初识AJAX&AJAX的基本用法
初识AJAX
Ajax是什么
Ajax是Asynchronous JavaScript and XML (异步 JavaScript 和 XML)的简写
Ajax中的异步:可以异步地向服务器发送请求,在等待响应的过程中,不会阻塞当前页面,浏览器可以做自己的事情。直到成功获取响应后,浏览器才开始处理响应数据
XML(可扩展标记语言)是前后端数据通信时传输数据的一种格式
XML现在已经不怎么用了,现在比较常用的是JSON
Ajax其实就是浏览器与服务器之间的一种异步通信方式
使用Ajax可以在不重新加载整个页面的情况下,对页面的某部分进行更新
慕课网注册检测
慕课网搜索提示
搭配Ajax开发环境
Ajax需要服务器环境,非服务器环境下,很多浏览器无法正常使用Ajax
Live Server
windows phpStudy
Mac MAMP
AJAX的基本用法
XMLHttpRequest
console.log(Ajax);
Ajax想要实现浏览器与服务器之间的异步通信,需要依靠XMLHttpRequest,它是一个构造函数
不论是XMLHttpRequest,还是Ajax,都没有和具体的某种数据格式绑定
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Ajax的基本用法</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//console.log(Ajax);
//1.Ajax的使用步骤
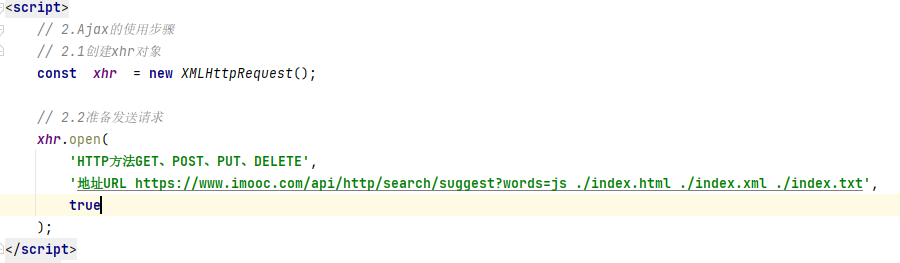
//2.1创建xhr对象
console xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
//2.2准备发送请求
/* xhr.open(
'HTTP方法GET、POST、PUT、DELETE',
'地址 URL https://www.imooc.com/api/http/search/suggest?words=js./index.html./index.xml./index.txt',true); */
// 调用open并不会真正请求发送,而只是做好发送请求前的准备工作
// 2.3.发送请求
//调用send()正式发送请求
//send()的参数是通过请求体携带的数据
//xhr.send(null);
//2.4监听时间,处理响应
//当获取到响应后,会触发xhr对象的readystatechange事件,可以在该事件中对响应进行处理
//xhr.addEventListener('readystatechange',()=>{},false);
/* xhr.onreadystatechange = () =>{
if(xhr.readyState!==4) return;
//HTTP COOE
//获取到响应后,响应的内容会自动填充xhr对象的属性
if(xhr.status>=200&xhr.status <300||
xhr.status === 304){
//console.log('正常使用响应数据');
console.log(xhr.responseTest);
}
}; */
//readystatechange 事件也可以配合addEventListener使用,不过要注意,IE6~8不支持addEventListener
//为了兼容性,readystatechange中不使用this,而是直接使用xhr
//readystatechange事件监听readyState 这个状态的变化
//它的值从0~4,一共五个状态
/* 0:未初始化。尚未调用open()
1:启动。已经调用open),但尚未调用send()
2:发送。已经调用send(),但尚未接收到响应
3:接收。已经接收到部分响应数据
4:完成。已经接收到全部响应数据,而且已经可以在浏览器中使用了 */
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Ajax的基本用法</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//console.log(Ajax);
//1.Ajax的使用步骤
//2.1创建xhr对象
//console xhr =new XMLHttpRequest();
//2.2准备发送请求
/* xhr.open(
'HTTP方法GET、POST、PUT、DELETE',
'地址 URL https://www.imooc.com/api/http/search/suggest?words=js./index.html./index.xml./index.txt',true); */
// 调用open并不会真正请求发送,而只是做好发送请求前的准备工作
// 2.3.发送请求
//调用send()正式发送请求
//send()的参数是通过请求体携带的数据
//xhr.send(null);
//2.4监听时间,处理响应
//当获取到响应后,会触发xhr对象的readystatechange事件,可以在该事件中对响应进行处理
//xhr.addEventListener('readystatechange',()=>{},false);
/* xhr.onreadystatechange = () =>{
if(xhr.readyState!==4) return;
//HTTP COOE
//获取到响应后,响应的内容会自动填充xhr对象的属性
if(xhr.status>=200&xhr.status <300||
xhr.status === 304){
//console.log('正常使用响应数据');
console.log(xhr.responseTest);
}
}; */
//readystatechange 事件也可以配合addEventListener使用,不过要注意,IE6~8不支持addEventListener
//为了兼容性,readystatechange中不使用this,而是直接使用xhr
//readystatechange事件监听readyState 这个状态的变化
//它的值从0~4,一共五个状态
/* 0:未初始化。尚未调用open()
1:启动。已经调用open),但尚未调用send()
2:发送。已经调用send(),但尚未接收到响应
3:接收。已经接收到部分响应数据
4:完成。已经接收到全部响应数据,而且已经可以在浏览器中使用了 */
//3.使用Ajax完成前后端通信
const url ='https://www.imooc.com/api/http/search/suggest?words=js';
const xhr =new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.onreadystatechange = () =>{
if(xhr.readyState!== 4) return;
if(xhr.status>= 200&&xhr.status < 300 ||xhr.status===304){
console.log(xhr.responseText);
}
};
xhr.open('GET',url,true);
xhr.send(null);
</script>
</body>
</html>



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号