shardingsphere5.1.0看源码记录
一、前言
shardingsphere整体处理流程为解析->路由->改写->执行->归并,以查询为例:
1.建立数据库连接
2.初始化statement,包括解析过程(在ShardingSpherePreparedStatement.java初始化中)。
3.建立执行上下文(createExecutionContext),包括路由``改写``执行过程(在ShardingSpherePreparedStatement.javaexecute()中)
4.归并结果
具体源码跟踪:
mybaits的SimpleExecutor执行doQuery:
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
List var9;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this.wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
stmt = this.prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
var9 = handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
this.closeStatement(stmt);
}
return var9;
}
执行prepareStatement:
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = this.getConnection(statementLog);
Statement stmt = handler.prepare(connection, this.transaction.getTimeout());
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
首先getConnection建立连接,mybatis的BaseExecutor执行getConnection方法建立数据库连接。
handler.prepare即为初始化ShardingSpherePreparedStatement,进行解析流程。
handler.parameterize(stmt)简单理解为将ShardingSpherePreparedStatement设置为参数流程。
prepareStatement执行完后返回执行var9 = handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);,调用PreparedStatementHandler的query方法:
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement)statement;
ps.execute();
return this.resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps);
}
ps即为ShardingSpherePreparedStatement:
public boolean execute() throws SQLException {
boolean var1;
try {
if (!this.statementsCacheable || this.statements.isEmpty()) {
this.clearPrevious();
LogicSQL logicSQL = this.createLogicSQL();
this.trafficContext = this.getTrafficContext(logicSQL);
boolean var3;
if (this.trafficContext.isMatchTraffic()) {
JDBCExecutionUnit executionUnit = this.createTrafficExecutionUnit(this.trafficContext);
var3 = (Boolean)this.executor.getTrafficExecutor().execute(executionUnit, (statement, sql) -> {
return ((PreparedStatement)statement).execute();
});
return var3;
}
this.executionContext = this.createExecutionContext(logicSQL);//路由+改写
if (this.metaDataContexts.getMetaData(this.connection.getSchema()).getRuleMetaData().getRules().stream().anyMatch((each) -> {
return each instanceof RawExecutionRule;
})) {
Collection<ExecuteResult> executeResults = this.executor.getRawExecutor().execute(this.createRawExecutionGroupContext(), this.executionContext.getLogicSQL(), new RawSQLExecutorCallback());
var3 = executeResults.iterator().next() instanceof QueryResult;
return var3;
}
if (this.executionContext.getRouteContext().isFederated()) {
ResultSet resultSet = this.executeFederationQuery(logicSQL);
var3 = null != resultSet;
return var3;
}
ExecutionGroupContext<JDBCExecutionUnit> executionGroupContext = this.createExecutionGroupContext();
this.cacheStatements(executionGroupContext.getInputGroups());
var3 = this.executor.getRegularExecutor().execute(executionGroupContext, this.executionContext.getLogicSQL(), this.executionContext.getRouteContext().getRouteUnits(), this.createExecuteCallback());//执行
return var3;
}
this.resetParameters();
var1 = ((PreparedStatement)this.statements.iterator().next()).execute();
} finally {
this.clearBatch();
}
return var1;
}
其中this.createExecutionContext方法如下:
private ExecutionContext createExecutionContext(LogicSQL logicSQL) {
SQLCheckEngine.check(logicSQL.getSqlStatementContext().getSqlStatement(), logicSQL.getParameters(), this.metaDataContexts.getMetaData(this.connection.getSchema()).getRuleMetaData().getRules(), this.connection.getSchema(), this.metaDataContexts.getMetaDataMap(), (Grantee)null);
ExecutionContext result = this.kernelProcessor.generateExecutionContext(logicSQL, this.metaDataContexts.getMetaData(this.connection.getSchema()), this.metaDataContexts.getProps());//路由+改写
this.findGeneratedKey(result).ifPresent((generatedKey) -> {
this.generatedValues.addAll(generatedKey.getGeneratedValues());
});
return result;
}
其中this.kernelProcessor.generateExecutionContext方法如下:
public ExecutionContext generateExecutionContext(LogicSQL logicSQL, ShardingSphereMetaData metaData, ConfigurationProperties props) {
RouteContext routeContext = this.route(logicSQL, metaData, props);//路由
SQLRewriteResult rewriteResult = this.rewrite(logicSQL, metaData, props, routeContext);//改写
ExecutionContext result = this.createExecutionContext(logicSQL, metaData, routeContext, rewriteResult);
this.logSQL(logicSQL, props, result);
return result;
}
在执行this.resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps)时由mybatis的DefaultResultSetHandler处理结果集并返回。
其handleResultSets方法如下:
public List<Object> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("handling results").object(this.mappedStatement.getId());
List<Object> multipleResults = new ArrayList();
int resultSetCount = 0;
ResultSetWrapper rsw = this.getFirstResultSet(stmt);//
List<ResultMap> resultMaps = this.mappedStatement.getResultMaps();
int resultMapCount = resultMaps.size();
this.validateResultMapsCount(rsw, resultMapCount);
while(rsw != null && resultMapCount > resultSetCount) {
ResultMap resultMap = (ResultMap)resultMaps.get(resultSetCount);
this.handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, multipleResults, (ResultMapping)null);
rsw = this.getNextResultSet(stmt);
this.cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
++resultSetCount;
}
String[] resultSets = this.mappedStatement.getResultSets();
if (resultSets != null) {
while(rsw != null && resultSetCount < resultSets.length) {
ResultMapping parentMapping = (ResultMapping)this.nextResultMaps.get(resultSets[resultSetCount]);
if (parentMapping != null) {
String nestedResultMapId = parentMapping.getNestedResultMapId();
ResultMap resultMap = this.configuration.getResultMap(nestedResultMapId);
this.handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, (List)null, parentMapping);
}
rsw = this.getNextResultSet(stmt);
this.cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
++resultSetCount;
}
}
return this.collapseSingleResultList(multipleResults);
}
其中this.getFirstResultSet(stmt)方法如下:
private ResultSetWrapper getFirstResultSet(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
ResultSet rs = stmt.getResultSet();//调用ShardingSpherePreparedStatement的getResultSet方法
while(rs == null) {
if (stmt.getMoreResults()) {
rs = stmt.getResultSet();
} else if (stmt.getUpdateCount() == -1) {
break;
}
}
return rs != null ? new ResultSetWrapper(rs, this.configuration) : null;
}
ShardingSpherePreparedStatement的getResultSet方法如下:
public ResultSet getResultSet() throws SQLException {
if (null != this.currentResultSet) {
return this.currentResultSet;
} else if (this.trafficContext.isMatchTraffic()) {
return this.executor.getTrafficExecutor().getResultSet();
} else if (this.executionContext.getRouteContext().isFederated()) {
return this.executor.getFederationExecutor().getResultSet();
} else {
if (this.executionContext.getSqlStatementContext() instanceof SelectStatementContext || this.executionContext.getSqlStatementContext().getSqlStatement() instanceof DALStatement) {
List<ResultSet> resultSets = this.getResultSets();
MergedResult mergedResult = this.mergeQuery(this.getQueryResults(resultSets));//合并结果集
this.currentResultSet = new ShardingSphereResultSet(resultSets, mergedResult, this, this.executionContext);
}
return this.currentResultSet;
}
}
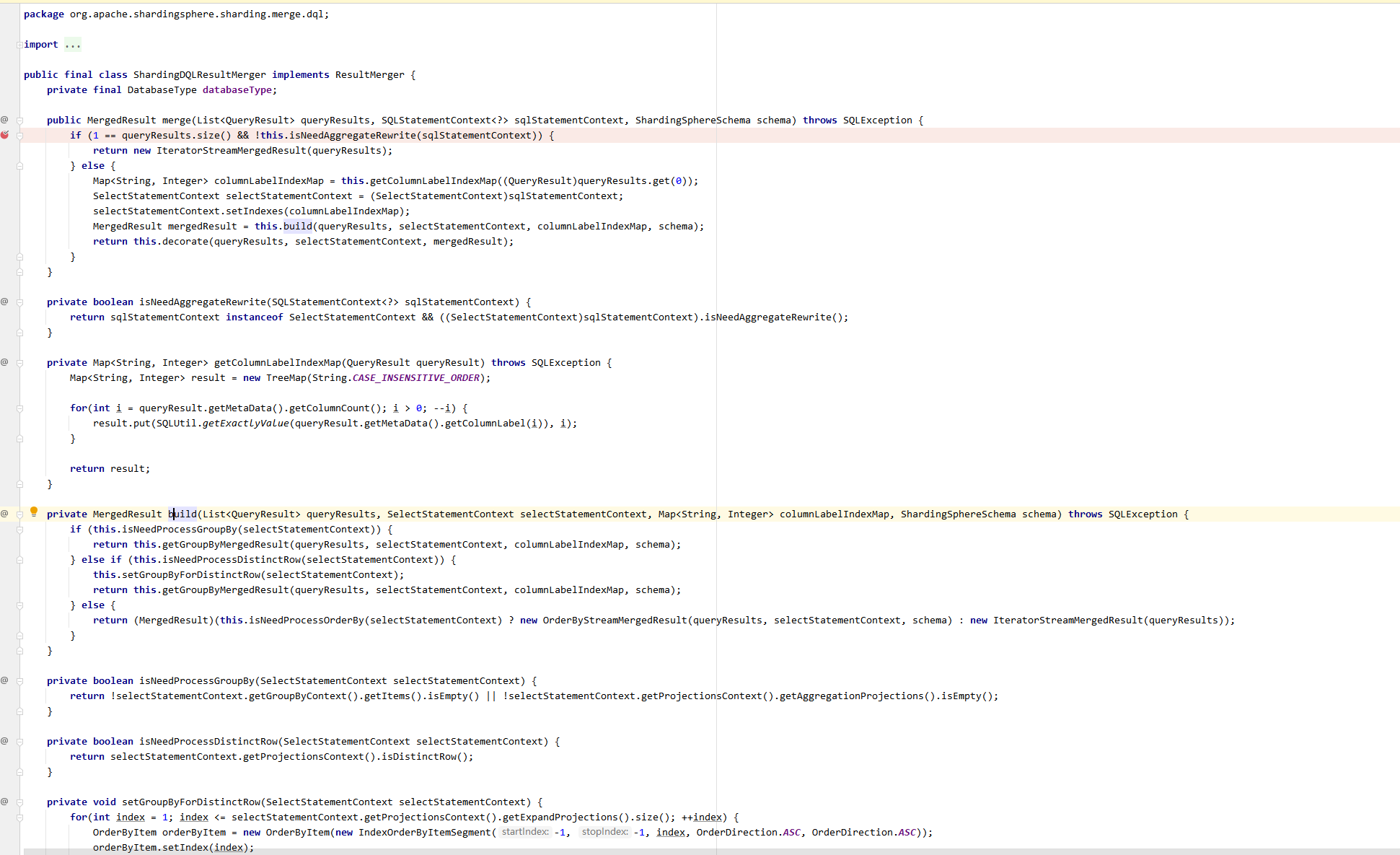
其中this.mergeQuery中调用归并引擎合并结果集合:
private MergedResult mergeQuery(List<QueryResult> queryResults) throws SQLException {
ShardingSphereMetaData metaData = this.metaDataContexts.getMetaData(this.connection.getSchema());
MergeEngine mergeEngine = new MergeEngine(this.connection.getSchema(), metaData.getResource().getDatabaseType(), metaData.getSchema(), this.metaDataContexts.getProps(), metaData.getRuleMetaData().getRules());//归并引擎
return mergeEngine.merge(queryResults, this.executionContext.getSqlStatementContext());
}
二、源码
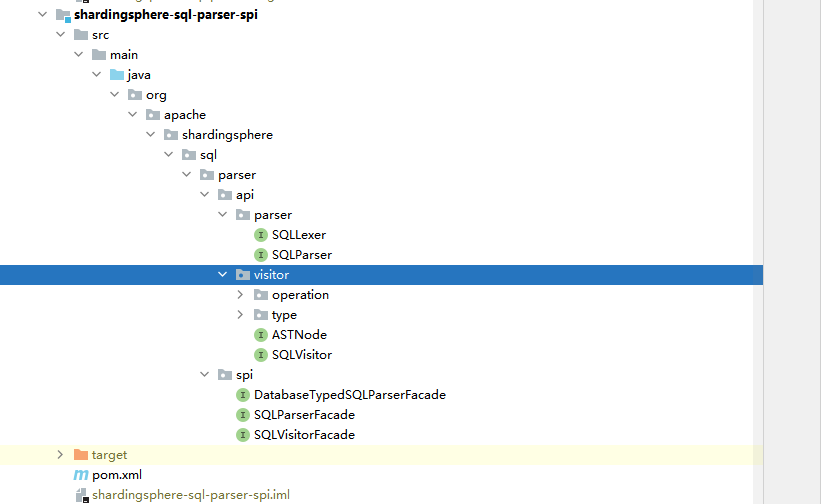
解析,获取sqlStatement
由antlr生成,包括lexer、parser、vistor,支持扩展。
路由
包shardingsphere-infra-route和org.apache.shardingsphere.sharding.route.engine
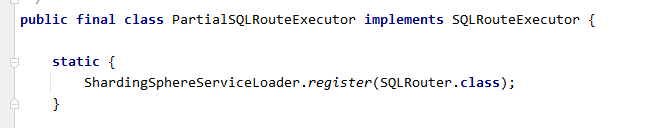
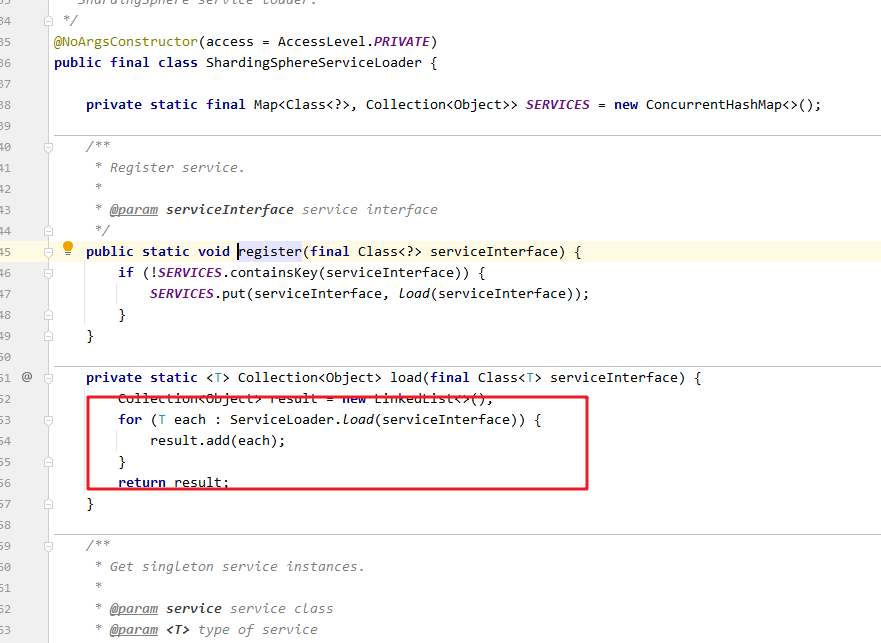
两种路由执行器AllSQLRouteExecutor和PartialSQLRouteExecutor,执行器支持spi扩展。
由路由引擎根据sqlstatement类型判断使用AllSQLRouteExecutor还是PartialSQLRouteExecutor
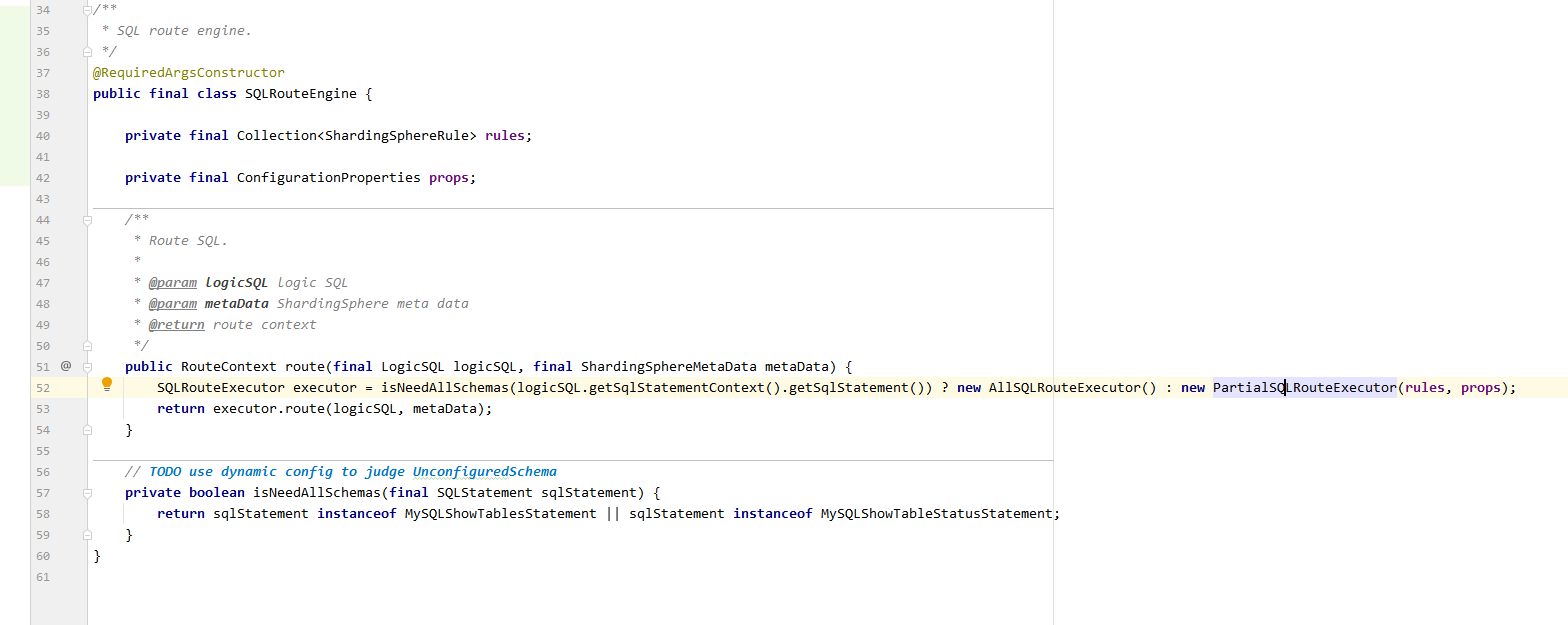
AllSQLRouteExecutor为不添加任何规则的直接路由
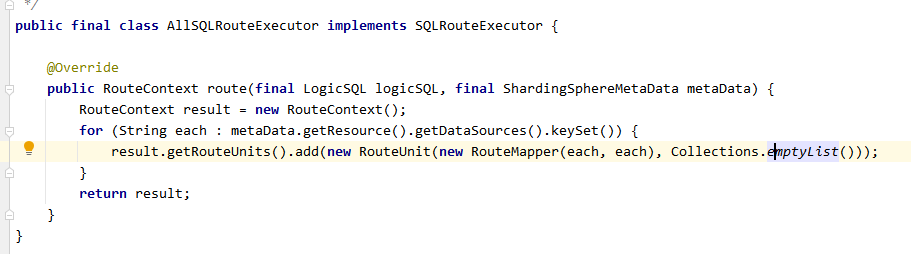
PartialSQLRouteExecutor首先判断是否是Hint强制路由,如果是则获取数据源直接返回,否则逐个添加路由规则。最后判断如果没有规则被添加,数据源唯一,则直接获取数据源返回。
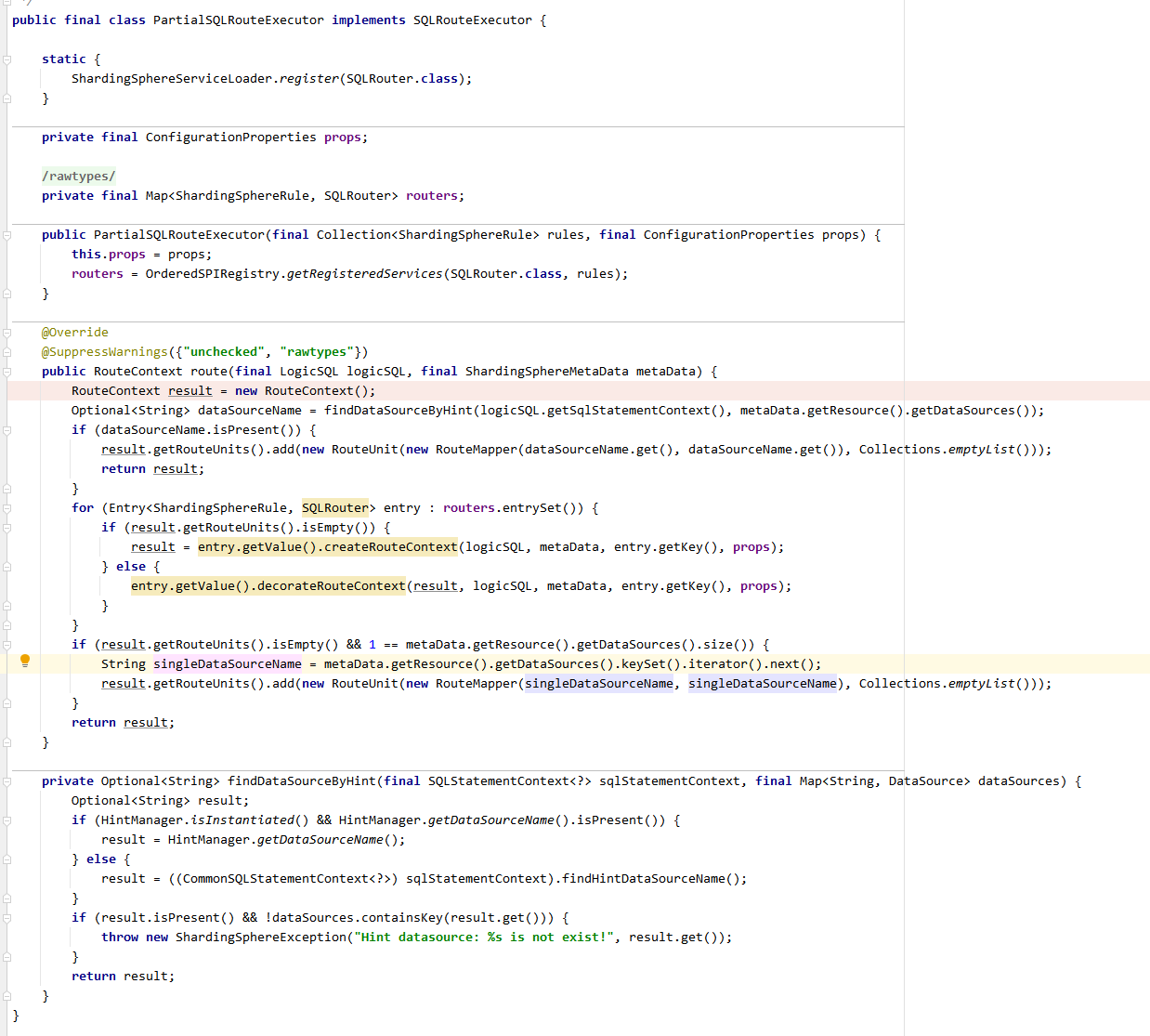
以查询,分片规则为例,构建RouteContext过程如下:
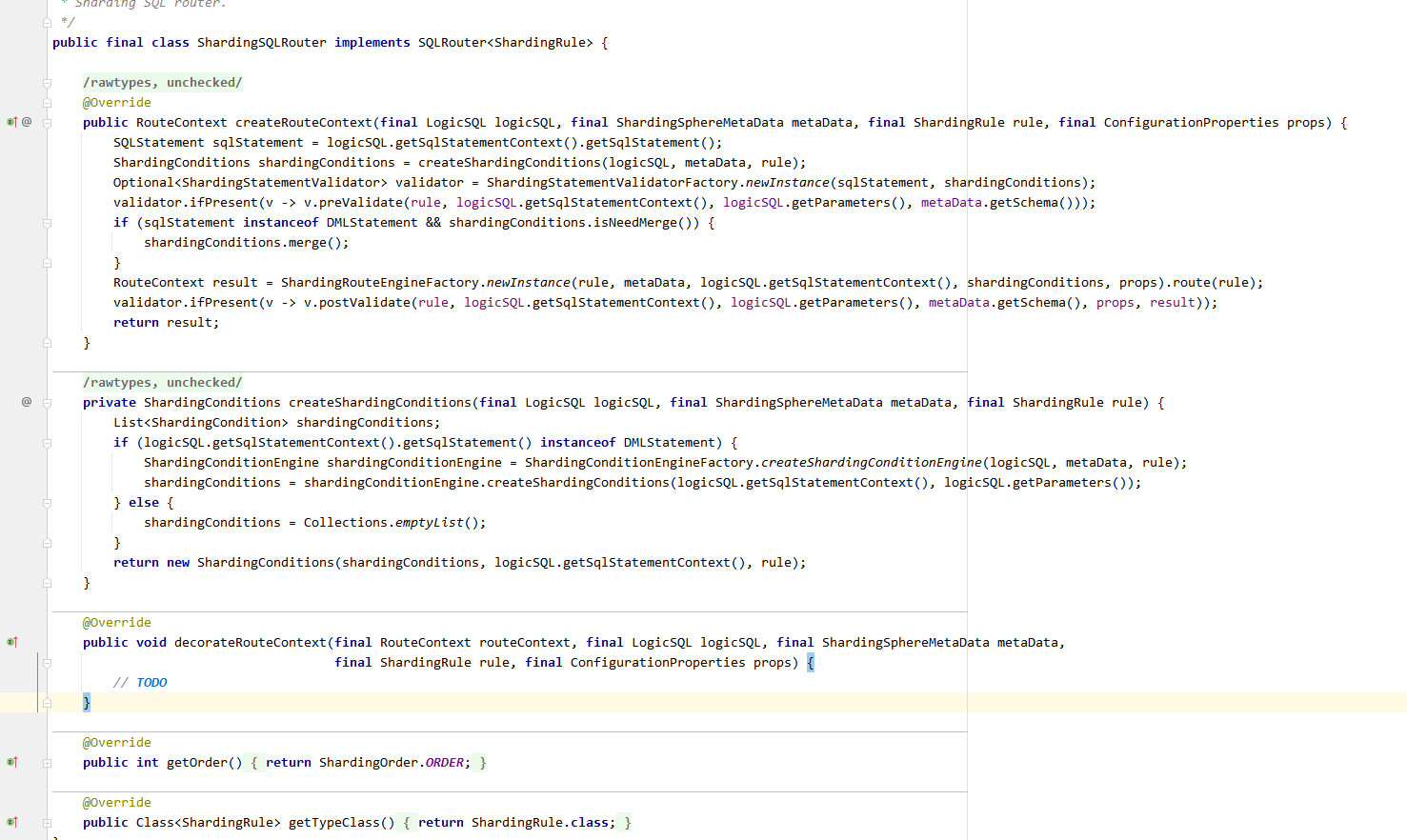
处理 WHERE子句分片条件后处理分库分表条件
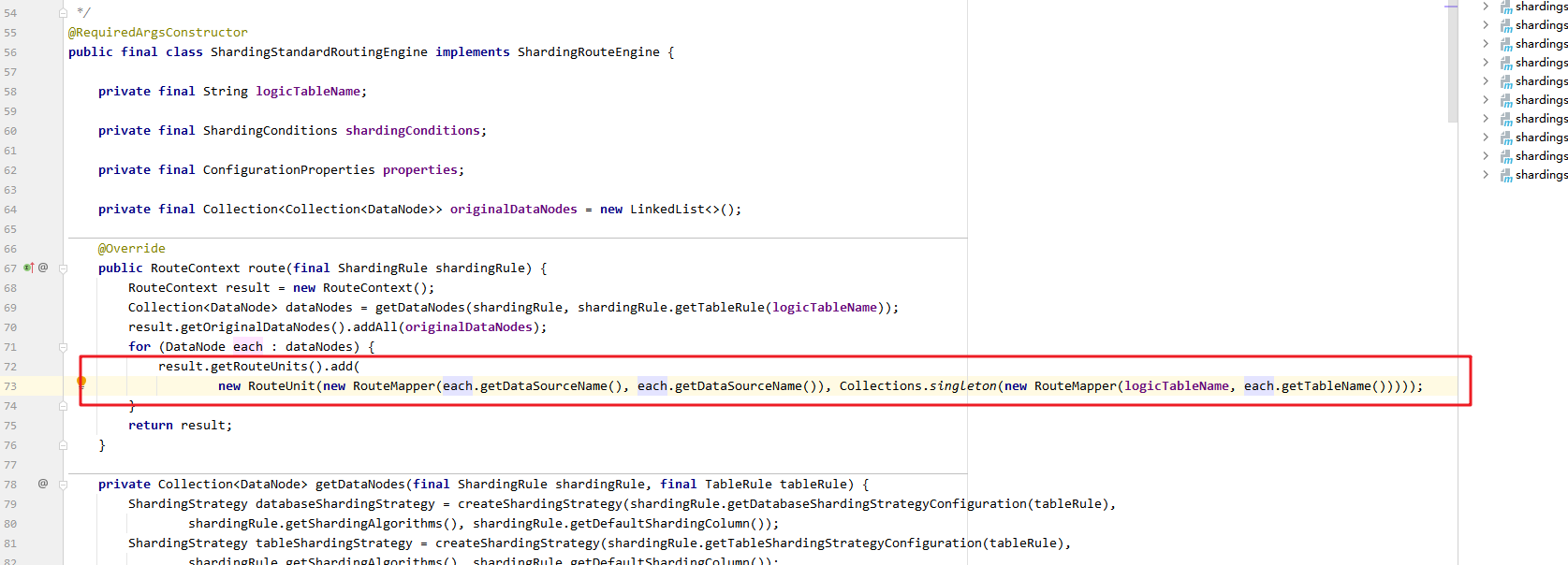
在获取每个实际数据节点后将每个实际数据节点加入RouteContext
改写
包org.apache.shardingsphere.infra.rewrite据路由结果对原始 SQL 进行改写,生成最终要执行的 SQL 和参数集合。
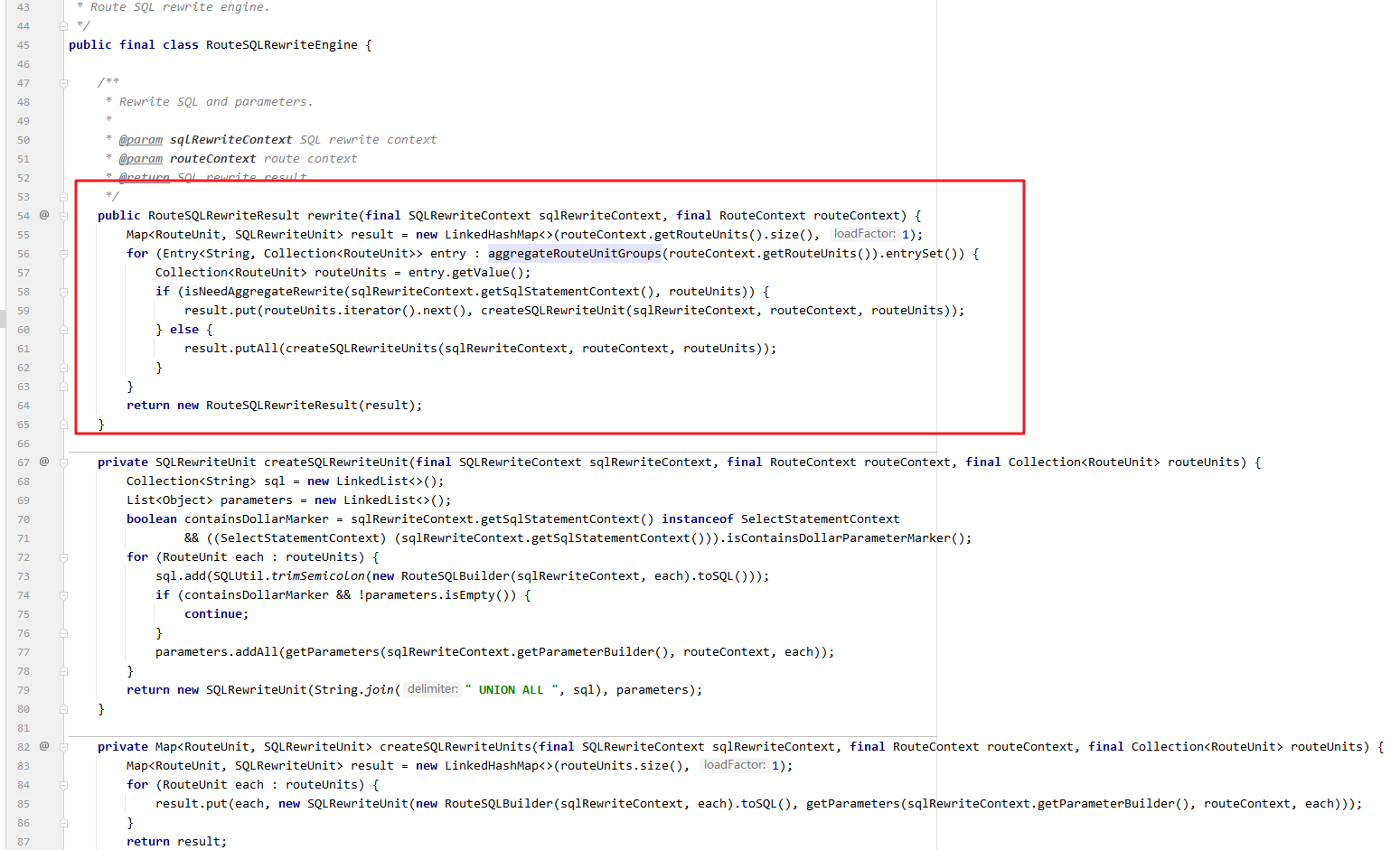
首先按数据源分组路由单元,接着判断是否需要聚合改写(UNION ALL),然后根据判断结果选择不同的重写策略,最后返回包含所有路由单元重写结果的对象
具体转sql代码如下:
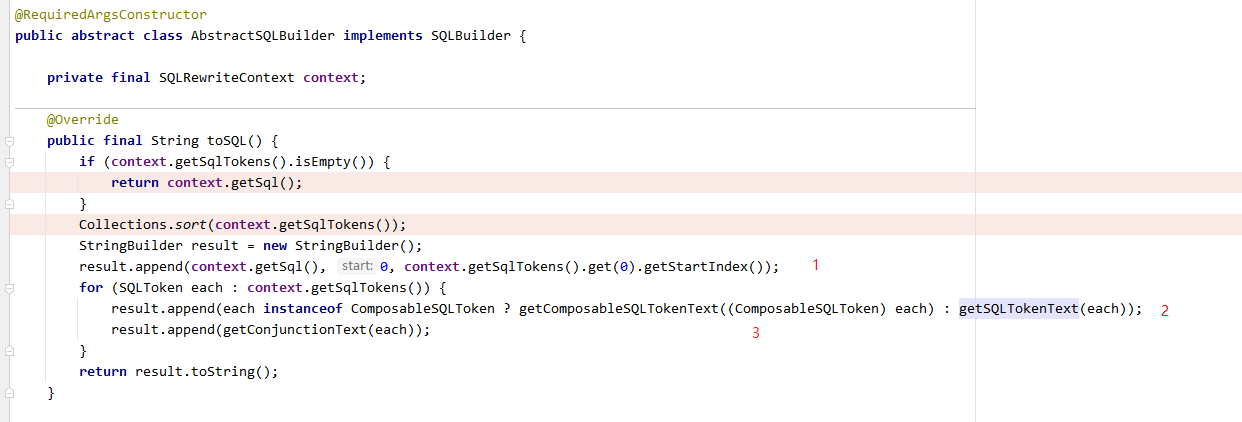
例如逻辑a表有a_0、a_1、a_2实际表,则select xx from a where xxx=xxx;拼接流程为第一步截取select xx from ,第二步拼接实际表名,第三步拼接末尾条件。
执行
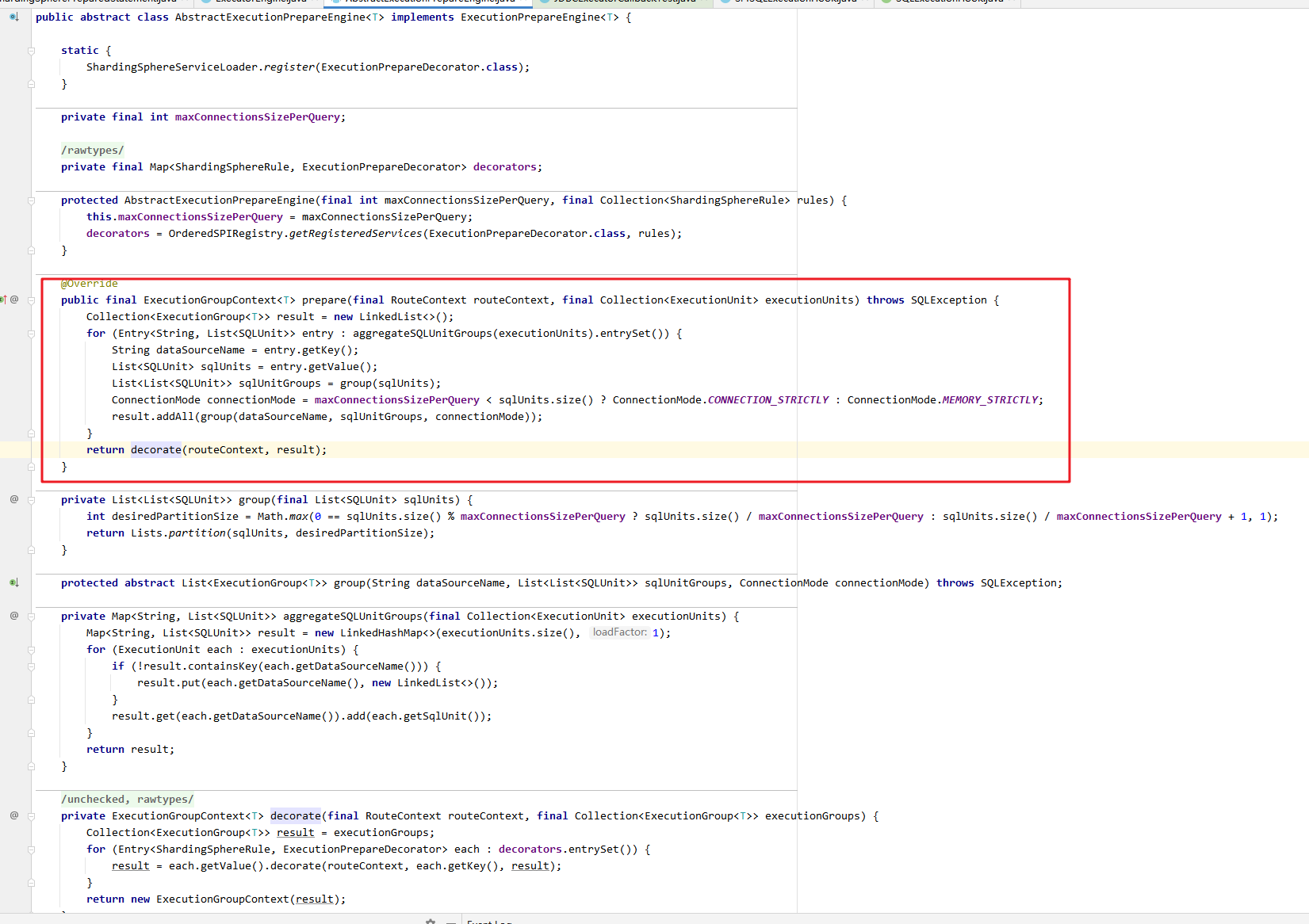
在执行前,ExecutionGroupContext<JDBCExecutionUnit> executionGroupContext = createExecutionGroupContext();里通过ExecutionPrepareEngine对需要执行的实际sql进行分组(根据maxConnectionsSizePerQuery),对连接模式进行选择(maxConnectionsSizePerQuery),并提供spi扩展支持规则特定的执行准备逻辑。
在sql执行前,提供了可扩展的钩子方法
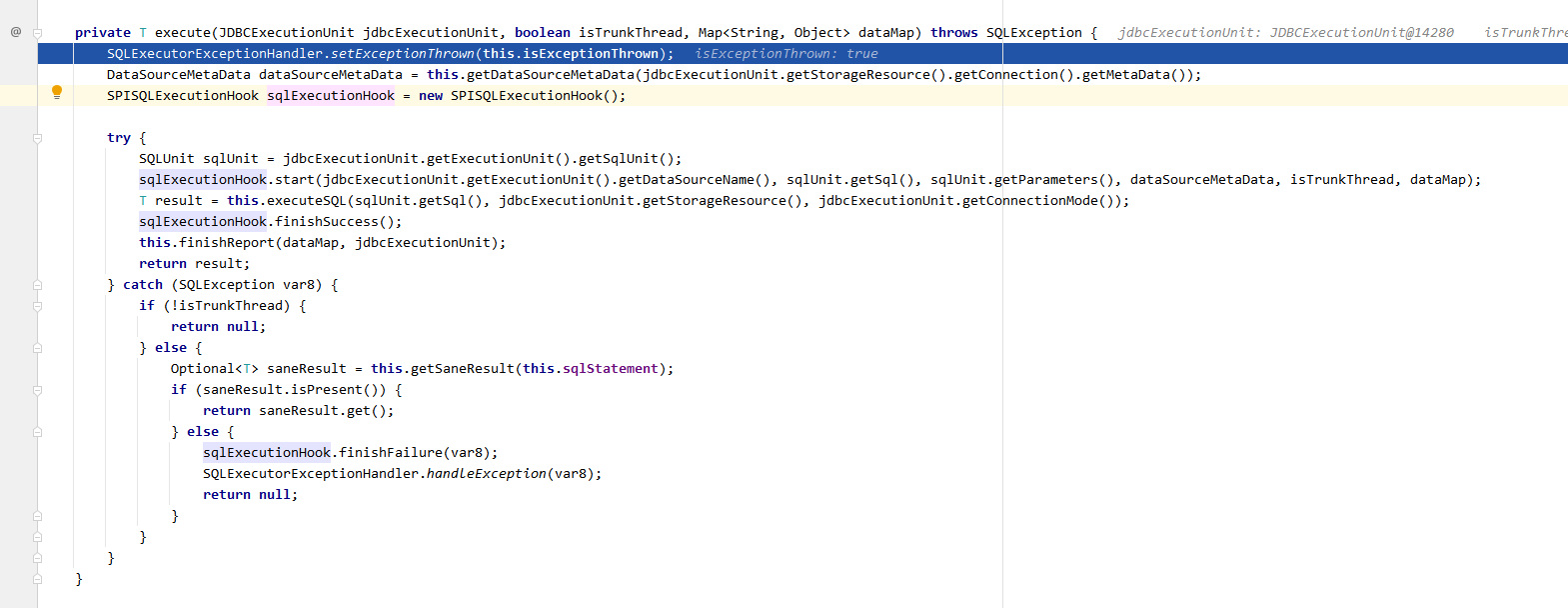
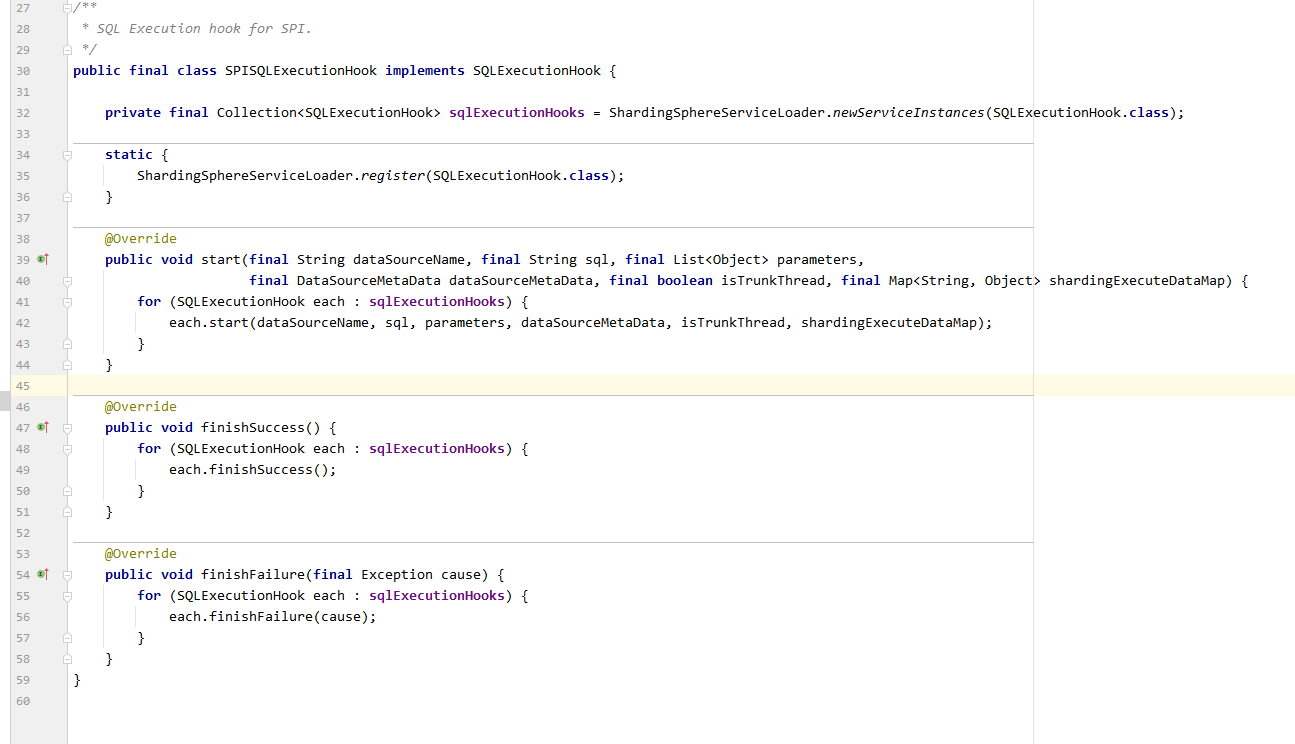
结果归并



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号