搜索二叉树删除节点和修减二叉树
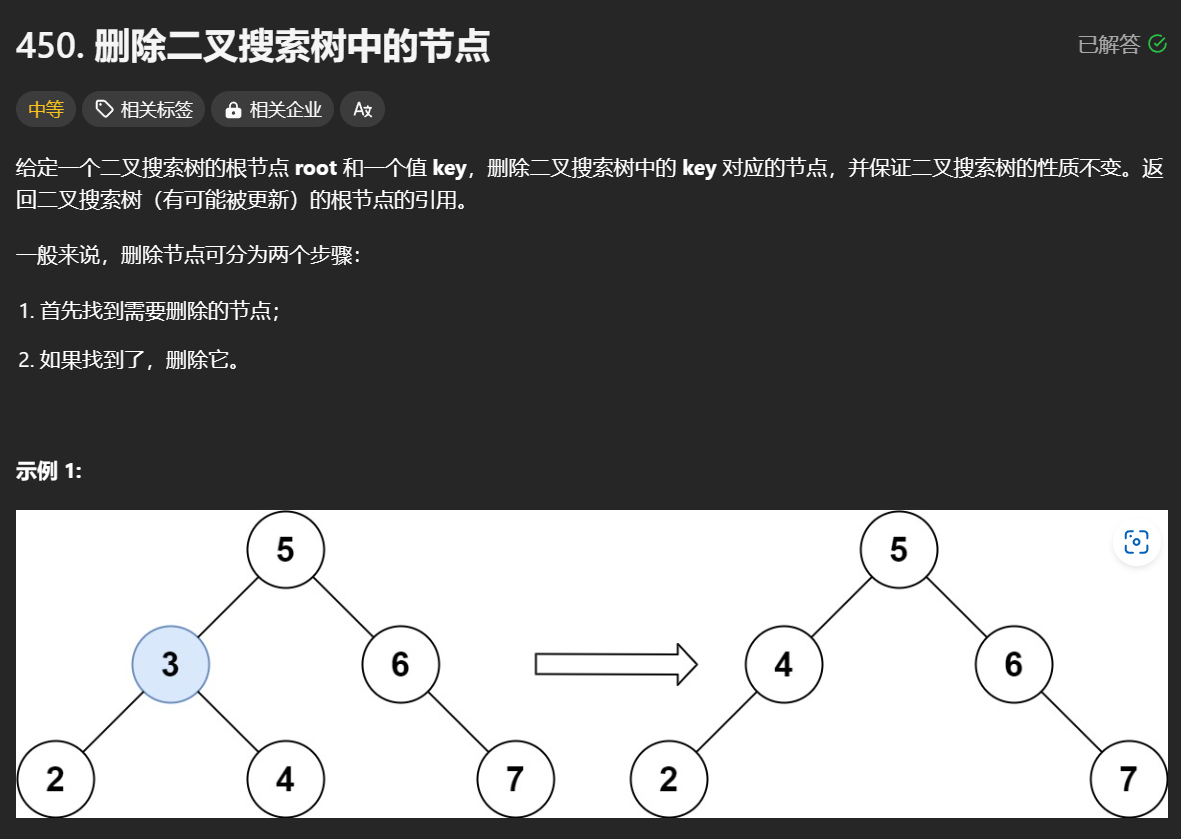
删除目标节点首先要找到该节点,因此用到搜索二叉树的性质去寻找,该节点比target大就看左子树部分,小就看右子树部分。
根据主函数可知,最后是返回一个节点,也可以看成是返回一个子树。因此查找的时候就要承接这子树,这子树就是删除好后的结果。
点击查看代码
if(!root){return NULL;}
if(root->val>key){root->left=deleteNode(root->left,key);}
else if(root->val<key){root->right=deleteNode(root->right,key);}
点击查看代码
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode*findmin(TreeNode*root){
while(root->left){
root=root->left;
}
return root;
}
TreeNode* deleteNode(TreeNode* root, int key) {
if(!root){return NULL;}
if(root->val>key){root->left=deleteNode(root->left,key);}
else if(root->val<key){root->right=deleteNode(root->right,key);}
else{
if(!root->left&&!root->right){return NULL;}
else if(!root->left&&root->right){
return root->right;
}
else if(root->left&&!root->right){
return root->left;
}
else{
TreeNode*place=findmin(root->right);
place->left=root->left;
return root->right;
}
}
return root;
}
};

修建二叉树看起来了要比删除树要复杂,因为他有多个节点要删除嘛。
但是实际代码要简单很多,这道题相当与重新构造一棵二叉搜索树,把符合条件的点都添加进来。
根据二叉搜索树的特性,把在范围外的子树都可以排除不仅仅是节点。
点击查看代码
if(root->val<low){return trimBST(root->right,low,high);}
if(root->val>high){return trimBST(root->left,low,high);}
完整代码
点击查看代码
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* trimBST(TreeNode* root, int low, int high) {
if(!root){return NULL;}
if(root->val<low){return trimBST(root->right,low,high);}
if(root->val>high){return trimBST(root->left,low,high);}
root->left=trimBST(root->left,low,high);
root->right=trimBST(root->right,low,high);
return root;
}
};



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号