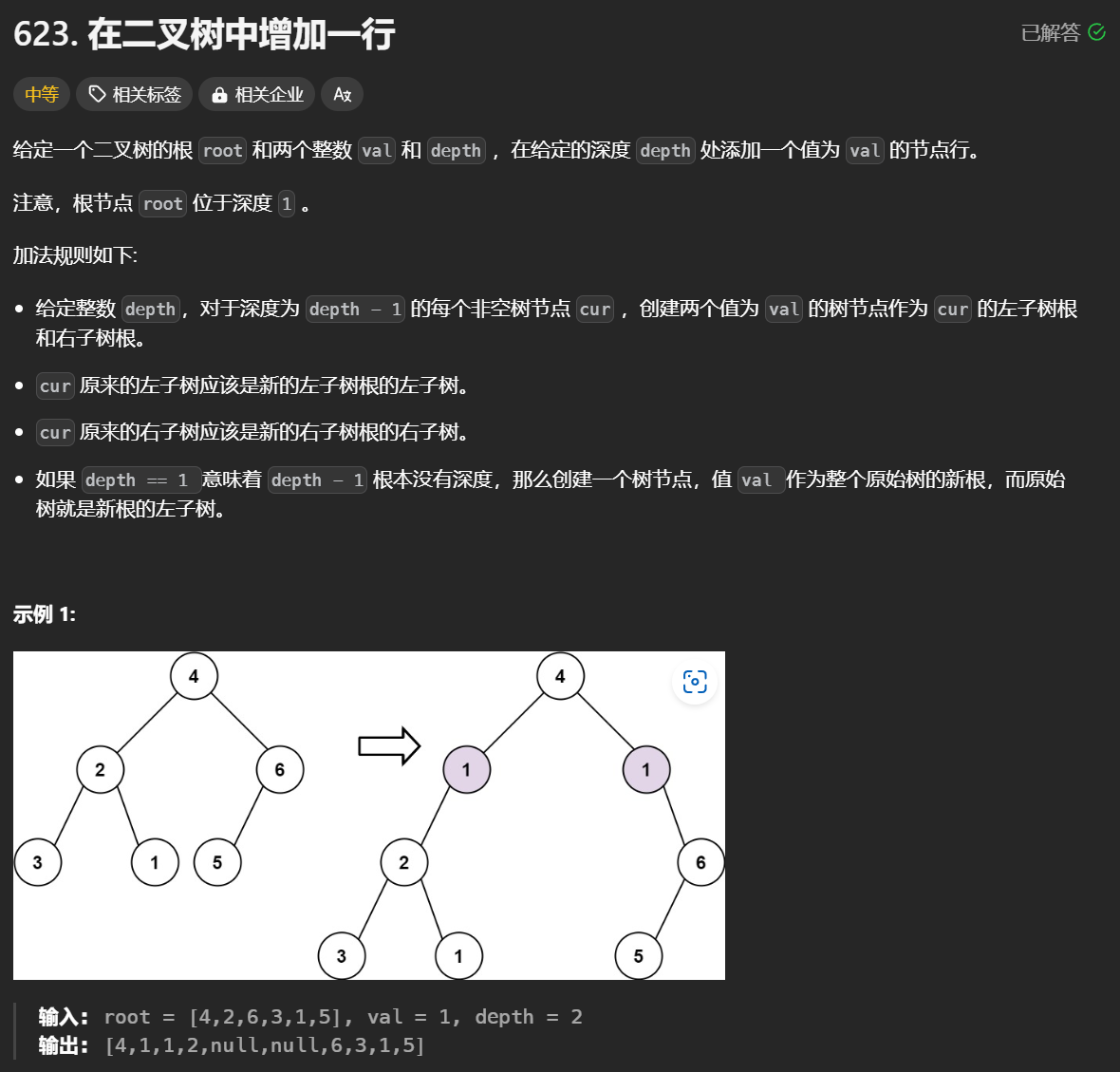
623 在二叉树中增加一行
深度遍历,就是遍历:
1.先要确定有几种情况,像这道题,深度为1,2就是最基本的情况,分为两种处理;
2.根据不同情况,进行不同处理,不需要考虑后面递归的传递。
3.确认传递的方式,如果函数返回的是指针,就需要left,right接住。
完整代码:
点击查看代码
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* addOneRow(TreeNode* root, int val, int depth) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return nullptr;
}
if (depth == 1) {
return new TreeNode(val, root, nullptr);
}
if (depth == 2) {
root->left = new TreeNode(val, root->left, nullptr);
root->right = new TreeNode(val, nullptr, root->right);
} else {
root->left = addOneRow(root->left, val, depth - 1);
root->right = addOneRow(root->right, val, depth - 1);
}
return root;
}
};
点击查看代码
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* addOneRow(TreeNode* root, int val, int depth) {
if (depth == 1) {
return new TreeNode(val, root, nullptr);
}
vector<TreeNode *> curLevel(1, root);
for (int i = 1; i < depth - 1; i++) {
vector<TreeNode *> tmpt;
for (auto &node : curLevel) {
if (node->left != nullptr) {
tmpt.emplace_back(node->left);
}
if (node->right != nullptr) {
tmpt.emplace_back(node->right);
}
}
curLevel = move(tmpt);
}
for (auto &node : curLevel) {
node->left = new TreeNode(val, node->left, nullptr);
node->right = new TreeNode(val, nullptr, node->right);
}
return root;
}
};



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号