实验3 类和对象Ⅱ
------------恢复内容开始------------
一、实验任务4
动态int型数组类Vector_int的定义实现源码(vector_int.hpp)
#pragma once #include<iostream> using namespace std; class Vector_int { public: Vector_int(int n) ; Vector_int(int n,int start); Vector_int(Vector_int& obj); ~Vector_int(); int& at(int i); void print(); private: int size; int* p; }; Vector_int::Vector_int(int n) { p = new int[n] {0}; size = n; cout << "Object is being created by constructor 1" << endl; }; Vector_int::Vector_int(int n, int start) { p = new int[n]; size = n; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) p[i] = start; cout << "Object is being created by constructor 2" << endl; }; Vector_int::Vector_int(Vector_int& x) { p = new int[x.size]; size = x.size; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) p[i] = x.p[i]; cout << "Object is being created by constructor 3" << endl; }; Vector_int::~Vector_int() { delete[] p; cout << "Object is being destructed" << endl; } int& Vector_int::at(int i) { return p[i]; }; void Vector_int::print() { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) cout << p[i] <<" "; cout << endl; };
测试类Vector_int的代码(文件task4.cpp)
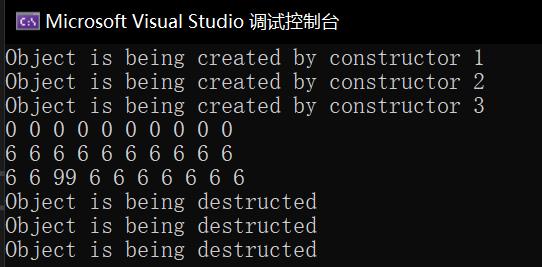
#include<iostream> #include "vector_int.hpp" int main() { int n = 10; Vector_int x1(n); Vector_int x2(n,6); Vector_int y(x2); y.at(2) = 99; x1.print(); x2.print(); y.print(); }
运行测试结果截图
二、实验任务5
类Matrix的定义和实现完整代码(Matrix.hpp)
#ifndef MATRIX_H #define MATRIX_H #include <iostream> #include <cassert> using namespace std; class Matrix { public: Matrix(int n); // 构造函数,构造一个n*n的矩阵 Matrix(int n, int m); // 构造函数,构造一个n*m的矩阵 Matrix(const Matrix &X); // 复制构造函数,使用已有的矩阵X构造 ~Matrix(); //析构函数 void set(const double *pvalue); // 用pvalue指向的连续内存块数据为矩阵赋值 void set(int i, int j, int value); //设置矩阵第i行第j列元素值为value double &at(int i, int j); //返回矩阵第i行第j列元素的引用 double at(int i, int j) const; // 返回矩阵第i行第j列元素的值 int get_lines() const; //返回矩阵行数 int get_cols() const; //返回矩列数 void print() const; // 按行打印输出矩阵 private: int lines; // 矩阵行数 int cols; // 矩阵列数 double *p; // 指向存放矩阵数据的内存块的首地址 }; Matrix::Matrix(int n) { lines = n; cols = n; p = new double[lines*cols]; } Matrix::Matrix(int n, int m) { lines = n; cols = m; p = new double[lines*cols]; } Matrix::Matrix(const Matrix& x) { lines = x.lines; cols = x.cols; p = new double[lines*cols]; for (int i = 0; i < lines * cols; i++) { p[i] = x.p[i]; } } Matrix::~Matrix() { delete[] p; } void Matrix::set(int i, int j, int value) { p[i * cols + j] = value; } void Matrix::set(const double* pvalue) { for (int i = 0; i < lines * cols; i++) { p[i] = pvalue[i]; } } double& Matrix::at(int i, int j) { return p[i * cols + j]; } double Matrix::at(int i, int j)const { return p[i * cols + j]; } int Matrix::get_lines()const { return lines; } int Matrix::get_cols()const { return cols; } void Matrix::print()const { for (int i = 0; i < lines; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) cout << p[i * cols + j] << " "; cout << endl; } } #endif
测试代码(task5.cpp)
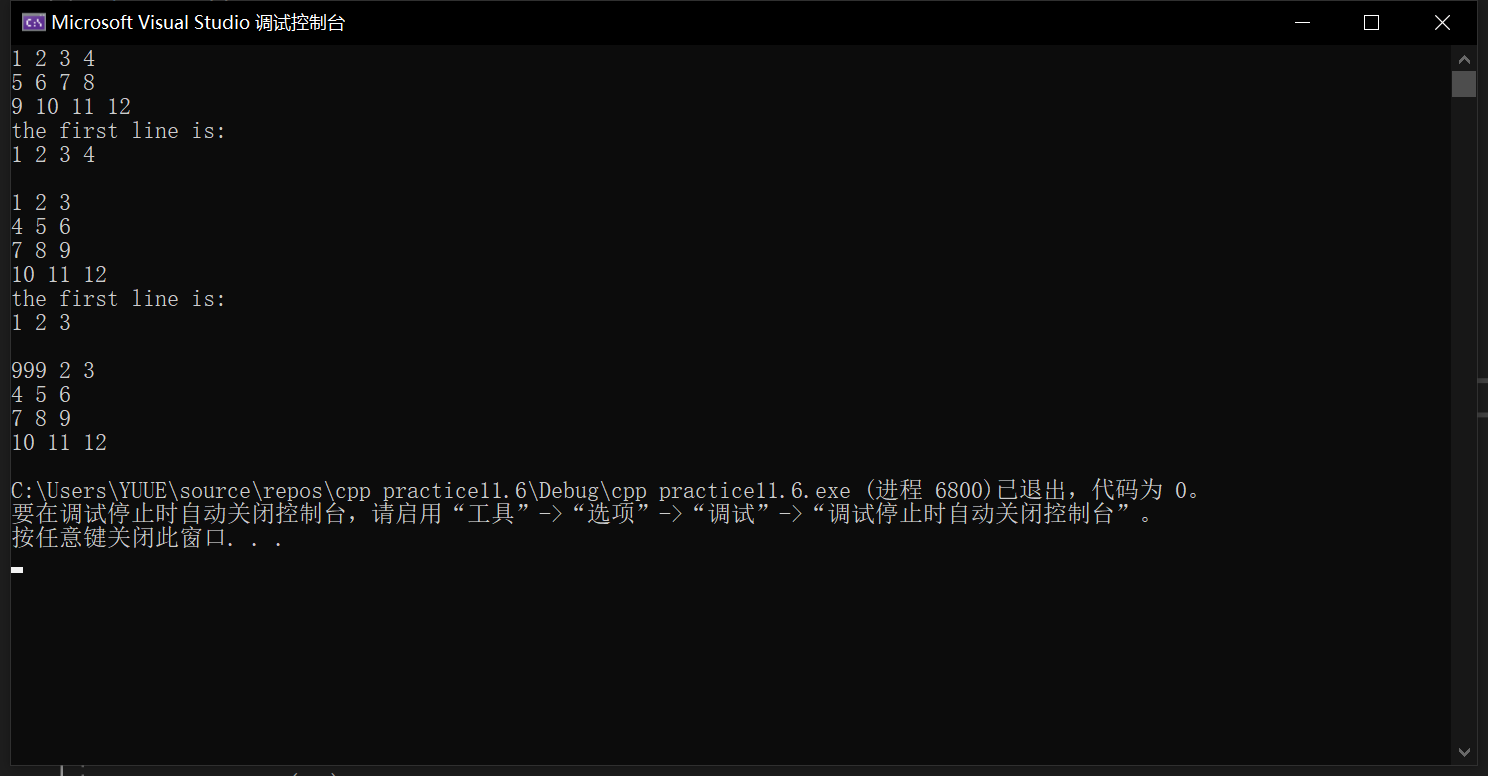
#include <iostream> #include "matrix.hpp" int main() { using namespace std; double x[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12}; Matrix m1(3, 4); // 创建一个3×4的矩阵 m1.set(x); // 用一维数组x的值按行为矩阵m1赋值 m1.print(); // 打印矩阵m1的值 cout << "the first line is: " << endl; cout << m1.at(0, 0) << " " << m1.at(0, 1) << " " << m1.at(0, 2)<< " " << m1.at(0, 3) << endl; cout << endl; Matrix m2(4, 3); m2.set(x); m2.print(); cout << "the first line is: " << endl; cout << m2.at(0, 0) << " " << m2.at(0, 1) << " " << m2.at(0, 2) << endl; cout << endl; Matrix m3(m2); m3.set(0, 0, 999); m3.print(); }
运行测试截图(换一组测试数据)
三、实验总结
1.Task1,2中,输出时加的hex一开始不太理解是啥。
2.Typeid是用来获取数据类型信息的,使用的格式是typeid(a).name()
3.Y是个一维数组,长度为1,这个存储单元存储了数组x的首地址。
4.Square1的函数,自动递归中的i是引用的形式。
而square2的i是单独的,与原来的数组x没有关系。
5.实验任务2中,如果把类ArrayOfPoints中复制构造函数的声明和实现注释起来。能运行,但是会陷入死循环,可能是y括号里的x类型是arrayofpoints,而不是int,所以系统识别不了。
6.Task3中,学习到了头文件#include <cstdlib>的使用,system("cls")代表清屏。
用 system("color 0A"),其中color后面的0是背景色代号,A是前景色代号。
string color = "color ";
color += bg;
color += fg;
以字符串的运算来构成“color 0A”
7.完成Task3时,开始没有思路,vector类构造数组如何返回数组给主函数呢,参考其他代码发现,vector类不能仅仅看做构造函数的工具,还有数组的属性包括数组本身和数组长度。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号