Vue3新特性-创建Vue3项目、setup选项、reactive 和 ref函数、computed、watch、生命周期函数、父子通信、模板引用、provide和inject、defineOptions、defineModel、Pinia及新工具
Vue3的新特性
Vue2不会新增功能,只是进行维护
Vue3的优势:
-
更易维护:
- 组合式API
- 更好的TS支持
-
更快的速度:
- 重写diff算法
- 模板编译优化
- 更高效的组件初始化
-
更小的体积:
- 良好的TreeShaking
- 按需引入
-
更优的数据响应式:
- proxy
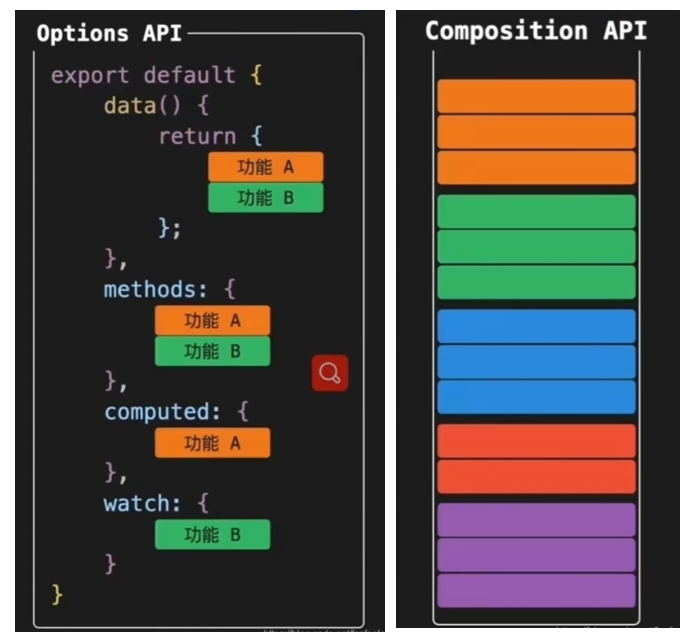
Vue2-选项式API与Vue3组合式API区别:
-
当代码量很大时,Vue2选项式API的代码不易维护;而Vue3的组合式API使得同功能的代码集中在一起(集合式管理同功能的代码)提高了代码的可维护性(Vue3的选项式API代码更易复用,进行封装)
-
App.vue:
- 脚本script和模板template顺序调整(结构和样式放在一起更易维护)
- 模板template不再要求唯一根元素
- 脚本script添加setup标识支持组合式API
例:
<!--Vue2选项式API-->
<script>
export default{
data(){
return{
count: 0
}
},
methods:{
addCount(){
this.count++
}
}
}
</script>
<!--Vue3组合式API-->
<script setup>
import {ref} from 'vue'
const count = ref(0)
const addCount = ()=> count.value++
</script>
创建Vue3项目
create-vue 是Vue官方新的脚手架工具,底层切换到了vite(下一代构建工具) 为开发提供极速响应
需要16.0版本以上的Node.js:node -v 查看node版本
-
创建Vue应用:
npm init vue@latest -
cd Vue3Demo切换到对应目录中 -
npm install安装相关依赖 -
启动项目:
npm run dev
Vite相比于Webpack创建项目的速度非常快

// main.js解读
import './assets/main.css'
// new Vue()创建一个应用实例 => createApp()
// createApp() createStore()
// 将创建实例进行了封装,保证每个实例的独立封闭性
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
// mount设置挂载点 #app(index.html中id为app的盒子)
createApp(App).mount('#app')
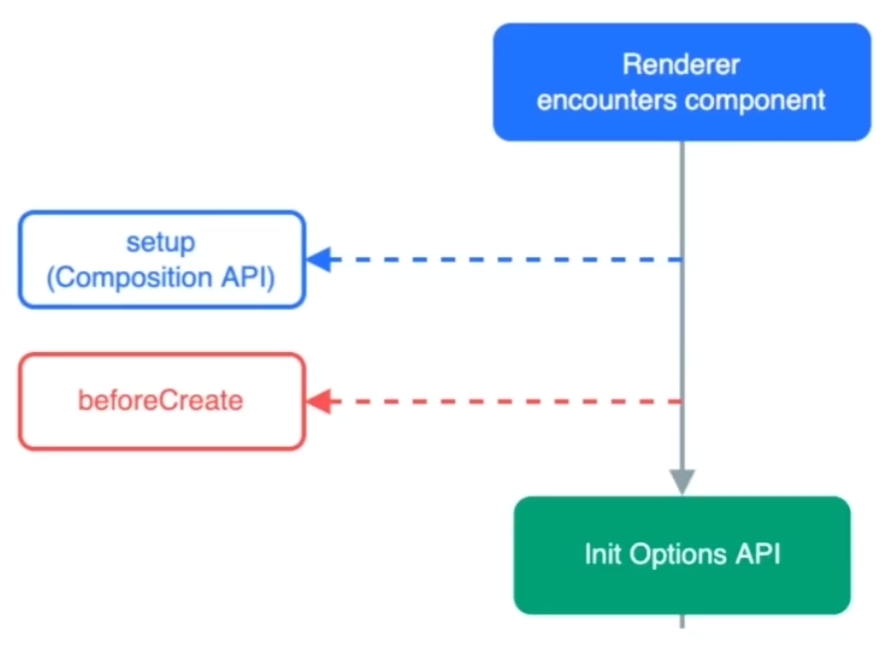
setup选项
export default{
setup(){
},
beforeCreate(){
}
}
注意:
-
setup的生命周期(执行时机)比beforeCreate还要早
-
由于执行时机过早,setup函数获取不到this(this是undefined)
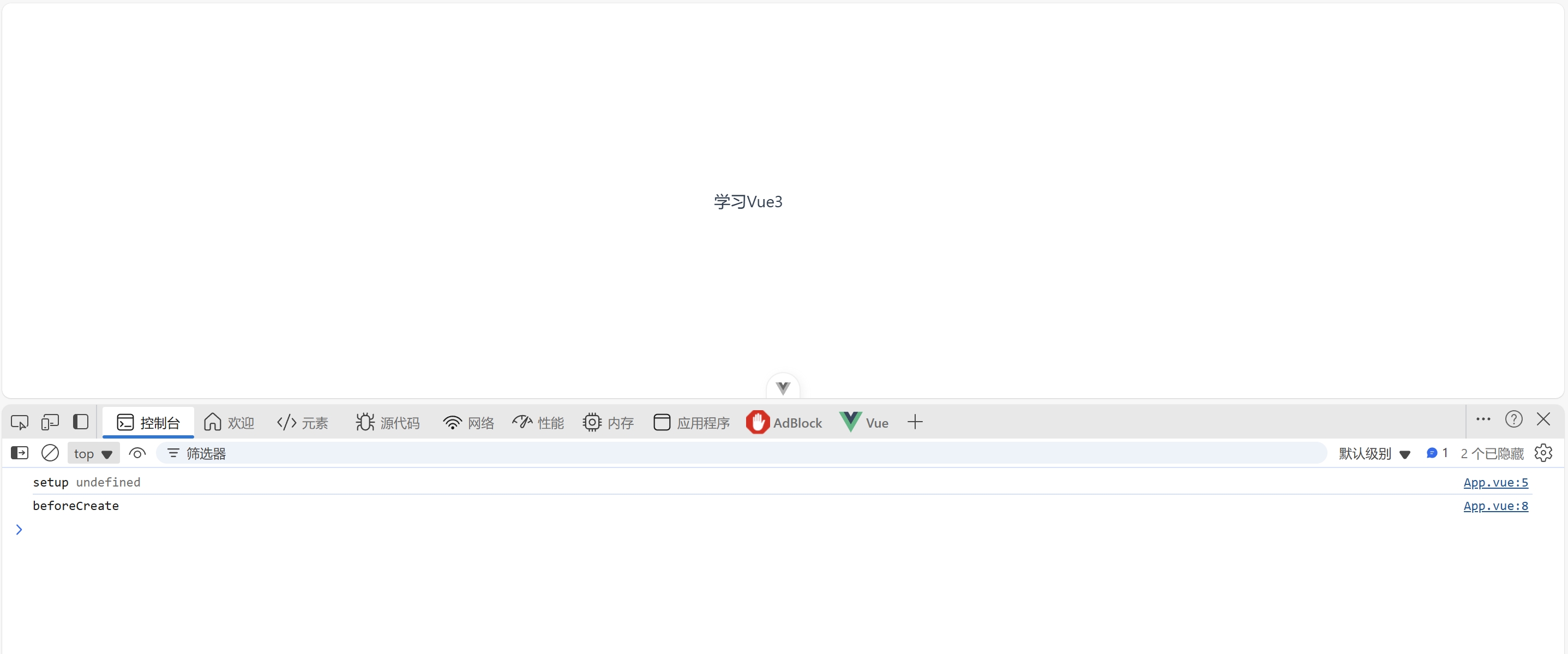
<script> // eslint-disable-next-line vue/no-export-in-script-setup export default { setup() { console.log('setup', this) }, beforeCreate() { console.log('beforeCreate') } } </script> <template> 学习Vue3 </template>![image]()
-
数据和函数需要在setup中return才能在模板中应用
<script> export default { setup() { // 数据 const message = 'this is a message' // 方法 const logMessage = () => { console.log(message) } return { message, logMessage } } } </script> <template> {{message}} <button @click="logMessage">打印</button> </template>![image]()
为了简化上述步骤,可使用<script setup> 语法糖
<script setup>
// 数据
const message = 'this is a message'
// 方法
const logMessage = () => {
console.log(message)
}
</script>
<template>
{{ message }}
<button @click="logMessage">打印</button>
</template>
<script setup>语法糖原理:
底层帮我写好了setup(){ return{}}
reactive 和 ref函数
共同作用:用函数调用的方式生成响应式数据
reactive接受对象类型的数据参数传入,并返回一个响应式的对象
步骤:
-
从vue包中导入reactive函数
-
在<script setup>中执行reactive函数并传入类型为对象的初始值,并使用变量接收返回值
<script setup>
import { reactive } from 'vue'
const state = reactive({复杂类型})
</script>
ref接收简单类型或对象类型的数据传入并返回一个响应式的对象
本质:在原有传入数据的基础上,外层包了一层对象,包成了复杂类型,在底层借助reactive实现响应式
因此,在脚本中访问ref中的值需要通过.value进行访问;在模板中则可以直接访问
例:
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
const state = ref(0)
const setCount = () => {
state.value++
}
</script>
<template>
{{ state }}
<button @click="setCount">+1</button>
</template>
computed
计算属性的基本思想与Vue2中完全一致,只是写法不一样
步骤:
-
导入computed函数
-
执行函数在回调参数中return基于响应式数据做计算的值,用变量接收
<script setup>
import { computed } from 'vue'
const somputedState = computed(() => {
return 基于响应式数据做计算后的值
})
</script>
例:
<script setup>
import { ref, computed } from 'vue'
const list = ref([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8])
const computedList = computed(() =>{
return list.value.filter(item => item > 2)
})
</script>
<template>
{{ computedList }}
</template>
上述所创建的计算属性是只读属性,不可被修改;可以通过配置set和get
const count = ref(1)
const newOne = computed({
get:() = > count.value +1,
set: (val) = > {
count.value =val -1
}
})
newOne.value = 1 //当newOne有值的时候set方法会被触发
console.log(count.value) //0
watch
作用:监听一个或多个数据变化,数据变化时执行回调函数
例:监听单个值的变化(注意: watch(ref对象) watch中监听的是ref对象)
语法:
watch(ref对象,(newValue,oldValue) => {...})
<template>
<div class="main">
<div>{{ count }}</div>
<button @click="changeNumber">changeNumber</button>
<div>{{ name }}</div>
<button @click="changeName">changeName</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, watch } from 'vue'
const count = ref(0)
const name = ref('ddd')
const changeNumber = () => {
count.value++
}
const changeName = () => {
name.value = 'ccc'
}
watch(count, (newVal, oldVal) => {
console.log(`newVal: ${newVal}, ${oldVal}`)
})
</script>
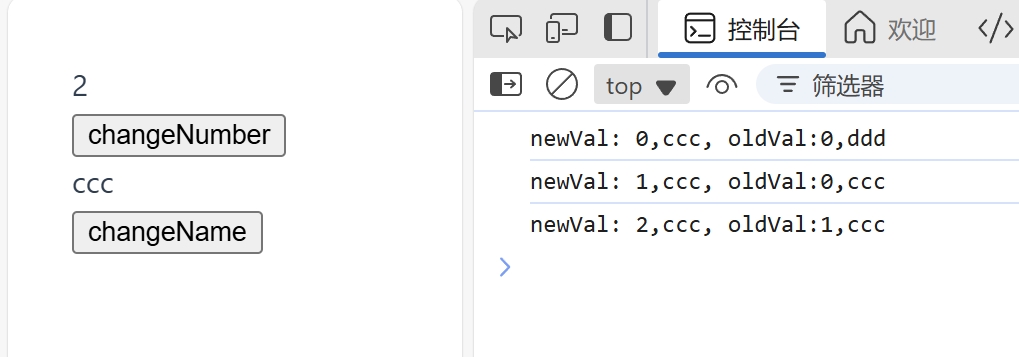
例:监听多个值的变化
语法:
watch([ref对象1,ref对象2],(newArr,oldArr) =>{...})
<template>
<div class="main">
<div>{{ count }}</div>
<button @click="changeNumber">changeNumber</button>
<div>{{ name }}</div>
<button @click="changeName">changeName</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, watch } from 'vue'
const count = ref(0)
const name = ref('ddd')
const changeNumber = () => {
count.value++
}
const changeName = () => {
name.value = 'ccc'
}
watch([count, name], (newVal, oldVal) => {
console.log(`newVal: ${newVal}, oldVal:${oldVal}`)
})
</script>
额外参数:
-
immediate(创建监听器时,立刻触发回调 ,即响应式数据变化后继续执行回调)
watch(count, (newVal, oldVal) => { console.log(`newVal: ${newVal}, oldVal:${oldVal}`) }, { immediate: true })一进入页面就触发
-
deep(深度监听 监听的是对象中的所有属性)
默认watch进行的浅层监听(可以监听简单类型的变化,监听不到复杂类型内部数据的变化)
<template> <div class="main"> <div>{{ userInfo }}</div> <button @click="changeUserInfo">changeUserInfo</button> </div> </template> <script setup> import { ref, watch } from 'vue' const userInfo = ref({ name: 'aaa', age: 18 }) const changeUserInfo = () => { userInfo.value.name = 'yuanyu' userInfo.value.age = 24 } watch(userInfo, (newValue, oldValue) => { console.log(newValue, oldValue) // 不会输出内容 }) </script>因为监听的是ref对象的value属性,如果是复杂数据类型,其value属性是该对象的地址,地址没有变化所以不会输出
<template> <div class="main"> <div>{{ userInfo }}</div> <button @click="changeUserInfo">changeUserInfo</button> </div> </template> <script setup> import { ref, watch } from 'vue' const userInfo = ref({ name: 'aaa', age: 18 }) const changeUserInfo = () => { userInfo.value = { // 修改了对象地址才能监听到 name: 'yuanyu', age: 24 } } watch(userInfo, (newValue) => { console.log(newValue) // 此处不需要输出旧的值,因为指向的是同一个地址,对象值发生变化,旧值是也是新的值 }) </script>输出:
Proxy(Object) {name: 'yuanyu', age: 24} Proxy(Object) {name: 'aaa', age: 18}
只监听对象的某个属性 把第一个参数写成函数写法,返回要监听的具体属性
<template> <div class="main"> <div>{{ userInfo }}</div> <button @click="changeUserInfo">changeUserInfo</button> </div> </template> <script setup> import { ref, watch } from 'vue' const userInfo = ref({ name: 'aaa', age: 18 }) const changeUserInfo = () => { userInfo.value.age++ } watch(()=>userInfo.value.age, (newVal, oldVal) => { console.log(newVal, oldVal); }) </script>
生命周期函数
| 选项式API | 组合式API |
|---|---|
| beforeCreate/created | setup |
| beforeMount | onBeforeMount |
| mounted | onMounted |
| beforeUpdate | onBeforeUpdate |
| updated | onUpdated |
| beforeUnmount | onBeforeUnmount |
| unmounted | onUnmounted |
<script setup>
import { onMounted } from 'vue'
const getList = () => {
console.log('getList')
}
getList() // 一进入页面的请求
// 需要在生命周期中执行的代码
onMounted(() => {
console.log('mounted生命周期函数-逻辑1');
})
onMounted(() => {
// 写成函数调用的方式,可以调用多次不会冲突,而是顺序依次执行互不影响
console.log('mounted生命周期函数-逻辑2');
})
</script>
注意:
-
Vue3中如果需要销毁不是destroy而是unmoutned
-
数据请求函数直接写在
<script setup></script>语法糖中,直接调用 -
其他生命周期函数写成函数调用的方式,可以调用多次不会冲突,而是顺序执行互不影响
父子通信
父传子
基本思想:
-
父组件给子组件绑定属性
-
子组件内部通过props选项接收
Vue3中父组件直接导入使用子组件(局部组件)即可
<template>
<div class="main">
<DemoOne></DemoOne>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import DemoOne from '@/components/DemoOne.vue'
</script>
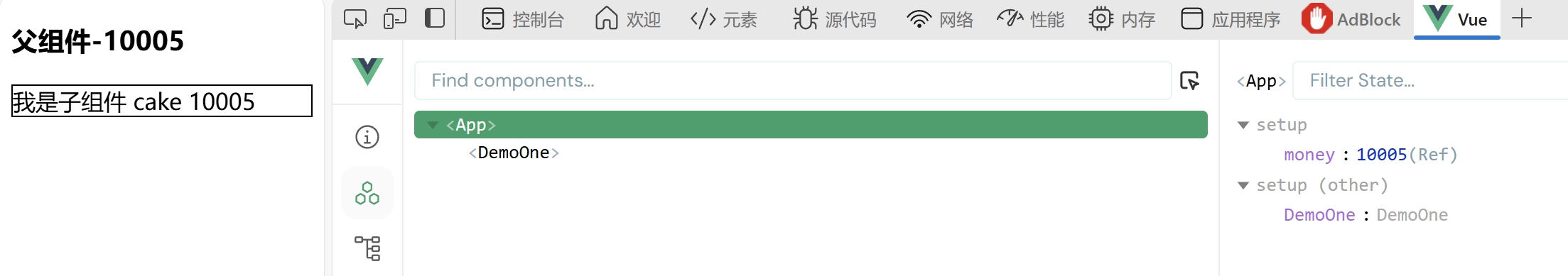
父组件以添加属性的方式给子组件传值,子组件需要借助编译器宏函数接收子组件传递的数据
父组件:
<template>
<div class="main">
<h3>父组件-{{ money }}</h3>
<DemoOne food="cake" :money="money"></DemoOne>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import DemoOne from '@/components/DemoOne.vue'
import { ref } from 'vue'
const money = ref(10000)
</script>
子组件:
<template>
<div class="main">
我是子组件
{{ food }} <!--模板中可以直接使用父组件传递过来的数据 -->
{{ money }}
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
const props = defineProps({
food: {
type: String,
},
money: {
type: Number,
}
})
console.log(props.food);
console.log(props.money);
</script>
<style scoped>
.main{
border: 1px solid black;
}
</style>
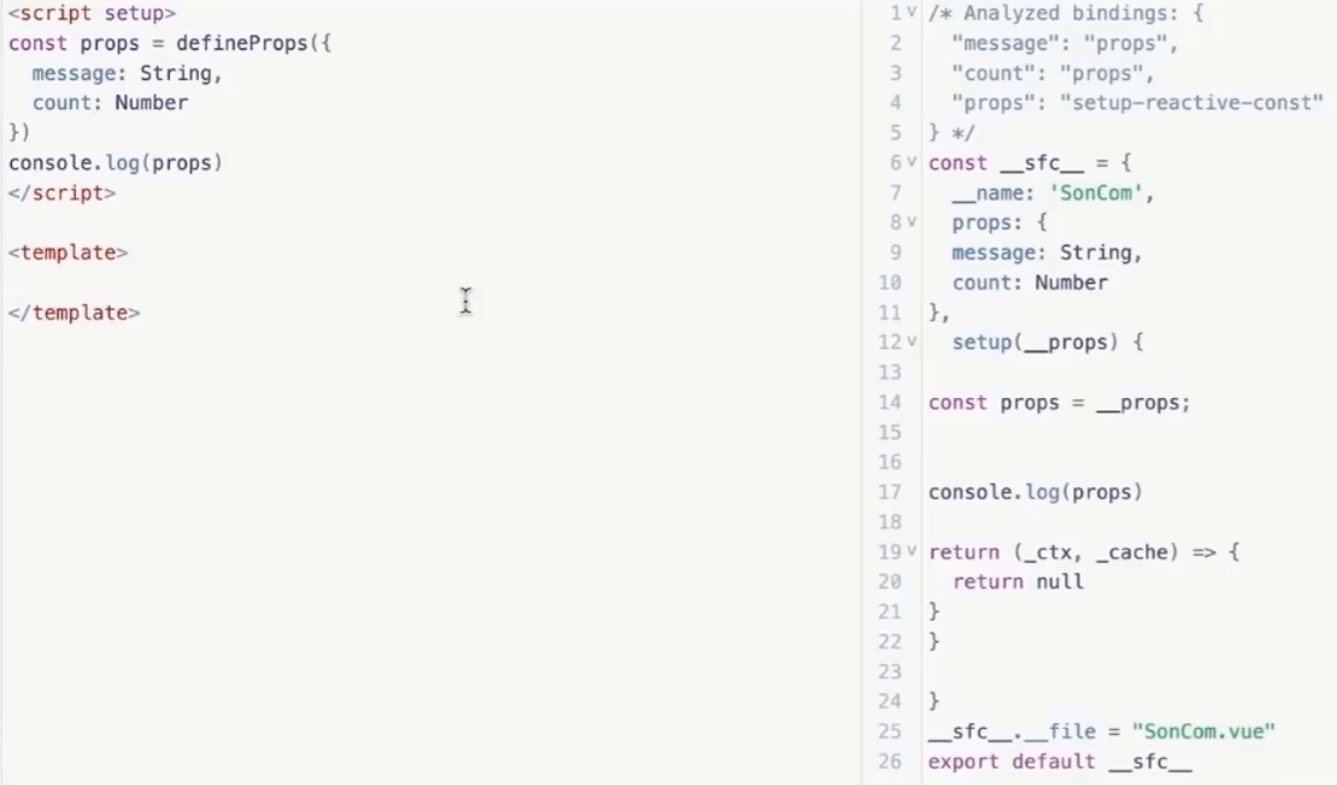
defineProps原理
defineProps是编译阶段的一个标识,实际编译器解析时,遇到后会进行编译转换,将其转换为props:{}形式
子传父
基本思想:
-
父组件中给子组件标签绑定事件
-
子组件内部通过emit方法触发自定义事件 (编译器宏defineEmits获取自定义事件)
父组件
<template>
<div class="main">
<h3>父组件-{{ money }} <button @click="getMoney">挣钱</button></h3>
<DemoOne food="cake" :money="money" @useMoney="changeFn"></DemoOne>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import DemoOne from '@/components/DemoOne.vue'
import { ref } from 'vue'
const money = ref(10000)
const getMoney = () => {
money.value += 100
}
const changeFn = (newMoney) => {
money.value = newMoney
}
</script>
子组件
<template>
<div class="main">
我是子组件
{{ food }} <!--模板中可以直接使用父组件传递过来的数据 -->
{{ money }}
<button @click="useMoney">花钱</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
const props = defineProps({
food: {
type: String,
},
money: {
type: Number,
}
})
console.log(props.food);
console.log(props.money);
const emit = defineEmits(['useMoney']) // 定义一个事件,用于子组件向父组件传递数据
const useMoney = () => {
emit('useMoney',5) // 触发事件,向父组件传递数据
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.main{
border: 1px solid black;
}
</style>
模板引用
通过ref标识获取真实的dom对象或组件实例
步骤:
-
调用ref函数生成一个ref对象
-
通过ref标识绑定ref对象到标签
-
通过ref对象,value即可访问到绑定的元素(必须渲染后才能拿到)
<script setup>
import TestCom from '@/components/test-com.vue'
import {onMounted, ref} from 'vue'
const inp= ref(null)
onMounted(()=>{
console.log(inp.value)
inp.value.focus()
})
</script>
<template>
<div>
<input ref="inp" type="text">
<button>点击让输入框聚焦</button>
</div>
<TestCom></TestCom>
</template>
默认情况下,<script setup>语法糖下组件内部的属性和方法是不开放给父组件访问的
可以通过defineExpose编译宏指定哪些属性和方法允许访问(显示暴露组件内部的属性和方法)
如:
<script setup>
import {ref} from 'vue'
const message= ref('This is a message')
defineExpose({
testMessage
})
</script>
provide和inject
顶层组件向任意的底层组件传递数据和方法,实现跨层组件通信
注意:传递的可以是数据和方法
顶层组件传递的方法可以允许底层组件修改顶层组件中的数据
步骤:
-
顶层组件通过provide函数提供数据:
provide('key',顶层组件中的数据) -
底层组件通过inject函数获取数据:
const message = inject('key')
例:
父组件
<template>
<div class="main">
<h1>我是父亲-{{ count }}</h1>
<DemoOne></DemoOne>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import DemoOne from '@/components/DemoOne.vue'
import { provide, ref } from 'vue'
const count = ref(100)
provide('color', 'pink')
provide('count', count)
provide('changeCount', () => {
count.value++
})
</script>
子组件
<template>
<div class="main">
<h2>我是儿子-{{ color }}</h2>
{{ count }}
<button @click="changeCount">修改数据</button>
<DemoTwo></DemoTwo>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import DemoTwo from '@/components/DemoTwo.vue';
import { inject } from 'vue'
const color = inject('color')
const count = inject('count')
const changeCount = inject('changeCount')
</script>
<style scoped>
.main{
border: 1px solid black;
}
</style>
孙子组件
<template>
<div class="main">
<h3>我是孙子</h3>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
</script>
<style scoped>
.main {
border: 1px solid saddlebrown;
}
</style>

defineOptions-Vue3.3新特性
由于setup语法糖,使得无法添加与setup平级的属性
为了解决这一问题引入了defineProps与defineEmits这两个宏,但只解决了props与emits这两个属性
defineOptions宏,主要用来定义OptionsAPI选项,可以用defineOptions定义任意的选项
props、emits、expose、slots除外(因为这些可以使用defineXXX来做到)
例:
<script setup>
defineOptions({
name: 'DemoTwo'
})
</script>
等价于
<script>
export default {
name: 'DemoTwo'
}
</script>
defineModel-Vue3.3新特性
Vue2中的v-model= :value + @input 需要先定义props,再定义emits
Vue3中的v-model= :modelValue + @update
defineModel可以实现父子组件的数据传递:
defineModel是Vue 3提供的一个函数,用于在组件中定义v-model绑定。它返回一个响应式的modelValue,这个值与父组件传递的v-model绑定。
例:
父组件
<template>
<div class="main">
<DemoOne v-model="txt"></DemoOne>
{{ txt }}
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
import DemoOne from '@/components/DemoOne.vue'
const txt = ref('123456')
</script>
子组件
<template>
<div class="main">
<input type="text" :value="modelValue" @input="e=>modelValue=e.target.value">
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { defineModel } from 'vue'
const modelValue = defineModel()
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>

Pinia
Pinia是最新的状态管理工具,是Vuex的替代品
相比于Vuex(state、mutations、actions、getters、modules),Pinia(state、actions、getters)的优点:
-
提供更简单的API(去掉了mutation,直接通过actions修改仓库数据)
-
提供符合组合式风格的API,和Vue3新语法统一
-
去掉了modules的概念,每一个store都是一个独立的模块
-
配合TS更加友好,提供可靠的类型推断
使用步骤:
-
安装pinia:
npm i pinia -
挂载到
main.js中:// 将创建实例进行了封装,保证每个实例的独立封闭性 import { createApp } from 'vue' import App from './App.vue' import { createPinia } from 'pinia' const pinia = createPinia() // mount设置挂载点 #app(index.html中id为app的盒子) createApp(App).app.use(pinia).mount('#app') //支持链式
Pinia的基本使用
定义Store:
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
// 第一个参数是你的应用中 Store 的唯一 ID。(仓库名)
export const useAlertsStore = defineStore('alerts', {
// 其他配置...
})
export const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', () => {
const count = ref(0)
const doubleCount = computed(() => count.value * 2)
function increment() {
count.value++
}
return { count, doubleCount, increment }
})
在 Setup Store 中:
-
ref()就是state属性 -
computed()就是getters -
function()就是actions
例:counter.js
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
import { ref, computed } from 'vue'
// 定义store
// defineStore(仓库唯一的标识,() => {...})
export const useCountStore = defineStore('counter', () => {
// 声明数据 state
const counter = ref(0)
// 声明操作数据的方法 actions
const addCounter = () => {
counter.value++
}
const subCounter = () => {
counter.value--
}
// 声明基于数据派生状态的计算属性 getters
const double = computed(() => counter.value * 2)
const msg = ref('hello pinia')
return {
counter,
msg,
addCounter,
subCounter,
double
}
})
<template>
<div class="main">
<h1>App.vue根组件 - 0</h1>
{{ countStore.counter }}
{{ countStore.msg }}
{{ countStore.double }}
<DemoOne></DemoOne>
<DemoTwo></DemoTwo>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import DemoOne from '@/components/DemoOne.vue'
import DemoTwo from '@/components/DemoTwo.vue'
import { useCountStore } from '@/store/counter'
const countStore = useCountStore()
</script>
<template>
<div class="main">
<h2>我是One -{{ countStore.counter }}- <button @click="countStore.subCounter">-</button></h2>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { useCountStore } from '@/store/counter'
const countStore = useCountStore()
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>

解构问题
不能对得到的仓库对象进行解构,否则会丢失数据的响应式
可以通过:
import {storeToRefs} from 'pinia'
const {count, msg} = storeToRefs(counterStore)
将解构出来的数据转化为响应式数据
store是一个用reactive包装的对象,如果进行解构只是将对象中的值赋值给了新的变量
此时可以通过storeToRefs()函数将变量转化为响应式属性
但是可以直接从store中解构action,因为方法不需要响应式
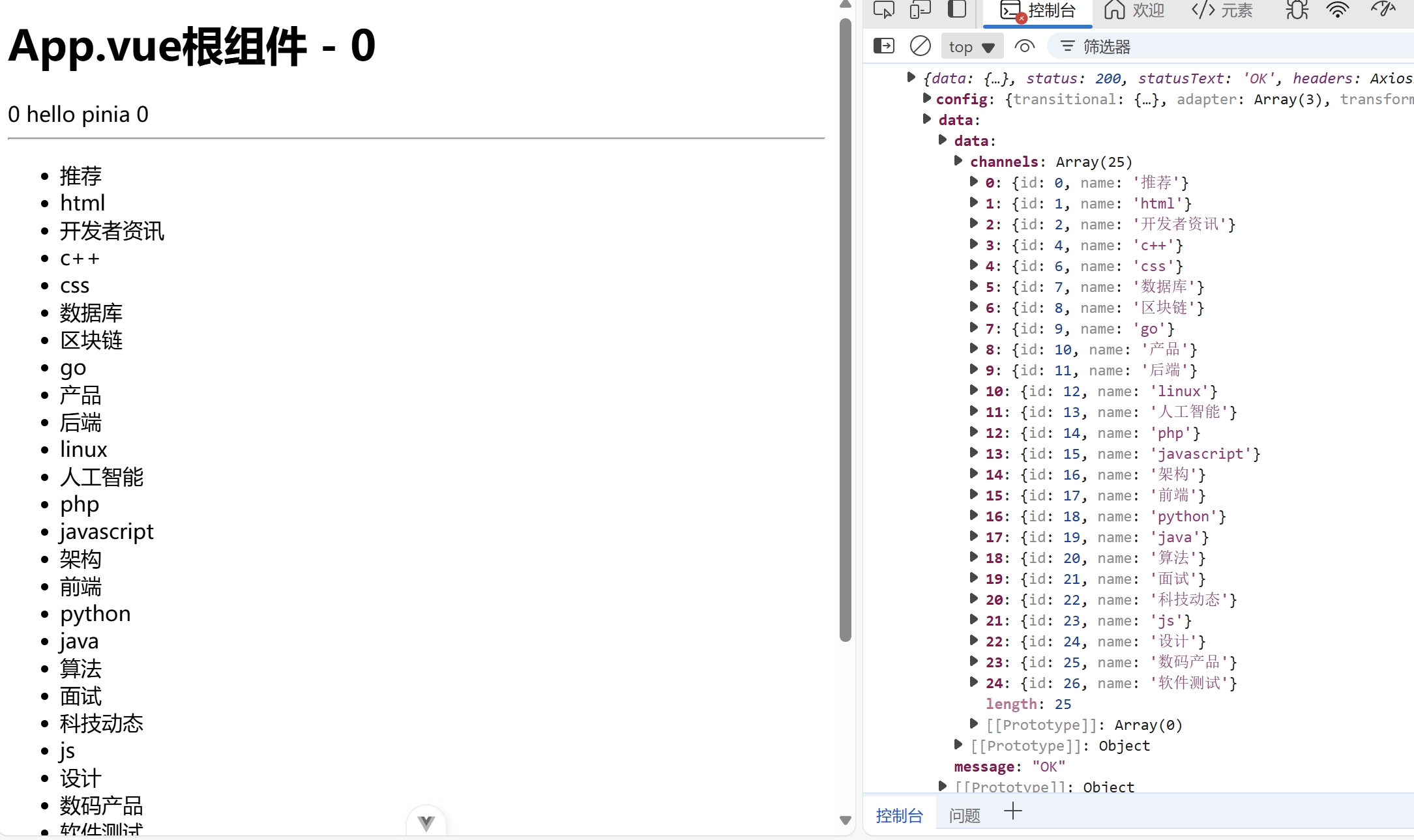
action异步实现
接口地址:http://geek.itheima.net/v1_0/channels
import { defineStore } from "pinia";
import { ref } from "vue";
import axios from "axios";
export const useChannelStore = defineStore('channel', () => {
const channelList = ref([]);
const getChannelList = async () => {
const res = await axios.get('http://geek.itheima.net/v1_0/channels')
channelList.value = res.data.data.channels;
console.log(res);
}
return {
channelList,
getChannelList
}
});
<template>
<div class="main">
<h1>App.vue根组件 - 0</h1>
{{ countStore.counter }}
{{ countStore.msg }}
{{ countStore.double }}
<hr>
<ul>
<li v-for="item in channelStore.channelList" :key="channelStore.channelList.id">{{ item.name }}</li>
</ul>
<button @click="channelStore.getChannelList">获取数据</button>
<DemoOne></DemoOne>
<DemoTwo></DemoTwo>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import DemoOne from '@/components/DemoOne.vue'
import DemoTwo from '@/components/DemoTwo.vue'
import { useCountStore } from '@/store/counter'
import { useChannelStore } from '@/store/channel'
const countStore = useCountStore()
const channelStore = useChannelStore()
</script>
持久化插件
官方网址:Pinia Plugin Persistedstate
使用步骤:
-
安装插件:
npm i pinia-plugin-persistedstate -
将插件添加到pinia实例中
import { createPinia } from 'pinia' import piniaPluginPersistedstate from 'pinia-plugin-persistedstate' const pinia = createPinia() pinia.use(piniaPluginPersistedstate) -
声明store时将persist 选项设置为true(第三个参数位置)
自动实现将数据存储在本地存储(默认)中
import { defineStore } from 'pinia' import { ref, computed } from 'vue' // 定义store // defineStore(仓库唯一的标识,() => {...}) export const useCountStore = defineStore('counter', () => { // 声明数据 state const counter = ref(0) // 声明操作数据的方法 actions const addCounter = () => { counter.value++ } // 声明基于数据派生状态的计算属性 getters const double = computed(() => counter.value * 2) return { counter, addCounter, double } }, { persist: true })可以通过配置persist中的属性实现键名、本地存储的改变、指定持久化的变量
persist:{ key:'newCounter', storage: sessionStorage, pick: ['save.me', 'saveMeToo'] //只对'save.me', 'saveMeToo'持久化 }
新工具
pnpm包管理器
npm => yarn => pnpm
优势:比同类工具快2倍左右,节省磁盘空间
安装:npm i -g pnpm
创建项目:pnpm create vue
项目初始化:pnpm install
启动项目:pnpm dev
区别:
| npm | yarn | pnpm |
|---|---|---|
| npm install | yarn | pnpm install |
| npm install axios | yarn add axios | pnpm add axios |
| npm install axios -D | yarn add axios -D | pnpm add axios -D |
| npm uninstall axios | yarn remove axios | pnpm remove axios |
| npm run dev | yarn dev | pnpm dev |
Eslint配置&prettier
-
prettier:美化代码的格式化工具
-
Eslint:校验代码,注重规范
二者通常一起使用
husky
代码进git仓库前的校验


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号