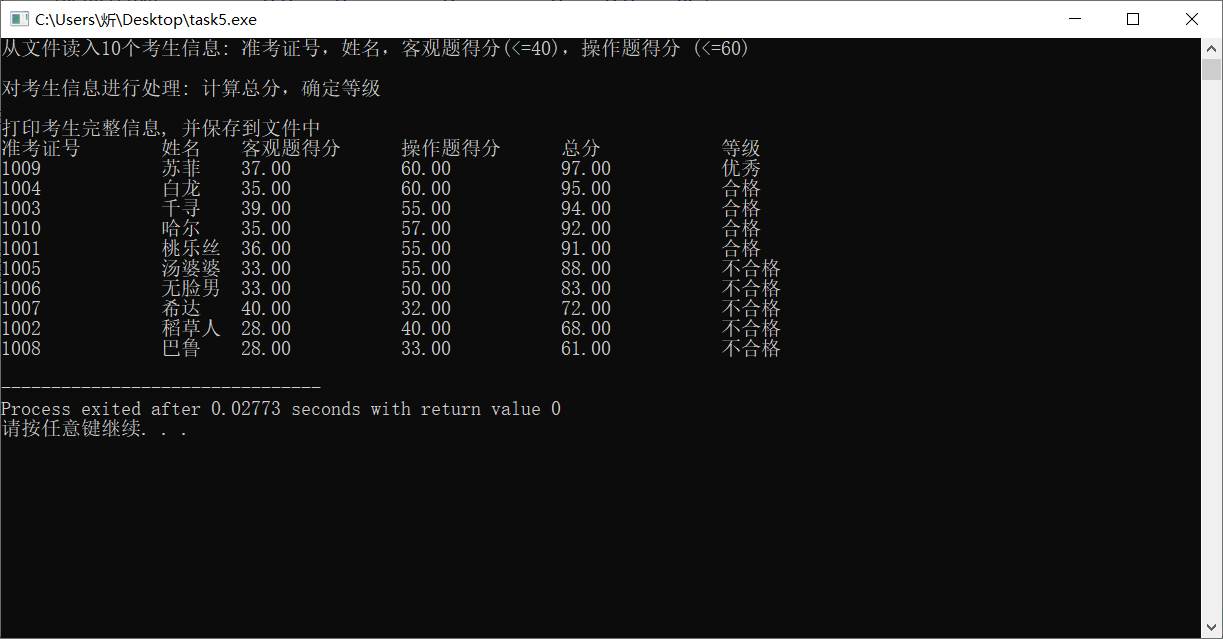
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define N 10 typedef struct{ long int id; char name[20]; float ob; float sub; float sum; char level[10]; }Stu; void input(Stu s[], int n); void output(Stu s[], int n); void process(Stu s[], int n); int main(){ Stu stu[N]; printf("从文件读入%d个考生信息: 准考证号,姓名,客观题得分(<=40),操作题得分 (<=60)\n", N); input(stu,N); printf("\n对考生信息进行处理: 计算总分,确定等级\n"); process(stu, N); printf("\n打印考生完整信息, 并保存到文件中"); output(stu, N); return 0; } void input(Stu s[],int n){ int i; FILE *fin; fin = fopen("examinee.txt", "r"); if (fin == NULL) { printf("fail to open file\n"); exit(0); } while (!feof(fin)) { for (i = 0; i < n; i++) fscanf(fin, "%ld %s %f %f", &s[i].id, s[i].name, &s[i].ob, &s[i].sub); } fclose(fin); } void output(Stu s[],int n){ FILE *fout; int i; printf("\n"); printf("准考证号\t姓名\t客观题得分\t操作题得分\t总分\t\t等级\n"); for (i = 0; i < n; i++) printf("%ld\t\t%s\t%.2f\t\t%.2f\t\t%.2f\t\t%s\n", s[i].id, s[i].name, s[i].ob, s[i].sub, s[i].sum, s[i].level); fout=fopen("result.txt","w"); if (!fout) { printf("fail to open or create result.txt\n"); exit(0); } fprintf(fout, "准考证号\t\t姓名\t客观题得分\t操作题得分\t总分\t\t等级\n"); for (i = 0; i < n; i++) fprintf(fout,"%ld\t\t%s\t%.2f\t\t%.2f\t\t%.2f\t\t%s\n", s[i].id, s[i].name, s[i].ob, s[i].sub, s[i].sum, s[i].level); fclose(fout); } void process(Stu s[],int n){ int i,j,k; float you,liang; Stu temp; for(i=0;i<n;i++) s[i].sum=s[i].ob+s[i].sub; for(i=1;i<n;i++) for(j=0;j<i;j++){ if(s[i].sum>s[j].sum){ k=j; temp=s[i]; for(j=i-1;j>=k;j--) s[j+1]=s[j]; s[k]=temp; } } you=s[(int)(n*0.1-1)].sum; liang=s[(int)(n*0.5-1)].sum; for(i=0;i<n;i++) if(s[i].sum>=you) strcpy(s[i].level,"优秀"); else if(s[i].sum>=liang) strcpy(s[i].level,"合格"); else strcpy(s[i].level,"不合格"); }
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include<time.h> #define N 80 #define M 5 typedef struct{ char data[N]; int flag; }Stu; int main(){ int i,j,k; Stu s[N],l[M]; FILE *fin,*fout; fin=fopen("list.txt","r"); if (fin == NULL) { printf("fail to open file\n"); return 0; } for(i=0;i<N;i++){ fgets(s[i].data,N,fin); printf("%s\n",s[i].data); s[i].flag=0; } fclose(fin); for(j=0;j<M;j++){ i=0; srand((unsigned) time(NULL)); k=rand()%(N-j); while(k){ if (s[i].flag==0) k--; i++; } l[j]=s[i]; } fout=fopen("result2.txt","w"); if (fout == NULL) { printf("fail to open file\n"); return 0; } for(j=0;j<M;j++){ fprintf(fout,"%s\n",l[j].data); } fclose(fout); return 0; }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号