ctf逆向常见算法----base64
ctf逆向常见算法----base64
base64顾名思义,即为使用A-Z,a-z,0-9,+,/,64个字符进行编码的一种方式,当然在日常的使用中还会出现=用作填充字符。
作为在ctf竞赛中最常用的一种编码形式,本篇文章将对其原理及代码实现进行详解
原理
base64算法首先运用到的是一张包含有64个字符的索引表
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J |
| 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| U | V | W | X | Y | Z | a | b | c | d |
| 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 | 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 |
| e | f | g | h | i | j | k | l | m | n |
| 40 | 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 | 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 |
| o | p | q | r | s | t | u | v | w | x |
| 50 | 51 | 52 | 53 | 54 | 55 | 56 | 57 | 58 | 59 |
| y | z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 60 | 61 | 62 | 63 | ||||||
| 8 | 9 | + | / |
如表中所示每一个字符都相对应这一个索引,共64个,由此便引申出base64中的要点,2的6次方等于64,即每个索引用6位二进制来表示,而在计算机中一个字符使用8位二进制来表示,二者的转化关系如图所示
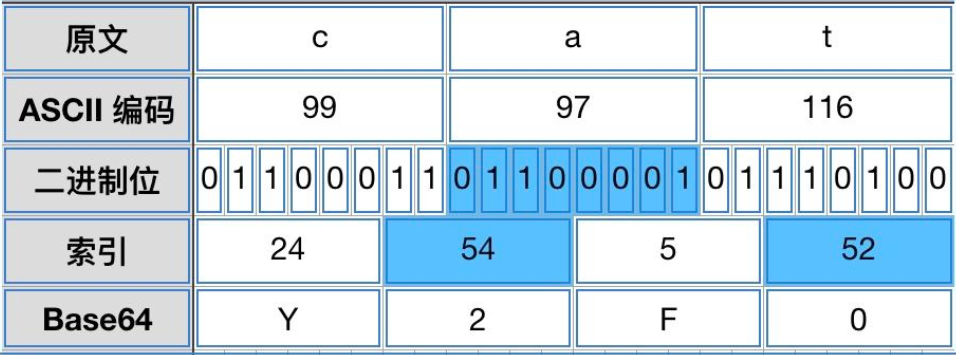
由图中的关系可以看出,三位文本字符则对应四位base64字符,而在实际运用中由于每次进行编码的文本并非都为3的倍数,故而在base64编码中加入=号进行填充
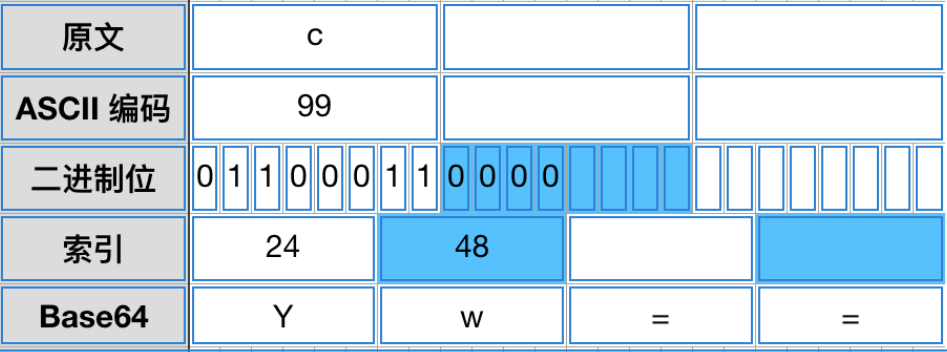
如果最后剩下一个字符,则在二进制编码中中加入4个0位,在base编码中加入==
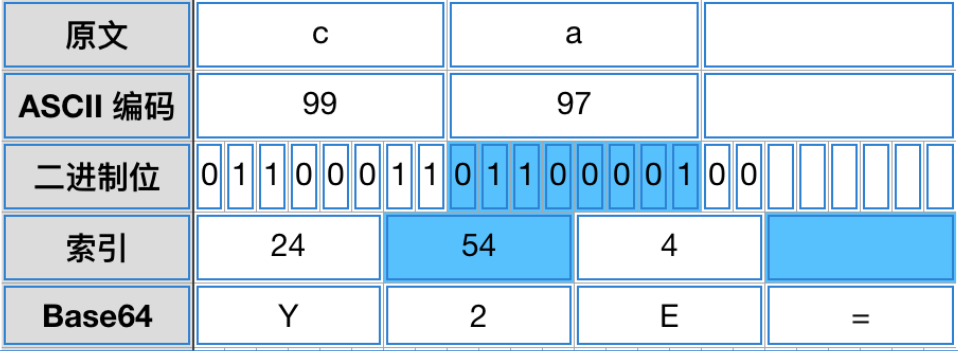
如果最后剩下两个字符,则在二进制编码中中加入2个0位,在base编码中加入=
代码
c语言实现
编码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
// Base64编码表
static const char base64_table[] = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/";
/**
* Base64编码函数
* @param data 要编码的原始数据
* @param input_length 原始数据长度
* @param output_length 编码后数据长度(输出参数)
* @return Base64编码字符串,需要调用者释放内存
*/
char *base64_encode(const unsigned char *data, size_t input_length, size_t *output_length) {
if (data == NULL || input_length == 0) {
return NULL;
}
// 计算输出缓冲区大小(每3字节输入转换为4字节输出)
size_t output_size = 4 * ((input_length + 2) / 3);
char *encoded_data = malloc(output_size + 1); // +1用于字符串结束符
if (encoded_data == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
size_t i, j;
for (i = 0, j = 0; i < input_length;) {
uint32_t octet_a = i < input_length ? data[i++] : 0;
uint32_t octet_b = i < input_length ? data[i++] : 0;
uint32_t octet_c = i < input_length ? data[i++] : 0;
uint32_t triple = (octet_a << 16) | (octet_b << 8) | octet_c;
encoded_data[j++] = base64_table[(triple >> 18) & 0x3F];
encoded_data[j++] = base64_table[(triple >> 12) & 0x3F];
encoded_data[j++] = base64_table[(triple >> 6) & 0x3F];
encoded_data[j++] = base64_table[triple & 0x3F];
}
// 处理填充
if (input_length % 3 != 0) {
size_t padding_count = 3 - (input_length % 3);
for (size_t k = 0; k < padding_count; k++) {
encoded_data[output_size - 1 - k] = '=';
}
}
encoded_data[output_size] = '\0'; // 添加字符串结束符
if (output_length != NULL) {
*output_length = output_size;
}
return encoded_data;
}
int main() {
const char *test_string = "Hello, World!";
size_t input_len = strlen(test_string);
size_t output_len;
char *encoded = base64_encode((const unsigned char *)test_string, input_len, &output_len);
if (encoded != NULL) {
printf("Original: %s\n", test_string);
printf("Base64: %s\n", encoded);
printf("Output length: %zu\n", output_len);
free(encoded);
} else {
printf("Encoding failed!\n");
}
return 0;
}
解码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdint.h>
// Base64解码表
static const unsigned char base64_decode_table[256] = {
['A'] = 0, ['B'] = 1, ['C'] = 2, ['D'] = 3, ['E'] = 4, ['F'] = 5, ['G'] = 6, ['H'] = 7,
['I'] = 8, ['J'] = 9, ['K'] = 10, ['L'] = 11, ['M'] = 12, ['N'] = 13, ['O'] = 14, ['P'] = 15,
['Q'] = 16, ['R'] = 17, ['S'] = 18, ['T'] = 19, ['U'] = 20, ['V'] = 21, ['W'] = 22, ['X'] = 23,
['Y'] = 24, ['Z'] = 25, ['a'] = 26, ['b'] = 27, ['c'] = 28, ['d'] = 29, ['e'] = 30, ['f'] = 31,
['g'] = 32, ['h'] = 33, ['i'] = 34, ['j'] = 35, ['k'] = 36, ['l'] = 37, ['m'] = 38, ['n'] = 39,
['o'] = 40, ['p'] = 41, ['q'] = 42, ['r'] = 43, ['s'] = 44, ['t'] = 45, ['u'] = 46, ['v'] = 47,
['w'] = 48, ['x'] = 49, ['y'] = 50, ['z'] = 51, ['0'] = 52, ['1'] = 53, ['2'] = 54, ['3'] = 55,
['4'] = 56, ['5'] = 57, ['6'] = 58, ['7'] = 59, ['8'] = 60, ['9'] = 61, ['+'] = 62, ['/'] = 63,
['='] = 0 // 填充字符视为0
};
// Base64解码函数
unsigned char *base64_decode(const char *data) {
if (!data || !*data) return NULL;
size_t len = strlen(data);
size_t padding = (data[len-1] == '=') + (data[len-2] == '=');
size_t out_size = (len * 3) / 4 - padding;
unsigned char *decoded = malloc(out_size + 1);
if (!decoded) return NULL;
uint32_t buf = 0;
int bits = 0, count = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < len; i++) {
unsigned char c = data[i];
if (c == '=') break; // 遇到填充字符停止
uint8_t value = base64_decode_table[c];
if (value == 0 && c != 'A') continue; // 跳过无效字符('A'的值为0)
buf = (buf << 6) | value;
bits += 6;
if (bits >= 8) {
bits -= 8;
decoded[count++] = (buf >> bits) & 0xFF;
}
}
decoded[count] = '\0';
return decoded;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
if (argc != 2) {
printf("Usage: %s <base64_string>\n", argv[0]);
return 1;
}
unsigned char *decoded = base64_decode(argv[1]);
if (decoded) {
printf("%s\n", decoded);
free(decoded);
return 0;
} else {
printf("Error: Invalid Base64 input\n");
return 1;
}
}
python实现
编码:
import base64
text = input("请输入文本")
encoded = base64.b64encode(text.encode('utf-8')).decode('utf-8')
print(encoded)
解码:
import base64
encoded_text = input("请输入要解码的 Base64 字符串: ")
decoded = base64.b64decode(encoded_text).decode()
print(decoded)
实战
下载附件后先使用die进行查壳
使用ida打开后,
使用shift+F12,查看字符串后可以看到base64索引表,在部分题目中会对此字符串进行变化

进入encode_one,可以看到base64加密过程
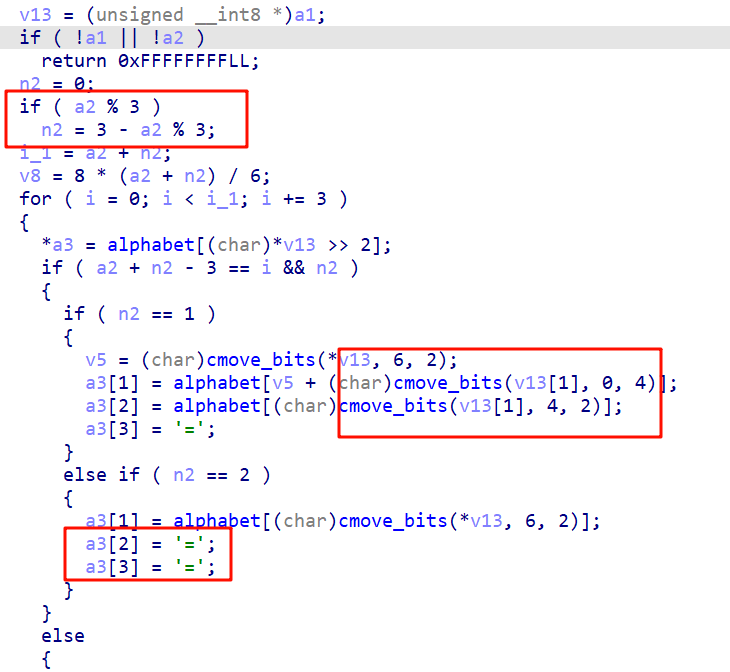
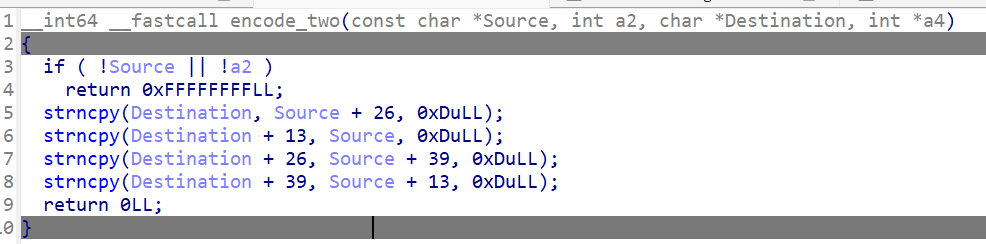
encode_two相当于将加密后的字符串以13为单位重新排列
encode_three使用到了凯撒变换
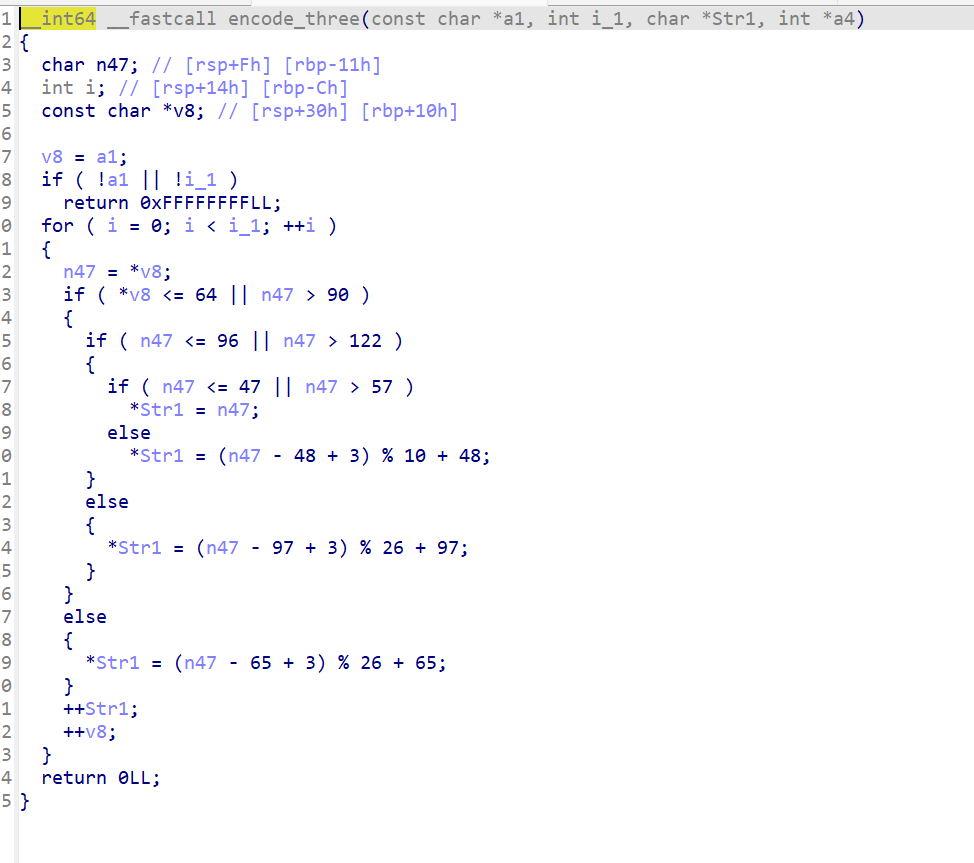
加密逻辑就是
首先将输入的字符串进行base64编码,再进行移位,最后再使用凯撒
本博客只介绍base64编码,具体解题过程我放在下面了
参考文章
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/111700349
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_73644864/article/details/128792247




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号