用Java写一个生产者-消费者队列
生产者消费者的模型作用
- 通过平衡生产者的生产能力和消费者的消费能力来提升整个系统的运行效率,这是生产者消费者模型最重要的作用。
- 解耦,这是生产者消费者模型附带的作用,解耦意味着生产者和消费者之间的联系少,联系越少越可以独自发展
使用阻塞队列来实现
package yunche.test.producer; import java.util.Random; import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; /** * @ClassName: Producer * @Description: 生产者 * @author: yunche * @date: 2018/08/26 */ public class Producer implements Runnable { private final BlockingQueue<Integer> queue; public Producer(BlockingQueue q) { this.queue = q; } @Override public void run() { try { while(true) { //模拟耗时1s Thread.sleep(1000); queue.put(produce()); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private int produce() { int n = new Random().nextInt(10000); System.out.println("Thread: " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " produce: " + n); return n; } } package yunche.test.producer; import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; /** * @ClassName: Consumer * @Description: 消费者 * @author: yunche * @date: 2018/08/26 */ public class Consumer implements Runnable { private final BlockingQueue<Integer> queue; public Consumer(BlockingQueue q) { this.queue = q; } @Override public void run() { while (true) { try { //模拟耗时 Thread.sleep(2000); consume(queue.take()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } private void consume(Integer n) { System.out.println("Thread:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " consume: " + n); } } package yunche.test.producer; import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; /** * @ClassName: Main * @Description: 测试类 * @author: yunche * @date: 2018/08/26 */ public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { BlockingQueue<Integer> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(100); Producer p = new Producer(queue); Consumer c1 = new Consumer(queue); Consumer c2 = new Consumer(queue); Thread producer = new Thread(p); producer.setName("生产者线程"); Thread consumer1 = new Thread(c1); consumer1.setName("消费者1"); Thread consumer2 = new Thread(c2); consumer2.setName("消费者2"); producer.start(); consumer1.start(); consumer2.start(); } }
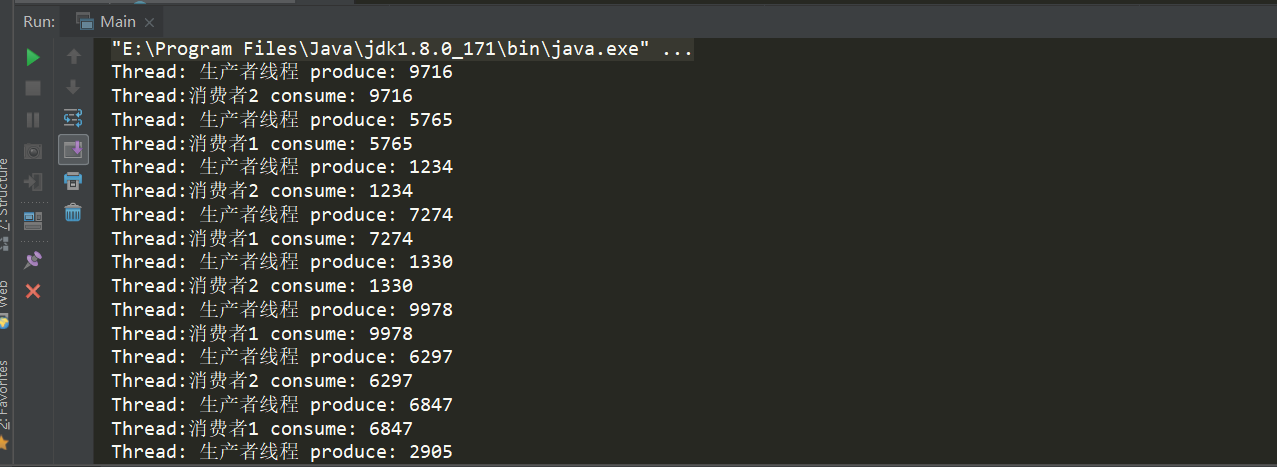
使用wait-notify来实现
package yunche.test.producer; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Random; /** * @ClassName: Producer * @Description: 生产者 * @author: yunche * @date: 2018/08/26 */ public class Producer implements Runnable { private final LinkedList<Integer> list; /** * 缓冲区大小 */ private final int maxSize; public Producer(LinkedList list, int size) { this.list = list; maxSize =size; } @Override public void run() { try { while(true) { //模拟耗时1s Thread.sleep(1000); synchronized (list) { if(list.size()==maxSize) { System.out.println("缓冲区已满,正在等待消费者消费..." + System.currentTimeMillis()); list.wait(); } else { list.add(produce()); list.notifyAll(); } } } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private int produce() { int n = new Random().nextInt(10000); System.out.println("Thread: " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " produce: " + n); return n; } } package yunche.test.producer; import java.util.Date; import java.util.LinkedList; /** * @ClassName: Consumer * @Description: 消费者 * @author: yunche * @date: 2018/08/26 */ public class Consumer implements Runnable { private final LinkedList<Integer> list; public Consumer(LinkedList list) { this.list = list; } @Override public void run() { while (true) { try { synchronized(list) { //模拟耗时 Thread.sleep(1000); if(list.isEmpty()) { System.out.println("缓冲区已空,正在等待生产者生产..." + System.currentTimeMillis() + Thread.currentThread().getName()); list.wait(); } else { consume(list.poll()); list.notifyAll(); } } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } private void consume(Integer n) { System.out.println("Thread:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " consume: " + n); } } package yunche.test.producer; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.List; /** * @ClassName: Main * @Description: 测试类 * @author: yunche * @date: 2018/08/26 */ public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>(); Producer p = new Producer(list, 10); Consumer c1 = new Consumer(list); Consumer c2 = new Consumer(list); Thread producer = new Thread(p); producer.setName("生产者线程"); Thread consumer1 = new Thread(c1); consumer1.setName("消费者1"); Thread consumer2 = new Thread(c2); consumer2.setName("消费者2"); producer.start(); consumer1.start(); consumer2.start(); } }
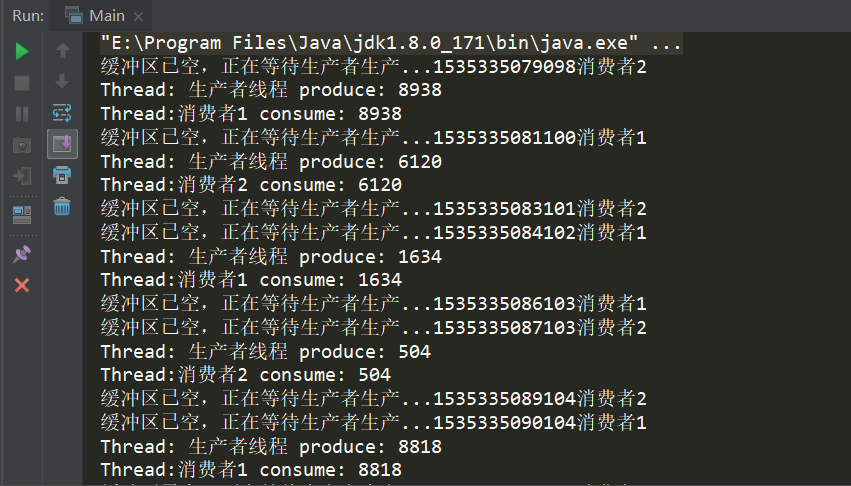
参考资料
不积跬步,无以至千里;不积小流,无以成江海



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号