实验1:类与对象
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cmath> 3 4 class Complex 5 { 6 7 public: 8 Complex() {}; 9 Complex(double x) :real{ x }, imag{ 0 }{} 10 Complex(double x, double y) :real{ x }, imag{ y }{} 11 Complex(const Complex& obj):real{ obj.real }, imag{ obj.imag }{}; 12 ~Complex() = default; 13 double get_real() const {return real;} 14 double get_imag() const {return imag;} 15 void show() const; 16 void add(Complex c); 17 friend Complex add(Complex x1, Complex x2); 18 friend bool is_equal(Complex obj1, Complex obj2); 19 friend double abs(Complex obj); 20 private: 21 double real, imag; 22 23 }; 24 25 26 void Complex::show() const 27 { 28 using namespace std; 29 if (imag > 0) 30 cout << real << "+" << imag << "i" << endl; 31 else if (imag == 0) 32 cout << real << endl; 33 else 34 cout << real << imag << "i" << endl; 35 } 36 37 void Complex::add(Complex obj) 38 { 39 real += obj.real; 40 imag += obj.imag; 41 } 42 43 Complex add(Complex c1, Complex c2) 44 { 45 Complex c(c1.real + c2.real, c1.imag + c2.imag); 46 return c; 47 } 48 49 50 double abs(Complex obj) 51 { 52 double x = sqrt(obj.get_imag() * obj.get_imag() + obj.get_real() * obj.get_real()); 53 return x; 54 } 55 56 57 bool is_equal(Complex obj1, Complex obj2) { 58 if (obj1.get_real() == obj2.get_real() && obj1.get_imag() == obj2.get_imag()) 59 return true; 60 else return false; 61 }
以下为task3.cpp:
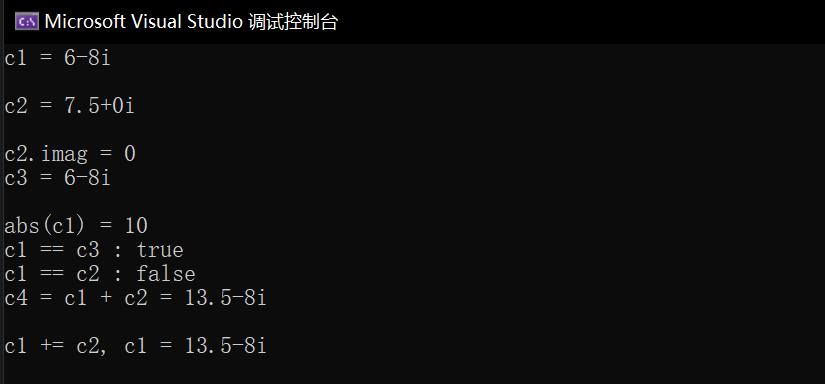
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "Complex.hpp" 3 4 int main() 5 { 6 using namespace std; 7 8 Complex c1(6,-8); 9 const Complex c2(2.5); 10 Complex c3(c1); 11 12 cout << "c1 = "; 13 c1.show(); 14 cout << endl; 15 16 cout << "c2 = "; 17 c2.show(); 18 cout << endl; 19 cout << "c2.imag = " << c2.get_imag() << endl; 20 21 cout << "c3 = "; 22 c3.show(); 23 cout << endl; 24 25 cout << "abs(c1) = "; 26 cout << abs(c1) << endl; 27 28 cout << boolalpha; 29 cout << "c1 == c3 : " << is_equal(c1, c3) << endl; 30 cout << "c1 == c2 : " << is_equal(c1, c2) << endl; 31 32 Complex c4; 33 c4 = add(c1, c2); 34 cout << "c4 = c1 + c2 = "; 35 c4.show(); 36 cout << endl; 37 38 c1.add(c2); 39 cout << "c1 += c2, " << "c1 = "; 40 c1.show(); 41 cout << endl; 42 }
以下为运行结果截图:
二,实验任务4
以下为User.hpp.源码
1 #pragma once 2 #pragma once 3 #include <string> 4 #include<iostream> 5 using namespace std; 6 class User 7 { 8 public: 9 User(); 10 User(string name1) :name{ name1 }, passwd{ "111111" }, email{ " " } { 11 n++; 12 }; 13 User(string name1, string passwd1, string email1) 14 :name{ name1 }, passwd{ passwd1 }, email{ email1 }{ 15 n++; 16 }; 17 ~User(); 18 void set_email(); 19 void change_passwd(); 20 void print_info() {cout << "name:" << name << endl 21 << "passwd:" << "******" <<endl 22 << "email:" << email <<endl; 23 }; 24 static void print_n() { 25 cout << "There are " << n << " users" << endl; 26 } 27 private: 28 string name; 29 string passwd; 30 string email; 31 static int n; 32 }; 33 int User::n = 0; 34 35 User::User() 36 { 37 n++; 38 } 39 40 User::~User() 41 { 42 n--; 43 } 44 void User::set_email() { 45 string email1; 46 cout << "Enter email address:" ; 47 cin >> email1; 48 email = email1; 49 cout << "email is set successfully!" << endl; 50 } 51 void User::change_passwd() { 52 int a = 1,n = 2; 53 string passwd1,passwd0; 54 cout << "Enter old password:" << endl; 55 cin >> passwd1; 56 a = passwd1.compare(passwd); 57 while (a != 0&&n--) { 58 cout << "Please reenter again:"; 59 cin >> passwd1; 60 a = passwd1.compare(passwd); 61 } 62 if (a == 0){ 63 cout << "Enter new password:"; 64 cin >> passwd1; 65 passwd = passwd1; 66 } 67 else { 68 cout << "password input error,please try after a while" << endl; 69 } 70 }
以下为task4.cpp的源码(已修改数据):
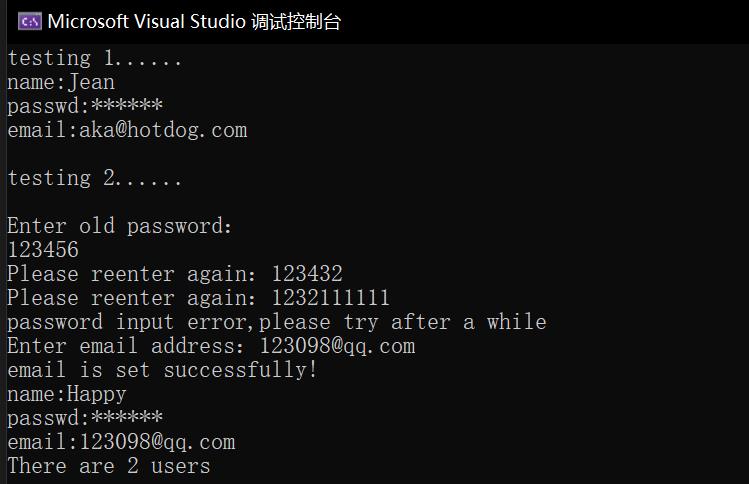
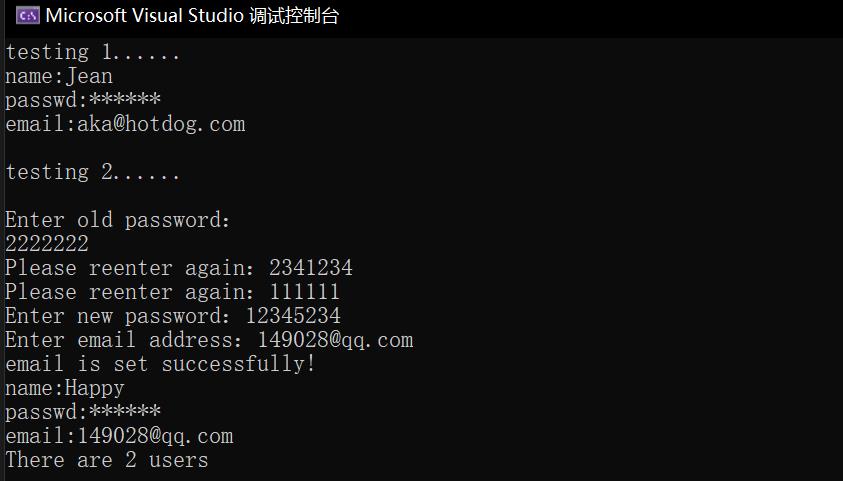
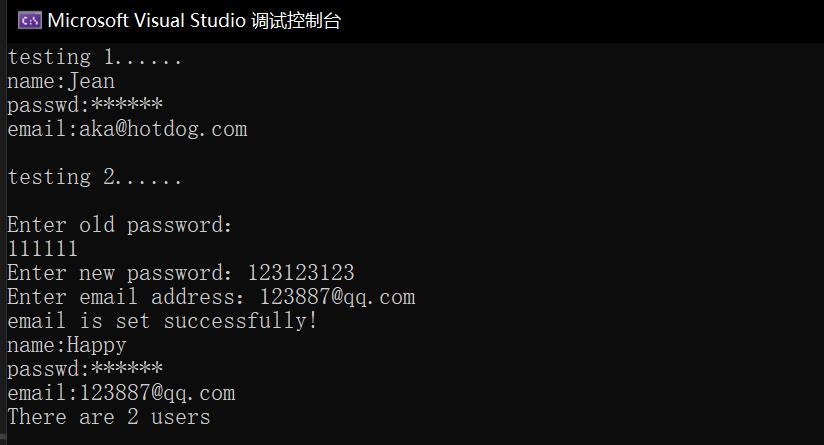
1 #include "User.hpp" 2 #include <iostream> 3 4 int main() 5 { 6 using namespace std; 7 8 cout << "testing 1......" << endl; 9 User user1("Jean", "666666", "aka@hotdog.com"); 10 user1.print_info(); 11 12 cout << endl 13 << "testing 2......" << endl 14 << endl; 15 User user2("Happy"); 16 user2.change_passwd(); 17 user2.set_email(); 18 user2.print_info(); 19 20 User::print_n(); 21 }
以下为运行结果截图:
实验总结
此次实验学到的新东西,掌握的新的运用方法很多。
(1)在正式实践时,总是提示开头文件包含失败。结合实验二分析之后,才知道包含其他源文件时,应该将放在同一个路径文件之上,不能仅仅在默认路径创建一个新文件,然后再导入别的路径下的现有文件。
(2)对const的应用有了更好的掌握。
const放在成员函数之后,表示不会对成员属性进行修改;
放在函数的最前面,表示不能修改返回值;
放在括号中的形参前面,表示函数体内不能修改形参的值。
常量对象只能调用const的函数。普通对象都可以调用。
(3)类内函数的参数不需要使用引用形式,可以直接修改属性。
(4)用静态的成员变量来统计类对象的数量,初始化必须在类外实现,格式如下
<数据类型><类名>::<静态数据成员名>=<值>
前面不用加static,以免与一般静态变量或对象相混淆。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号