动手学深度学习v2-08-2 线性回归的从零开始实现
线性回归的从零开始实现
1 生成数据集
- 导入需要的包
%matplotlib inline #默认嵌入到matplotlib里面
import random
import torch
from d2l import torch as d2l
- 构造数据集
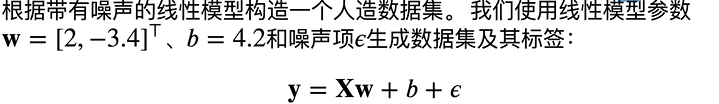
def synthetic_data(w,b,num_examples):# 表示根据w,b生成num_examples个样本
"""生成y=X*w+b+噪声"""
X=torch.normal(0,1,(num_examples,len(w)))# 表示0,1随机分布,行num_examples,列 len(w)
y=torch.matmul(X,w)+b #计算y
y+=torch.normal(0,0.01,y.shape) #随机噪音,形状跟Y的长度是一样
return X,y.reshape((-1,1))# 最后把x,y做成列向量进行返回
# 真实的w,b
true_w=torch.tensor([2,-3.4])
true_b=4.2
features,lables=synthetic_data(true_w, true_b, 1000)
- features中每一行都包含一个二维数据样本,labels的每一行都包含一维标签值(一个标量)
print('feature:',features[0],'\nlable:',lables[0])

- 通过生成第二个特征features[:, 1]和labels的散点图,可以直观地观察到两者之间的线性关系。
d2l.set_figsize()
d2l.plt.scatter(features[:, (1)].detach().numpy(), labels.detach().numpy(), 1);
2 读取数据集
- 定义一个data_iter函数, 该函数接收批量大小、特征矩阵和标签向量作为输入,生成大小为batch_size的小批量。每个小批量包含一组特征和标签。
def data_iter(batch_size,features,labels):
num_examples=len(features) #有多少个样本
indices=list(range(num_examples))#为这些样本生成下标
random.shuffle(indices) # 将这些下标打乱
for i in range(0,num_examples,batch_size):
batch_indices=torch.tensor(indices[i:min(i+batch_size,num_examples)])
yield features[batch_indices],labels[batch_indices]
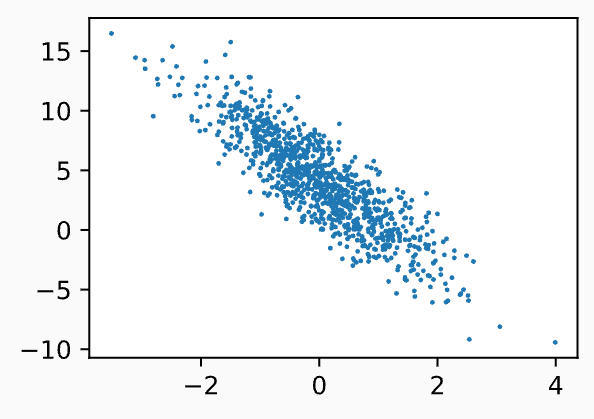
- 读取第一个小批量数据样本并打印。每个批量的特征维度说明了批量大小和输入特征数
batch_size = 10
for X, y in data_iter(batch_size, features, labels):
print(X, '\n', y)
break
3 初始化模型参数
- 我们通过从均值为0、标准差为0.01的正态分布中采样随机数来初始化权重,并将偏置初始化为0。
w = torch.normal(0, 0.01, size=(2,1), requires_grad=True)
b = torch.zeros(1, requires_grad=True)
4 定义模型
def linreg(X, w, b): #@save
"""线性回归模型。"""
return torch.matmul(X, w) + b
5 定义损失函数
def squared_loss(y_hat, y): #@save
"""均方损失。"""
return (y_hat - y.reshape(y_hat.shape)) ** 2 / 2
6 定义优化算法
def sgd(params, lr, batch_size): #@save
"""小批量随机梯度下降。"""
with torch.no_grad():
for param in params:
param -= lr * param.grad / batch_size
param.grad.zero_()
7 训练
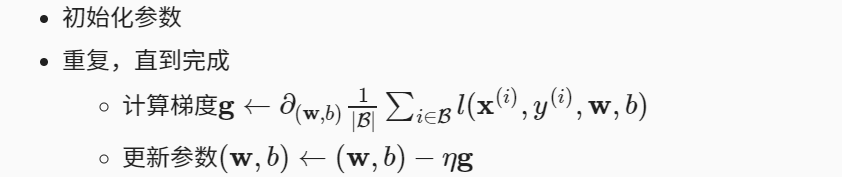
在每个迭代周期(epoch)中,我们使用data_iter函数遍历整个数据集,并将训练数据集中所有样本都使用一次(假设样本数能够被批量大小整除)。这里的迭代周期个数num_epochs和学习率lr都是超参数,分别设为3和0.03。
lr = 0.03
num_epochs = 3
net = linreg
loss = squared_loss
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for X, y in data_iter(batch_size, features, labels):
l = loss(net(X, w, b), y) # `X`和`y`的小批量损失
# 因为`l`形状是(`batch_size`, 1),而不是一个标量。`l`中的所有元素被加到一起,
# 并以此计算关于[`w`, `b`]的梯度
l.sum().backward()
sgd([w, b], lr, batch_size) # 使用参数的梯度更新参数
with torch.no_grad():
train_l = loss(net(features, w, b), labels)
print(f'epoch {epoch + 1}, loss {float(train_l.mean()):f}')

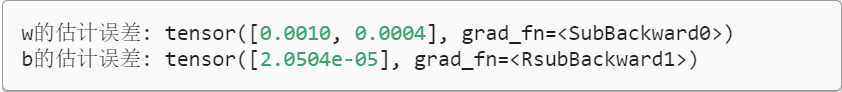
8 计算w和b的误差
print(f'w的估计误差: {true_w - w.reshape(true_w.shape)}')
print(f'b的估计误差: {true_b - b}')


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号