Numpy基本操作
1.生成数组的方法
1.1 生成0和1的数组
- np.ones(shape, dtype)
- np.ones_like(a, dtype)
- np.zeros(shape, dtype)
- np.zeros_like(a, dtype)
举例:
ones = np.ones([4,8])
返回结果:
array([[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]])
举例:
np.zeros_like(ones)
返回结果:
array([[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]])
1.2 从现有数组生成
两种生成方式:
- np.array(object, dtype)
- np.asarray(a, dtype)
a = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
# 从现有的数组当中创建
a1 = np.array(a)
# 相当于索引的形式,并没有真正的创建一个新的
a2 = np.asarray(a)
运行结果:

表示原始数组该之后,a1不会发生改变,但是a2会发生改变。
1.3 固定范围的数组
1.3.1 等差数组-指定数量
np.linspace (start, stop, num, endpoint)
参数:
- start:序列的起始值
- stop:序列的终止值
- num:要生成的等间隔样例数量,默认为50
- endpoint:序列中是否包含stop值,默认为ture
举例:
# 生成等间隔的数组
np.linspace(0, 100, 11)
返回结果:
array([ 0., 10., 20., 30., 40., 50., 60., 70., 80., 90., 100.])
等差数组--指定步长
np.arange(start,stop, step, dtype)
参数:
- step:步长,默认值为1
举例:
np.arange(10, 50, 2)
返回结果
array([10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32, 34, 36, 38, 40, 42,
44, 46, 48])
1.3.3 等比数组
np.logspace(start,stop, num)
参数:
- num:要生成的等比数列数量,默认为50
举例:
# 生成10^x
np.logspace(0, 2, 3)
返回结果:
array([ 1., 10., 100.])
1.4 生成随机数组--np.random模块
1.4.1 正态分布
函数:
- np.random.randn(d0, d1, …, dn)
从标准正态分布中返回一个或多个样本值 - np.random.normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=None)
参数:
loc:float 概率分布的均值(整个分布的中心centre)
scale:float 概率分布的标准差(整个分布的宽度,越大越矮胖,越小越瘦高)
size:int or tuple of ints 输出的shape,默认为None,只输出一个值 - np.random.standard_normal(size=None)
返回指定形状的标准正态分布的数组。
举例:
# 生成均匀分布的随机数
x1 = np.random.normal(1.75, 1, 100000000)
# 画图看分布状况
# 1)创建画布
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 10), dpi=100)
# 2)绘制直方图
plt.hist(x1, 1000)
# 3)显示图像
plt.show()
结果:
1.4.2 均匀分布
- np.random.rand(d0, d1, ..., dn)
返回[0.0,1.0)内的一组均匀分布的数。 - np.random.uniform(low=0.0, high=1.0, size=None)
功能:从一个均匀分布[low,high)中随机采样,注意定义域是左闭右开,即包含low,不包含high.
参数介绍:
low: 采样下界,float类型,默认值为0;
high: 采样上界,float类型,默认值为1;
size: 输出样本数目,为int或元组(tuple)类型,例如,size=(m,n,k), 则输出mnk个样本,缺省时输出1个值。
返回值:ndarray类型,其形状和参数size中描述一致。 - np.random.randint(low, high=None, size=None, dtype='l')
从一个均匀分布中随机采样,生成一个整数或N维整数数组,取数范围:若high不为None时,取[low,high)之间随机整数,否则取值[0,low)之间随机整数。
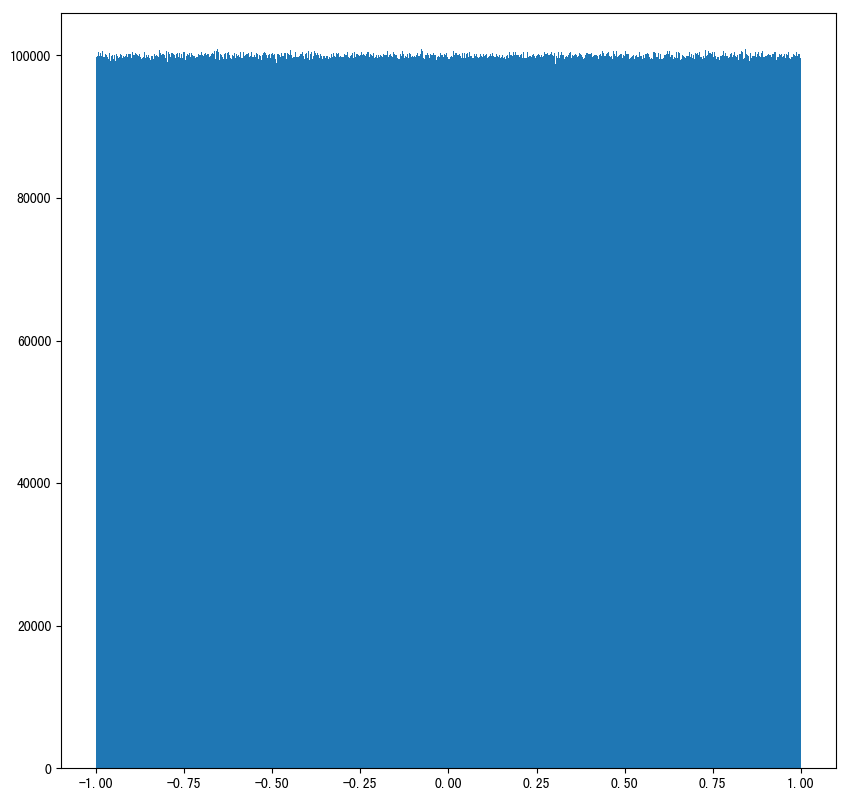
举例:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 生成均匀分布的随机数
x2 = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, 100000000)
# 画图看分布状况
# 1)创建画布
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10), dpi=100)
# 2)绘制直方图
plt.hist(x=x2, bins=1000) # x代表要使用的数据,bins表示要划分区间数
# 3)显示图像
plt.show()
结果展示:

2 数组的索引、切片
索引:对象[:, :] -- 先行后列
二维数组举例:获取第一个股票的前3个交易日的涨跌幅数据
# 二维的数组,两个维度
stock_change[0, 0:3]
三维数组举例:
重点: 首先表示三维中第几个二维,再选择二维中第几个一维,最后选择一维中哪个数字。
# 三维
a1 = np.array([ [[1,2,3],[4,5,6]], [[12,3,34],[5,6,7]]])
# 返回结果
array([[[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6]],
[[12, 3, 34],
[ 5, 6, 7]]])
# 索引、切片
>>> a1[0, 0, 1] # 输出: 2
3 形状修改
- ndarray.reshape(shape, order)
返回一个具有相同数据域,但shape不一样的视图,行、列不进行互换 - ndarray.resize(new_shape)
修改数组本身的形状(需要保持元素个数前后相同,行、列不进行互换 - ndarray.T
数组的转置,将数组的行、列进行互换
4 类型修改
- ndarray.astype(type)
返回修改了类型之后的数组
举例:
stock_change.astype(np.int32) - ndarray.tostring([order])或者ndarray.tobytes([order])
构造包含数组中原始数据字节的Python字节 - 注意:jupyter输出太大可能导致崩溃问题
IOPub data rate exceeded.
The notebook server will temporarily stop sending output
to the client in order to avoid crashing it.
To change this limit, set the config variable
`--NotebookApp.iopub_data_rate_limit`.
5 数组去重
np.unique()
举例:
temp = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4],[3, 4, 5, 6]])
>>> np.unique(temp)
array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号