react4-TS、TS&React
TS
下载
-
TS:TypeScript:如何设置 TypeScript
npm install -g typescript -
Node.Js
-
ts-node:
npm install -g ts-node typescript-
找到npm的全局安装目录:
npm config get prefix -
将npm的安装路径添加到path的系统变量中
-
重启CMD输入
ts-node --version、tsc --version
-
-
vscode插件:
-
JavaScript and TypeScript Nightly
-
Code Runner(可直接运行ts代码)
-
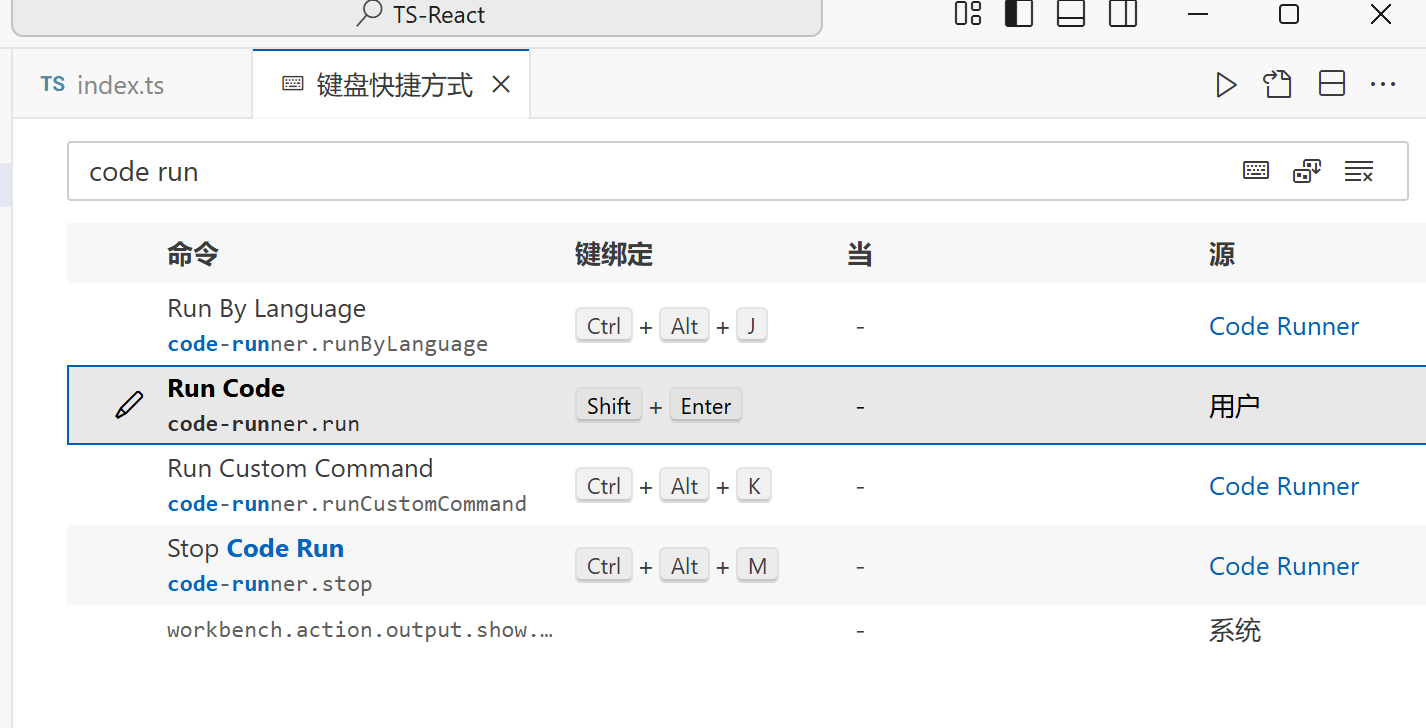
修改code runner的快捷键为:shift + enter
编译
-
在终端中输入:
tsc -init会生成tsconfig.json文件,接着可成功运行TS代码 -
输入:
tsc .\xx.ts可生成对应的JS代码,但是这样生成JS代码是老版本(使用var、无箭头函数) -
在tsconfig.json中配置:
target: xxx版本JS -
在终端 中输入:
tsc即可得到新版本的JS代码(编译所有) -
通过include/exclude配置需要/不需要编译的文件
TypeScript: TSConfig Reference - Docs on every TSConfig option
-
输入:
npm init -y可生成package.json文件
运行
type Person = {
name: string
}
const person: Person = {
name: 'yuanyu'
}
console.log(person.name)

语法
注解Annotations
-
允许指定可以分配给定变量的值类型
-
类型确定了就不能再更改
function multiple (x: number, y:number) :number{
return x*y
}
类型推断:没有明确指定类型时,编译器会自动推断
数据类型
-
any类型:可表示任意类型、任意值,会禁用所有该变量及其属性的类型检查
-
void类型:表示任意值缺失的类型,常用于方法不返回值
-
never类型:表示函数无返回值或变量永远没有值 ,可在编译时捕获错误
场景:
-
总是抛出错误的方法
function throwError(msg: string) :never { throw new Error(msg) } -
无限循环的方法
function infiteLoop() :never{ while(true){} } -
永远没有值的变量
let x:never function neverReturn() :never{ while(true){} } x=neverReturn()
-
-
Array数组类型:存储相同数据类型的多值对象
const num: number[] = [1,2,3] const num: number[][] = [[1,2,3]] const num: number[][][] = [[[1,2,3]]] const num: Array<number> = [1,2,3] -
Object对象类型:属性集合(键值对形式)
const person: { name: string, age: number, address: string } = { name: 'yuanyu', age: 24, address: '江西省' }
交集类型&
集合了多个类型
type Person = {
name: string,
age: number
}
type Employee = {
id: number,
title: string
}
type PersonAndEmployee = Person & Employee
const alice: PersonAndEmployee = {
name: 'sha',
age: 12,
id: 1,
title: 'sdk'
}
联合类型|
可以包含一个或多个可能的类型
let myVar: number | string
const items: (number | string)[] = [1,2,'aaa']
type Person = {
name: string,
age: number
}
type Employee = {
id: number,
title: string
}
type PersonAndEmployee = Person | Employee
const alice: PersonAndEmployee = {
name: 'sha',
age: 12,
id: 1
}
console.log(alice)
字面量类型Literal
字面量类型的变量只能有一个特定值
let color: 'red' | 'blue' | 'green'
color = 'red'
color = 'yellow' //不能将类型“"yellow"”分配给类型“"red" | "blue" | "green"”
元组类型tuple
元素可以有不同数据类型的数组,有序且序列长度已知
let myTuple: [string, number] = ['hello', 42]
let [first, second] = myTuple
console.log(first) //hello
console.log(second) //42
枚举类型Enums
定义一组常量类型的方法
enum Weather {
sunny = 'Sunny',
windy = 'Windy',
rainy = 'Rainy'
}
let today : Weather
today = Weather.rainy
console.log(today) //Rainy
类型别名Alias
创建类型新名称
type User = {
name: string,
age: number,
location: string
}
const printUserInfo = (user:User) => {
return `Name: ${user.name} Age: ${user.age} Location: ${user.location}`
}
const res = printUserInfo({
name: 'yuanyu',
age: 24,
location: 'China'
})
console.log(res)
可选属性
type User = {
name: string,
age: number,
location?: string
}
修饰符
-
public:可在任何地方访问,无论内部还是外部
-
private:只能从类的内部访问
-
protected:可从内部和扩展子类访问
class Animal{
public name: string
private age: number
protected species: string
constructor(name:string, age: number, species: string){
this.name = name
this.age = age
this.species = species
}
public getName() :string{
return this.name
}
private getAge() :number{
return this.age
}
protected getSpecies() : string{
return this.species
}
// 类内部可访问所有修饰符的属性(补充)
public getAnimalDetails(): string {
return `类内部访问: Name=${this.name}, Age=${this.age}, Species=${this.species}`;
}
}
const dog = new Animal('GXH', 30, '恋爱脑')
console.log(dog) // Animal { name: 'GXH', age: 30, species: '恋爱脑' }
// console.log(dog.age) // 属性“age”为私有属性,只能在类“Animal”中访问
class Cat extends Animal{
constructor(name:string, age: number, species: string){
super(name, age, species)
}
// 子类中访问父类属性
public getCatInfo(): string {
let info = `子类访问: Name=${this.name}`
info += `, Species=${this.species}`
// info += `, Age=${this.age}` // 属性“age”为私有属性,只能在类“Animal”中访问
// info += `, Age=${this.getAge()}` // 属性“getAge”为私有属性,只能在类“Animal”中访问
return info;
}
}
getter/setter
用于访问和修改类属性
class MyClass {
private _myProperty: number = 0
get myProperty() : number{
return this._myProperty
}
set myProperty(value: number){ // 无返回值
if (value > 0) this._myProperty = value
}
}
const myInstance = new MyClass()
console.log(myInstance.myProperty) // 0
myInstance.myProperty = 10
console.log(myInstance.myProperty) // 10
接口interface
一种定义对象/函数/类形状的方式,指定对象必须有的属性及其类型
interface Person {
firstName: string
lastName: string
age: number
}
const person: Person = {
firstName: 'abc',
lastName: 'ddd',
age: 20
}
interface MathOperation {
(x: number, y: number): number
}
const add: MathOperation = (a, b) => a + b
const multiply: MathOperation = (a, b) => a * b
interface Vehicle {
start() : void
stop(): void
}
class Car implements Vehicle{
start() {
console.log('start')
}
stop() {
console.log('stop')
}
}
interface和type的区别
-
基本语法:
// interface 语法 interface User { name: string; age: number; } // type 语法 type User = { name: string; age: number; }; -
扩展方式:
- interface:使用extends关键字扩展
- type:使用&符号扩展
interface Person { name: string; } interface Student extends Person { grade: number; } ------------------------ type Person = { name: string; }; type Student = Person & { grade: number; }; -
interface具有声明合并,如果同名会自动合并,type则会报错
-
type可以表示联合类型、交叉类型、基本类型等,而interface主要用于描述对象/函数/类的形状
-
interface可用原型为已有类型添加新属性‘
interface String { padLeft(n: number): string; } String.prototype.padLeft = function(n: number) { // 实现... };
泛型
能够定义函数、类、接口,以便可以与不同类型的数据一起工作
可以创建针对不同类型数据的通用函数、类、接口
const printString = (x: string) => console.log(x)
const printNumber = (x: number) => console.log(x)
const printBoolean = (x: boolean) => console.log(x)
printString('hello')
printNumber(1)
printBoolean(true)
优化①:使用any类型
const myPrint = (x:any) => console.log(x)
myPrint('hello')
myPrint(1)
myPrint(true)
优化②:使用泛型
function myPrint<T>(x: T) {
console.log(x)
}
myPrint('hello')
myPrint(1)
myPrint(true)
function uniqueDataFunc<Type>(
item: Type,
defaultValue: Type
): [Type, Type] {
return [item, defaultValue]
}
const res1 = uniqueDataFunc<number>(10, 20)
const res2 = uniqueDataFunc<string>('a', 'b')
console.log(res1) // [ 10, 20 ]
console.log(res2) // [ 'a', 'b' ]
function uniqueDataFunc<T>(
item: T,
defaultValue: T
): [T, T] {
return [item, defaultValue]
}
interface Dog {
name: string
breed: string
}
const dog = uniqueDataFunc<Dog>(
{name: '1', breed:'abc'},
{name: '2', breed:'abc'}
)
console.log(dog)
// 随机获取键值对
function getRandomValuePair<T>(obj: { [key: string]: T }): {
key: string
value: T
} {
const keys = Object.keys(obj)
const randomKey = keys[Math.floor(Math.random() * keys.length)]
return {
key: randomKey,
value: obj[randomKey]
}
}
const stringObject = { a: 'apple', b: 'banana', c: 'cherry' }
const randomStringPair = getRandomValuePair(stringObject)
console.log(randomStringPair)
const numberObject = { one: 1, two: 2, three: 3 }
const randomNumberPair = getRandomValuePair(numberObject)
console.log(randomNumberPair)
// 过滤数组
function filterArray<T>(array: T[], condition: (item: T) => boolean): T[] {
return array.filter((item) => condition(item))
}
const numberArray = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
const evenNumbers = filterArray<number>(numberArray, (num) => num % 2 === 0)
console.log(evenNumbers) // [ 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 ]
const stringArray = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry', 'date']
const shortWords = filterArray<string>(stringArray, (word) => word.length < 6)
console.log(shortWords) // [ 'apple', 'date' ]
interface Fruit {
name: string
color: string
}
const fruitArray: Fruit[] = [
{ name: 'apple', color: 'red' },
{ name: 'banana', color: 'yellow' },
{ name: 'cherry', color: 'red' }
]
const redFruit = filterArray<Fruit>(fruitArray, (fruit) => fruit.color === 'red')
console.log(redFruit) // [ { name: 'apple', color: 'red' }, { name: 'cherry', color: 'red' } ]
对象的泛型:obj: { [key: string]: T }
函数表达式的泛型:condition: (item: T) => boolean
// 交换值
function reversePair<T, U>(value1: T, value2: U): [U, T] {
return [value2, value1]
}
const reverse = reversePair(1, 2)
console.log(reverse) // [ 2, 1 ]
类型缩放
类型缩放是在一个条件代码块中精炼变量类型的过程
类型守卫
类型守卫是一种机制,帮助TS更精确理解和缩小类型
-
typeof操作符type MyType = string | number function exampleFunc(value: MyType): void { if (typeof value === 'string') console.log(value.toUpperCase()) else console.log(value.toFixed(2)) } exampleFunc('hello') // HELLO exampleFunc(42) // 42.00 -
instanceof操作符class Dog { bark(): void { console.log("Woof!") } } class Cat { meow(): void { console.log("Meow!") } } function animalSound(animal: Dog | Cat): void{ if (animal instanceof Dog) animal.bark() else animal.meow() } const myDog = new Dog() const myCat = new Cat() animalSound(myDog) // Woof! animalSound(myCat) // Meow! -
交集类型缩小类型:
交集类型:允许将多个类型组合成一个单一类型,有每个单独类的所有属性
type Employee = { id: number name: string } type Manager = { department: string role: string } type ManagerWithEmployeeInfo = Employee & Manager const manager: ManagerWithEmployeeInfo = { id: 123, name: "John Doe", department: "Engineering", role: "Team Lead" } console.log(manager.id) // 123 console.log(manager.name) // John Doe console.log(manager.department) // Engineering console.log(manager.role) // Team Lead
axios
import axios from 'axios'
import type { AxiosResponse } from 'axios'
interface Todo {
userId: number
id: number
title: string
completed: boolean
}
const fetchData = async () => {
try {
const res: AxiosResponse<Todo> = await axios.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1')
console.log(res.data)
} catch (error: any) {
if (axios.isAxiosError(error)) console.error(error.message)
if (error.response) {
console.log(error.response.status)
console.log(error.response.data)
} else {
console.log(error.message)
}
}
}
fetchData() // { userId: 1, id: 1, title: 'delectus aut autem', completed: false }
// package.json
{
"dependencies": {
"axios": "^1.11.0"
}
}
// tsconfig.json
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "ES5",
"lib": [
"ES2015",
"DOM"
]
}
}
Express
import express = require('express')
import { Request, Response } from 'express'
const app = express()
const port = 3000
app.get('/', (req: Request, res: Response) => {
res.send('Hello TS with Express')
})
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log('node server is running');
})
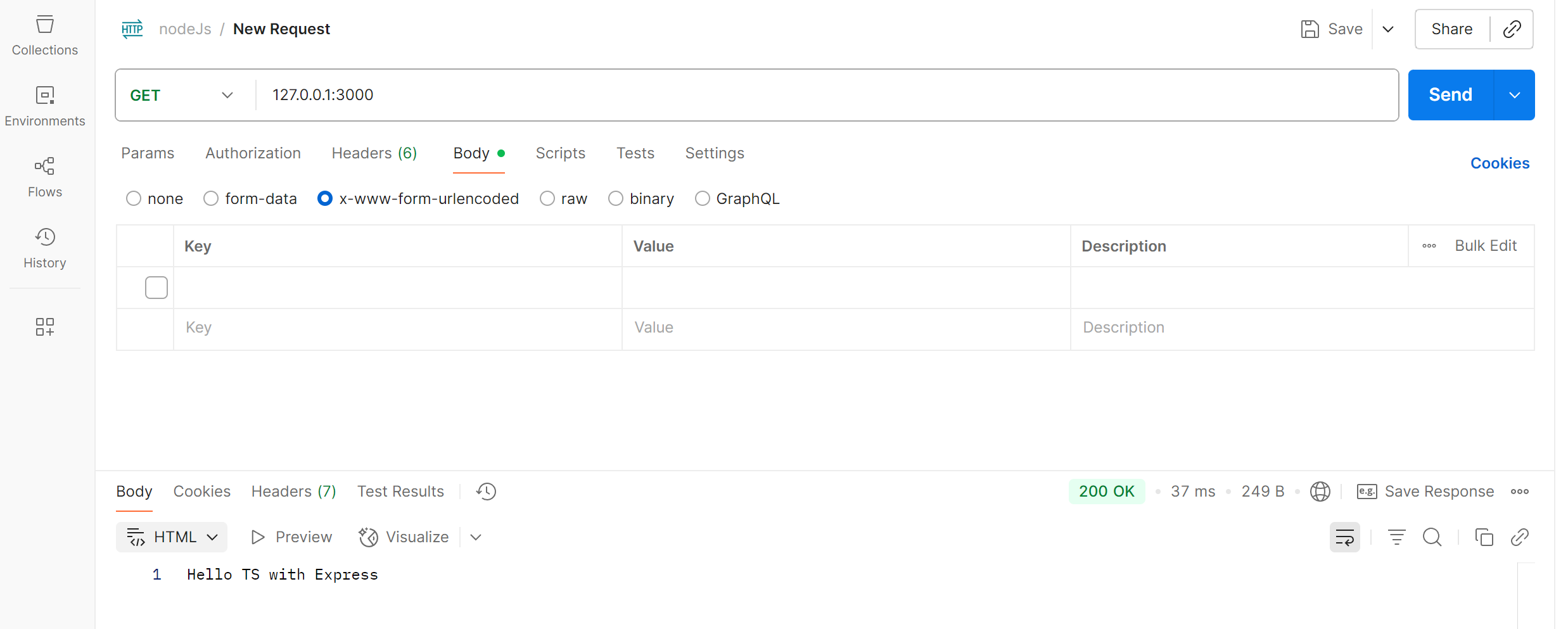
TS & React
创建项目:npm i vite@latest
选择react、Typescript
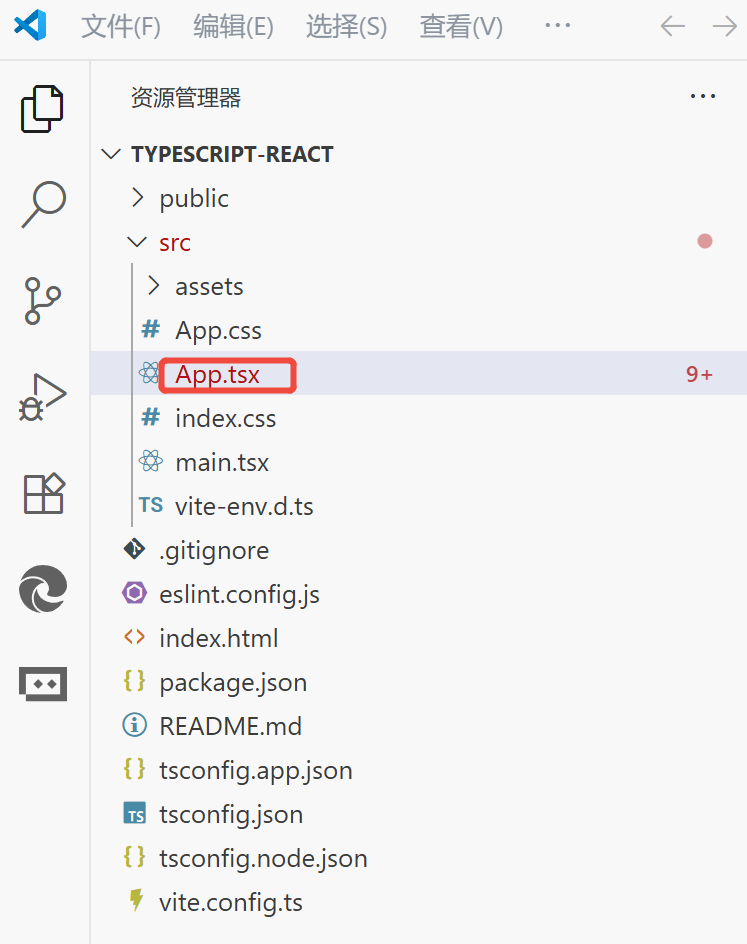
扩展是tsx后缀,创建的文件需要tsx后缀
传递参数
// type UserShape = {
// name: string
// age: number
// isStudent: boolean
// }
interface UserShape {
name: string
age: number
isStudent: boolean
}
// const User = ({name, age, isStudent}:UserShape) => {
// FC表示函数式组件(Functional Component)的类型
const User: FC<UserShape> = ({name, age, isStudent}) => {
return (
<div>
<h2>name: {name} </h2>
<h2>age: {age} </h2>
<h2>isStudent: {isStudent ? 'Yes' : 'False'} </h2>
</div>
)
}
export default User
import User from './Components/User'
const App = () => {
return (
<div>
<User name='yuanyu' age={24} isStudent={true} />
</div>
)
}
export default App

带children
import User from './Components/User'
const App = () => {
return (
<div>
<User>
<h2>hello</h2>
</User>
</div>
)
}
export default App
import type { ReactNode } from "react"
interface UserShape {
children: ReactNode
}
const User = ({children}: UserShape) => {
return (
<div>
{children}
</div>
)
}
export default User
带函数
import Button from "./Components/Button"
const App = () => {
const handleClick = () => {
console.log('click button')
}
return (
<div>
<Button label='This is a text paragraph' handleClick={handleClick} disable={false} />
</div>
)
}
export default App
import React, { type FC } from 'react'
type ButtonInfo = {
label: string
handleClick: () => void
disable: boolean
}
const Button: FC<ButtonInfo> = ({label, handleClick, disable}) => {
return (
<button onClick={handleClick} disabled={disable}>
<span>{label}</span>
</button>
)
}
export default Button
useState
import { useState } from 'react'
const Counter = () => {
const [count, setCount] = useState<number>(0)
return (
<div>
<h1>{count}</h1>
<button onClick={() => setCount(count+1)}>+</button>
<button onClick={() => setCount(count-1)}>-</button>
</div>
)
}
export default Counter
import { useRef, useState, type FormEvent } from 'react'
interface FormData {
name: string
email: string
password: string
}
const Form = () => {
const [submittedData, setSubmittedData] = useState<FormData>({
name: '',
email: '',
password: ''
})
const name = useRef<HTMLInputElement>(null)
const email = useRef<HTMLInputElement>(null)
const password = useRef<HTMLInputElement>(null)
const handleSubmit = (e: FormEvent<HTMLFormElement>) => {
e.preventDefault()
const nameValue = name.current!.value
const emailValue = email.current!.value
const passwordValue = password.current!.value
setSubmittedData({
name: nameValue,
email: emailValue,
password: passwordValue
})
}
return (
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<input type="text" placeholder='enter your name' ref={name}/>
<input type="email" placeholder='enter your email' ref={email}/>
<input type="password" placeholder='enter your password' ref={password}/>
<button type='submit'>Submit</button>
<section>
<h2>Name:{submittedData.name}</h2>
<h2>Email:{submittedData.email}</h2>
<h2>Password:{submittedData.password}</h2>
</section>
</form>
)
}
export default Form
事件:
- KeyboardEvent
- FocusEvent
- DragEvent
- ClipboardEvent
- TouchEvent
- WheelEvent:处理鼠标滚轮操作
- AnimationEvent
- TransitionEvent
- SyntheticEvent:所有 React 合成事件的基类,其他事件类型都继承自它
元素
- 表单相关元素
<HTMLTextAreaElement>:文本域元素(<textarea>)<HTMLSelectElement>:下拉选择框元素(<select>)<HTMLFormElement>:表单元素(<form>)<HTMLLabelElement>:标签元素(<label>)<HTMLFieldSetElement>:字段集元素(<fieldset>)
- 媒体相关元素
<HTMLImageElement>:图片元素(<img>)<HTMLVideoElement>:视频元素(<video>)<HTMLAudioElement>:音频元素(<audio>)<HTMLMediaElement>:媒体元素的基类(包含视频和音频的共同属性)
- 容器与文本元素
<HTMLDivElement>:div 容器元素<HTMLSpanElement>:span 文本容器元素<HTMLParagraphElement>:段落元素(<p>)<HTMLHeadingElement>:标题元素(<h1>到<h6>的统称)<HTMLUListElement>:无序列表(<ul>)<HTMLOListElement>:有序列表(<ol>)<HTMLLIElement>:列表项(<li>)
- 链接与框架元素
<HTMLAnchorElement>:链接元素(<a>)<HTMLIFrameElement>:iframe 框架元素
- 其他常用元素
<HTMLBodyElement>:body 元素<HTMLTableElement>:表格元素(<table>)<HTMLInputElement>:输入框元素(包括 text、checkbox、radio 等类型)<HTMLButtonElement>:按钮元素<HTMLCanvasElement>:画布元素(<canvas>)<HTMLProgressElement>:进度条元素(<progress>)<HTMLMeterElement>:度量元素(<meter>)
useContext
// MyContext.tsx
import { createContext, useState, type FC, type ReactNode } from "react"
interface MyContextProps {
count: number
increment: () => void
decrement: () => void
}
export const MyContext = createContext<MyContextProps>({
count: 0,
increment: () => { },
decrement: () => { }
})
interface MyProviderProps {
children: ReactNode
}
export const MyProvider: FC<MyProviderProps> = ({ children }) => {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
const increment = () => setCount(count + 1)
const decrement = () => setCount(count - 1)
return <MyContext.Provider value={{ count, increment, decrement }}>
{children}
</MyContext.Provider>
}
// main.tsx
import { StrictMode } from 'react'
import { createRoot } from 'react-dom/client'
import App from './App.tsx'
import { MyProvider } from './MyContext.tsx'
createRoot(document.getElementById('root')!).render(
<StrictMode>
<MyProvider>
<App />
</MyProvider>
</StrictMode>,
)
使用:
import {useContext} from 'react'
import { MyContext } from '../MyContext'
const Counter = () => {
const {count, increment, decrement} = useContext(MyContext)
return (
<div>
<p>{count}</p>
<button onClick={increment}>+</button>
<button onClick={decrement}>-</button>
</div>
)
}
export default Counter
useReducer
import React, { useReducer } from 'react'
type State = {count: number}
type Action = {type: 'INCREMENT'} | {type: 'DECREMENT'}
const reducer = (state: State, action: Action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'INCREMENT':
return { count: state.count + 1 }
case 'DECREMENT':
return { count: state.count - 1 }
default:
return state
}
}
const Counter = () => {
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(reducer, { count: 0 })
return (
<div>
<p>{state.count}</p>
<button onClick={() => dispatch({type:'INCREMENT'})}>+</button>
<button onClick={() => dispatch({type:'DECREMENT'})}>-</button>
</div>
)
}
export default Counter

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号