实验四:继承
1.实验任务2
程序源码如下:

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include<typeinfo> 3 4 class Graph{ 5 public: 6 virtual void draw(){ 7 std::cout<<"Graph::draw():just as an interface\n"; 8 } 9 }; 10 11 class Rectangle : public Graph 12 { 13 public: 14 void draw(){ 15 std::cout<<"Rectangle::draw(): programs of draw a rectangle\n"; 16 } 17 }; 18 19 class Circle : public Graph 20 { 21 public: 22 void draw(){ 23 std::cout<<"Circle::draw(): programs of draw a circle\n"; 24 } 25 }; 26 27 void fun(Graph *ptr){ 28 std::cout << "Pointer type:"<<typeid(ptr).name()<<"\n"; 29 std::cout << "RTTI type:"<<typeid(*ptr).name()<<"\n"; 30 ptr -> draw(); 31 } 32 int main(){ 33 Graph g1; 34 Rectangle r1; 35 Circle c1; 36 g1.draw(); 37 r1.draw(); 38 c1.draw(); 39 40 std::cout << "\n"; 41 42 r1.Graph::draw(); 43 c1.Graph::draw(); 44 45 std::cout << "\n"; 46 fun(&g1); 47 fun(&r1); 48 fun(&c1); 49 }
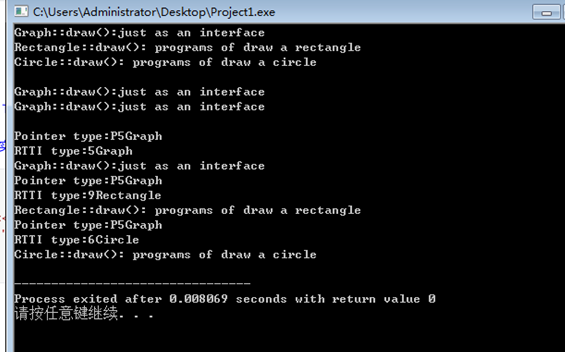
修改之前截图为:
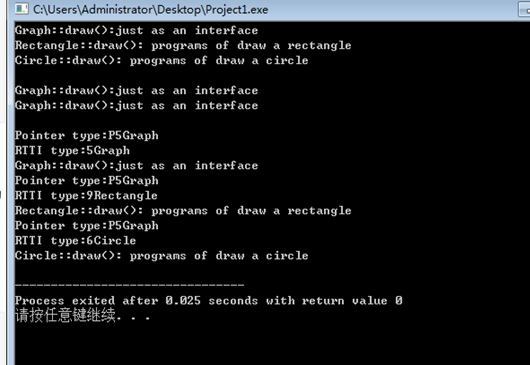
加virtual修改后的运行结果如图:
归纳总结:
1.可以观察到运行时ptr成功指向了派生类,但ptr指针本身还是Graph类的。前面的5,6,9数字和字母P是什么还暂时不知道。
2.当派生类出现与基类同名成员时,会优先运行派生类的函数成员,用二元作用域分辨符标识后可运行基类成员
如r1.Graph::draw(); c1.Graph::draw();
3.类型兼容原则:派生类对象可以被当作基类对象使用,但当作基类对象使用时,只能使用作为基类的那一部分接口。因此函数声明成员类型是Graph,draw()必然显示是基类。
2.实验任务3
以下为Battery.hpp

1 #pragma once 2 class Battery { 3 public: 4 int get_capacity() { 5 return capacity; 6 } 7 Battery(int obj = 70):capacity(obj){} 8 private: 9 int capacity; 10 };
以下为Car.hpp

1 #pragma once 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 class Car { 6 private: 7 string maker; 8 string model; 9 int year; 10 int odometers; 11 public: 12 Car(); 13 Car(string m1, string m2, int y) :maker(m1), model(m2), year(y), odometers(0) {}; 14 void info(); 15 void update_odometers(int n); 16 }; 17 void Car::info() { 18 cout << maker << endl; 19 cout << model << endl; 20 cout << year << endl; 21 cout << odometers << endl; 22 } 23 void Car::update_odometers(int n) { 24 if (n >= odometers) 25 odometers = n; 26 else 27 cout << "data is error!"; 28 }
以下为ElectricCar.hpp
 ElectricCar.hpp
ElectricCar.hpp以下为task3.cpp

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "electricCar.hpp" 3 4 int main() 5 { 6 using namespace std; 7 8 // test class of Car 9 Car oldcar("Audi", "a6", 2016); 10 cout << "--------oldcar's info--------" << endl; 11 oldcar.update_odometers(25000); 12 oldcar.info(); 13 14 cout << endl; 15 16 // test class of ElectricCar 17 ElectricCar newcar("Tesla", "model s", 2016); 18 newcar.update_odometers(12500); 19 cout << "\n--------newcar's info--------\n"; 20 newcar.info(); 21 }
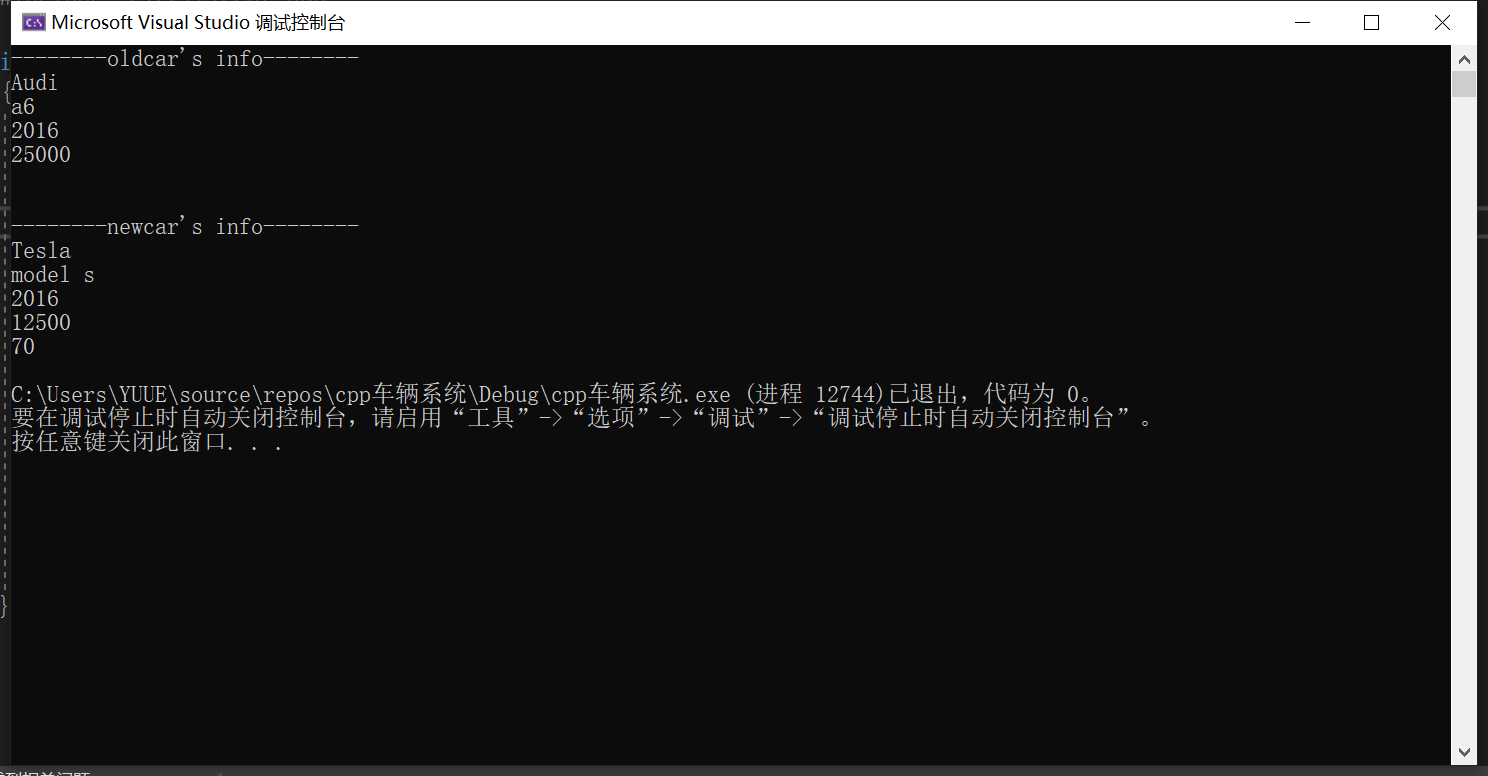
3.实验任务四
pets.hpp

1 #pragma once 2 #include<string> 3 #include<iostream> 4 using namespace std; 5 class MachinePets { 6 private: 7 string nickname; 8 public: 9 MachinePets(); 10 MachinePets(const string s):nickname(s){} 11 const string get_nickname() { 12 return nickname; 13 } 14 virtual string talk() { 15 return"talk~"; 16 } 17 }; 18 class PetCats : public MachinePets{ 19 public: 20 PetCats(const string st):MachinePets(st){} 21 string talk() { 22 return "miao wu~"; 23 } 24 }; 25 class PetDogs :public MachinePets{ 26 public: 27 PetDogs(); 28 PetDogs(const string s1):MachinePets(s1){ 29 30 } 31 string talk() { 32 return "wang!wang!"; 33 } 34 };
task4.cpp

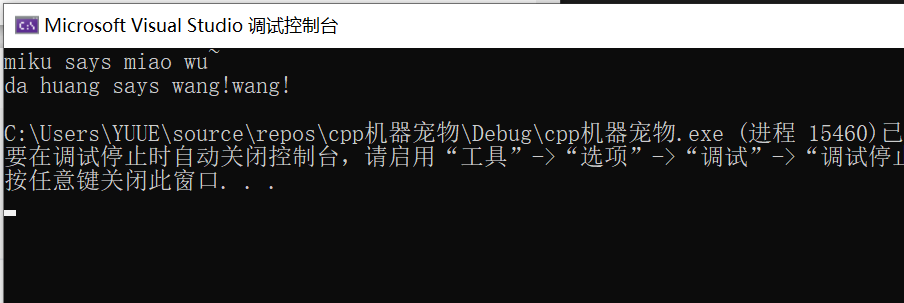
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "pets.hpp" 3 4 void play(MachinePets* ptr) 5 { 6 std::cout << ptr->get_nickname() << " says " << ptr->talk() << std::endl; 7 } 8 9 int main() 10 { 11 PetCats cat("miku"); 12 PetDogs dog("da huang"); 13 14 play(&cat); 15 play(&dog); 16 }
测试截图如下:
归纳总结:
1.可以观察到运行时ptr成功指向了派生类,但ptr指针本身还是Graph类的。前面的5,6,9数字和字母P是什么还暂时不知道。
2.当派生类出现与基类同名成员时,会优先运行派生类的函数成员,用二元作用域分辨符标识后可运行基类成员
如r1.Graph::draw(); c1.Graph::draw();
3.类型兼容原则:派生类对象可以被当作基类对象使用,但当作基类对象使用时,只能使用作为基类的那一部分接口。因此函数声明成员类型是Graph,draw()必然显示是基类
4.用typeid().name()获取类型名
5.在继承类中初始化时,构造函数放在大括号前面,不然会出现重定义的问题。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号