QNX下进程间通信
https://blog.csdn.net/dh314552189/article/details/87879016

server.cpp #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <errno.h> #include <sys/neutrino.h> #include <sys/dispatch.h> #include <string.h> #define ATTACH_POINT "percent" #define VERSION "V1.2.0" int rcvid = 0; struct version_message { int type; char data[100]; }; int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { name_attach_t *attach; struct version_message rmsg; struct version_message smsg; int rcvid; /* Create a local name (/dev/name/local/...) */ if ((attach = name_attach(NULL, ATTACH_POINT, 0)) == NULL) { printf("name_attach error!\n"); return EXIT_FAILURE; } while(1) { rcvid = MsgReceive(attach->chid, &rmsg, sizeof(rmsg), NULL); if(rcvid > 0) { /* name_open() sends a connect message, must EOK this */ if (rmsg.type == _IO_CONNECT ) { printf("connect received!\n"); MsgReply( rcvid, EOK, NULL, 0 ); continue; } /* Some other QNX IO message was received; reject it */ if (rmsg.type > _IO_BASE && rmsg.type <= _IO_MAX ) { printf("wrong msg type received!\n"); MsgError( rcvid, ENOSYS ); continue; } /* reply the bsp version */ if(0x1 == rmsg.type) { printf("version request received!\n"); printf("version request received data = %s \n",rmsg.data); MsgReply( rcvid, EOK, NULL, 0 ); } } else if(0 == rcvid) { printf("pulse msg received!\n"); } } /* Remove the name from the space */ name_detach(attach, 0); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }

client.cpp #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <errno.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <limits.h> #include <sys/mman.h> #include <sys/iofunc.h> #include <sys/dispatch.h> #define ATTACH_POINT "percent" struct version_message { int type; char data[100]; }; int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { struct version_message smsg; struct version_message rmsg; int server_coid; int rcvid; if ((server_coid = name_open(ATTACH_POINT, 0)) == -1) { printf("name_open error!"); return EXIT_FAILURE; } /* We would have pre-defined data to stuff here */ smsg.type = 0x01; strcpy(smsg.data,"ygy"); /* Do whatever work you wanted with server connection */ printf("Client sending %d \n", smsg.type); if (MsgSend(server_coid, &smsg, sizeof(smsg), &rmsg, sizeof(rmsg)) == -1) { printf("MsgSend error!"); name_close(server_coid); return EXIT_FAILURE; } /* Close the connection */ name_close(server_coid); }
cmakelist

# 1. Project Name project(test.IPC) # 2. Project Env (Include/Lib Path, C/CXX/LD FLAGS) include_directories( ) link_directories( ${COMMONAPI_LIBDIR} ) # 3. Project Build #set(TEST_NAME "svp.test.client") set(TEST_NAME "svp.test.server") set(TEST_SRC_FILES # client.cpp server.cpp ) add_executable(${TEST_NAME} ${TEST_SRC_FILES}) target_link_libraries(${TEST_NAME} svp_basic ${upgrade_CAPI_GEN_LIB} CommonAPI m ) # 4. Project Install install(TARGETS ${TEST_NAME} RUNTIME DESTINATION ${CMAKE_INSTALL_BINDIR} LIBRARY DESTINATION ${CMAKE_INSTALL_LIBDIR} ARCHIVE DESTINATION ${CMAKE_INSTALL_LIBDIR})
其实是有fifo也是可行的。

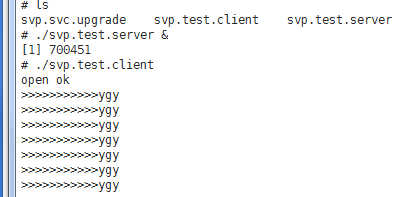
#include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <errno.h> #include <sys/neutrino.h> #include <sys/dispatch.h> #include <string.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { if (access("/aaa", F_OK) == -1) { if (mkfifo("/aaa", S_IRUSR|S_IWUSR) != 0) { printf("mkfifo error!\n"); return 1; } } int fd = open("/aaa",O_WRONLY); if (fd == -1) { printf("open error!\n"); return 1; } while(1){ write(fd, "ygy\n", 4); sleep(2); } return EXIT_SUCCESS; }

#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <errno.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <limits.h> #include <sys/mman.h> #include <sys/iofunc.h> #include <sys/dispatch.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int res = 0; int fd = open("/aaa", O_RDONLY); char buffer[128]; if (fd != -1) { printf("open ok\n"); while ((res = read(fd, buffer, 128)) > 0) { printf(">>>>>>>>>>>%s", buffer); } } }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号