JDBC事务管理、概述、实现
JDBC事务管理
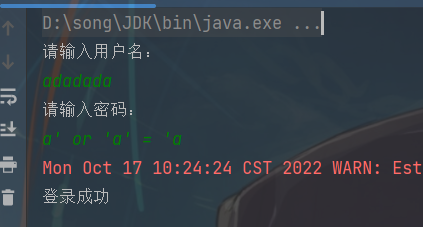
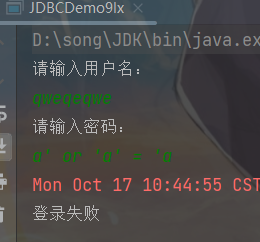
sql注入问题:
用户名随便输入,密码输入:a' or 'a' = 'a,它居然登录成功了!
注意:后期都会使用PrrparedStatement来完成增删改查的所有操作
1.可以防止sql注入
2.效率更高
优化代码
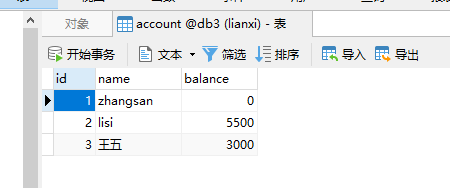
配置文件
JDBCUtiles工具类不用改,还是原来的
public class JDBCUtils { private static String url; private static String user; private static String password; private static String driver; /** * 文件的读取,只需要读取一次即可拿到这些值,使用静态代码块 */ static{ //读取资源文件,获取值 try { //1.创建Properties集合 Properties properties = new Properties(); //获取src路径下的文件的方式---》ClassLoader 类加载器 ClassLoader classLoader = JDBCUtils.class.getClassLoader(); URL resource = classLoader.getResource("jdbc.properties"); String path = resource.getPath(); //System.out.println(path); //2.加载文件 properties.load(new FileReader(path)); //3.获取数据,赋值 url=properties.getProperty("url"); user=properties.getProperty("user"); password=properties.getProperty("password"); driver=properties.getProperty("driver"); //4.注册驱动 Class.forName(driver); } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } /** * 获取连接 * @return 连接对象 */ public static Connection getConnection()throws SQLException{ return DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password); } /** * 释放资源 * @param stmt * @param conn */ public static void close(Statement stmt,Connection conn){ if(stmt!=null){ try { stmt.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } if(conn!=null){ try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } } /** * 释放资源 * @param stmt * @param conn */ public static void close(ResultSet re, Statement stmt, Connection conn){ if (re!=null){ try { re.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } if(stmt!=null){ try { stmt.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } if(conn!=null){ try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }
优化后的代码
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException { //1.键盘录入,接受用户和密码 Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入用户名:"); String username=sc.nextLine(); System.out.println("请输入密码:"); String password=sc.nextLine(); //2.调用方法,非静态方法new一个对象 boolean flag = new JDBCDemo9lx().login(username, password); //3.判断结果,输出不同语句 if (flag){ System.out.println("登录成功"); }else{ System.out.println("登录失败"); } } /*写一个登陆方法,有参数用户和密码,返回是否登陆成功*/ public boolean login(String username, String password) throws SQLException { //判断录入的密码和用户名是否为空 if (username == null || password == null) { return false; } //连接数据库判断是否登陆成功 Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement stmt=null; ResultSet rs=null; //1.获取链接 try { conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); //2.定义sql语句 String sql="select * from user where username= ? and password = ?"; //3.获取执行sql的对象 stmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql); //给?赋值 stmt.setString(1,username); stmt.setString(2,password); //4.执行查询 rs = stmt.executeQuery(); //5.判断结果集是不是有数据 return rs.next(); //返回为布尔型数据,如果有下一行就返回true } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { //6.释放资源 JDBCUtils.close(rs,stmt,conn); } return false; }
JDBC事务管理-概述
事务:一个包含多个步骤的业务操作,如果这个业务操作被事务管理,则这多个步骤要么同时成功,要么同时失败
操作:开始事务
提交事务
回滚事务
使用Connection对象来管理事务
开启事务:setAttoCommit(boolean autoCommit):调用该方法设置参数为false。即开启事务
提交事务:commit();
回滚事务:rollback();
JDBC事务管理-实现
JDBCUtiles工具类
public class JDBCUtils {
private static String url;
private static String user;
private static String password;
private static String driver;
/**
* 文件的读取,只需要读取一次即可拿到这些值,使用静态代码块
*/
static{
//读取资源文件,获取值
try {
//1.创建Properties集合
Properties properties = new Properties();
//获取src路径下的文件的方式---》ClassLoader 类加载器
ClassLoader classLoader = JDBCUtils.class.getClassLoader();
URL resource = classLoader.getResource("jdbc.properties");
String path = resource.getPath();
//System.out.println(path);
//2.加载文件
properties.load(new FileReader(path));
//3.获取数据,赋值
url=properties.getProperty("url");
user=properties.getProperty("user");
password=properties.getProperty("password");
driver=properties.getProperty("driver");
//4.注册驱动
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
/**
* 获取连接
* @return 连接对象
*/
public static Connection getConnection()throws SQLException{
return DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
}
/**
* 释放资源
* @param stmt
* @param conn
*/
public static void close(Statement stmt,Connection conn){
if(stmt!=null){
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if(conn!=null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
/**
* 释放资源
* @param stmt
* @param conn
*/
public static void close(ResultSet re, Statement stmt, Connection conn){
if (re!=null){
try {
re.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if(stmt!=null){
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if(conn!=null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
JDBCDemo10类
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstm1 = null;
PreparedStatement pstm2 = null;
try {
// 1、 获取连接对象Connection
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
// 开启事务
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
// 2. sql语句
String sql1 = "update account set balance = balance - ? where id = ?";
String sql2 = "update account set balance = balance + ? where id = ?";
// 3. 获取预处理sql语句PreparedStatement的对象
pstm1 = conn.prepareStatement(sql1);
pstm2 = conn.prepareStatement(sql2);
// 4. ?赋值
pstm1.setDouble(1, 500);
pstm1.setInt(2, 1);
pstm2.setDouble(1, 500);
pstm2.setInt(2, 2);
// 5. 执行SQL操作
pstm1.executeUpdate();
// 模拟异常
// int x = 5/0;
pstm2.executeUpdate();
// 业务完成正常提交
conn.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
// 业务异常,回滚
try {
if(conn != null)
conn.rollback();
} catch (SQLException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 6. 释放资源
JDBCUtils.close(pstm1, conn);
JDBCUtils.close(pstm2, null);
}
}
配置文件
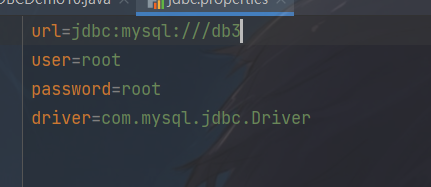
运行结果
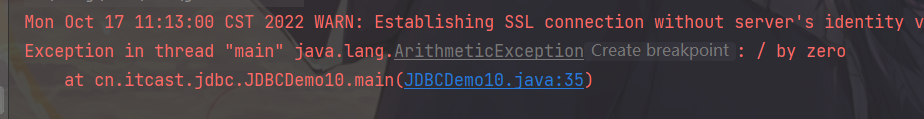
不会发生变化




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号