SpringBoot基础
SpringBoot
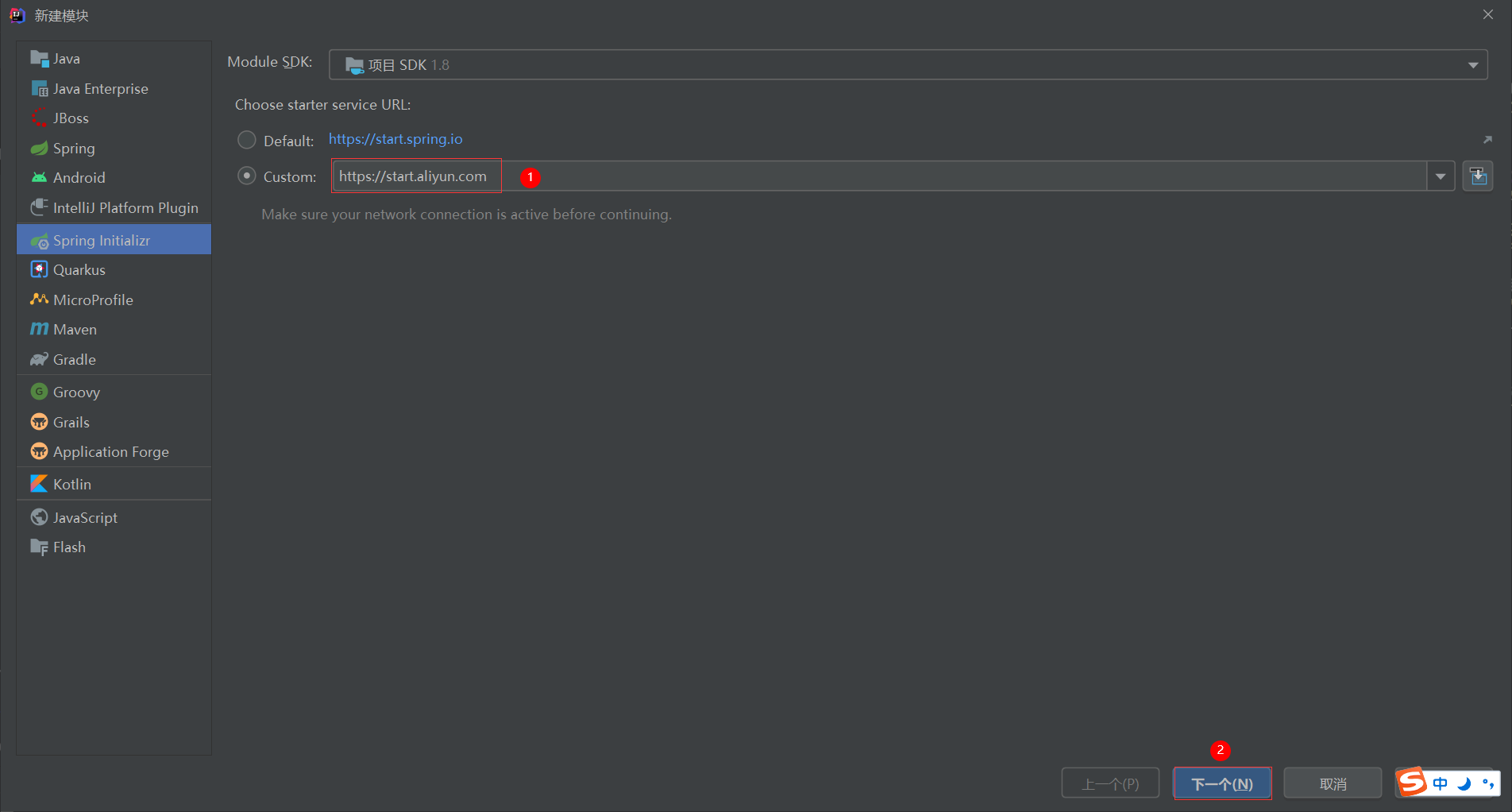
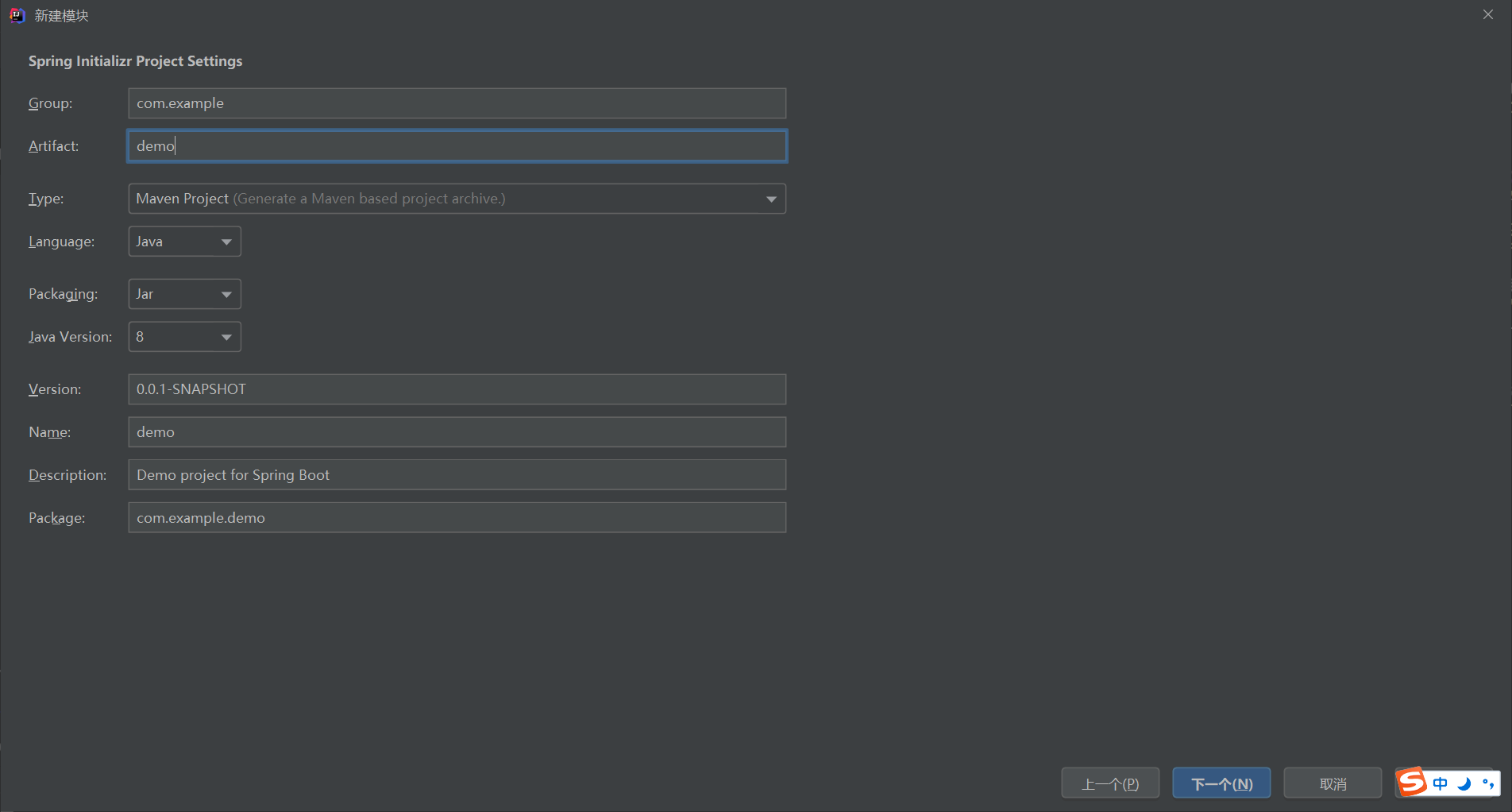
1、基于阿里云创建springboot项目
地址:https://start.aliyun.com
2、SpringBoot简介
springboot是由Pivotal团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程
springboot程序缺点:
- 依赖设置繁琐
- 配置繁琐
springboot程序优点:
- 起步依赖(简化依赖配置)
- 自动配置(简化常用工程相关配置)
- 辅助功能(内置服务,......)
3、常见问题
1、创建的springboot配置文件没有提示功能?
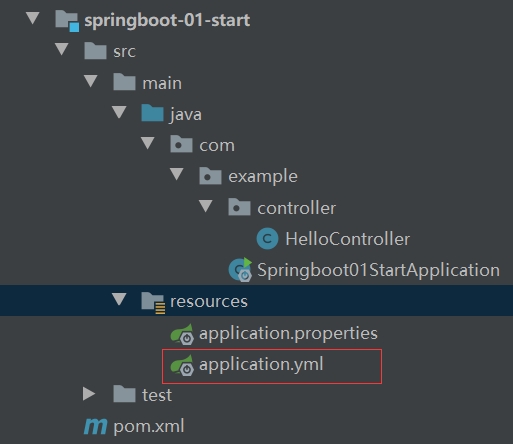
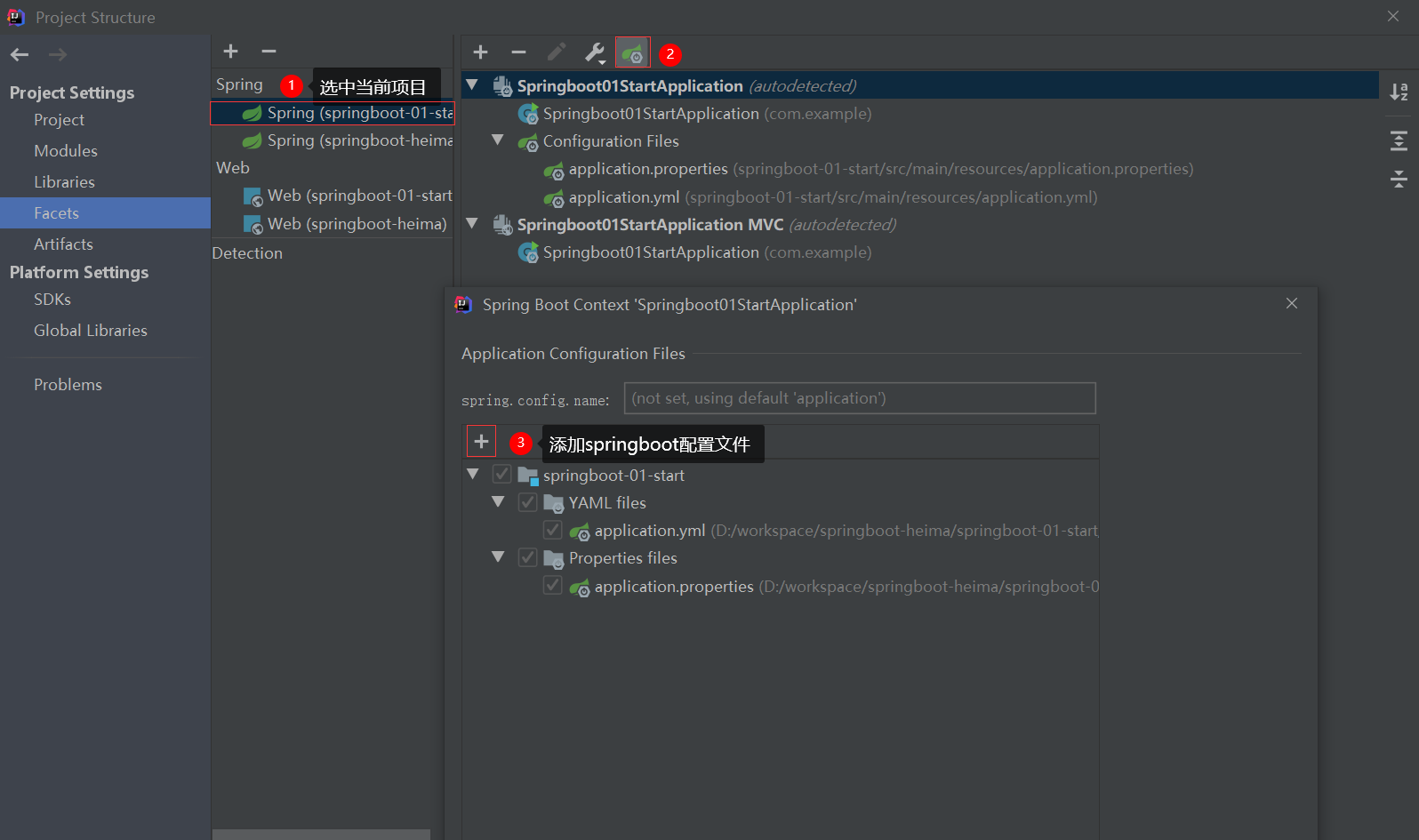
如果和上图所示的图标不一样的话,可以采用下面的方法将指定文件指定为springboot配置文件。
4、yaml格式
# 普通类型
name: zhangsan
age: 21
isTrue: true
birthday: 2021-10-01
# 数组-多行
likes_1:
- game
- sleep
- music
# 数组-行内
likes_2: [game, sleep, music]
# 对象-多行
person_1:
name: ${name} # 引用上面的普通类型数据
age: ${age}
# 对象-行内
person_2: {name: zhangsan, age: 21}
# 对象数组-多行
personList_1:
-
name: ${name}
age: ${age}
-
name: lisi
age: 20
# 对象数组-行内
personList_2: [{name: zhangsan, age: 21}, {name: lisi, age: 20}]
注意:
如果属性值中出现转义字符,需要使用双引号包裹。例:lesson: "spring\tboot\nlesson"
5、读取yaml数据
package com.example.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author admin
*/
@RestController
public class HelloController {
/**
* 读取普通数据
*/
@Value("${name}")
private String name;
/**
* 读取对象中的数据
*/
@Value("${person_1.name}")
private String personName;
/**
* 读取数组中的数据
*/
@Value("${likes_1[0]}")
private String like;
/**
* 读取对象数组中的数据
*/
@Value("${personList_1[0].name}")
private String personArrayName;
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(personName);
System.out.println(like);
System.out.println(personArrayName);
return "hello,springboot!";
}
}
6、使用Environment获取配置文件中的值
package com.example.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author admin
*/
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
System.out.println(environment.getProperty("name"));
System.out.println(environment.getProperty("person_1.name"));
System.out.println(environment.getProperty("likes_1[0]"));
System.out.println(environment.getProperty("personList_1[0].name"));
return "hello,springboot!";
}
}
7、使用@ConfigurationProperties读取yaml配置文件
application.yml
# 创建一个类用于封装下面的数据,由spring帮我们去加载数据到对象中
jdbc:
driver: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true&serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: 123456
Jdbc.java
package com.example.pojo;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 1. 定义数据模型封装yaml文件中对应的数据
* 2. 定义为spring管控的bean
* 3. 指定加载的数据
* @author admin
*/
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "jdbc")
public class Jdbc {
private String driver;
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Jdbc{" +
"driver='" + driver + '\'' +
", url='" + url + '\'' +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
'}';
}
public String getDriver() {
return driver;
}
public void setDriver(String driver) {
this.driver = driver;
}
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
测试
package com.example;
import com.example.pojo.Jdbc;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot01StartApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private Jdbc jdbc;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(jdbc);
}
}
8、整合第三方技术
8.1、整合MyBatis
maven依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0</version>
</dependency>
application.yml
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql:///test?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true&serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: 123456
UserDao.java
package com.example.dao;
import com.example.pojo.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
/**
* @author admin
*/
@Mapper
public interface UserDao {
/**
* 根据id获取用户
* @param id
* @return
*/
@Select("select * from user where id=#{id}")
User getUserById(int id);
}
测试
package com.example;
import com.example.dao.TestDao;
import com.example.dao.UserDao;
import com.example.pojo.User;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot02IntegrationApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
@Test
public void testGetUserById(){
User user = userDao.getUserById(1);
System.out.println(user);
}
}
8.2、整合MyBatis-Plus
maven依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.baomidou/mybatis-plus-boot-starter -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.2</version>
</dependency>
application.yml
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql:///test?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true&serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: 123456
UserDao.java
package com.example.dao;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.example.pojo.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
/**
* @author admin
*/
@Mapper
public interface UserDao extends BaseMapper<User> {
}
测试
package com.example;
import com.example.dao.TestDao;
import com.example.dao.UserDao;
import com.example.pojo.User;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot02IntegrationApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
@Test
public void testSelectById(){
User user = userDao.selectById(1);
System.out.println(user);
}
}
8.3、整合Druid
maven依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.alibaba/druid-spring-boot-starter -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.2.6</version>
</dependency>
application.yml
# 使用druid数据源方式一
#spring:
# datasource:
# driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
# url: jdbc:mysql:///test?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true&serverTimezone=UTC
# username: root
# password: 123456
# type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
# 使用druid数据源方式二
spring:
datasource:
druid:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql:///test?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true&serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: 123456
9、MyBatis-Plus实现service层
UserService.java
package com.example.service;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService;
import com.example.pojo.User;
/**
* @author admin
*/
public interface UserService extends IService<User> {
}
UserServiceImpl.java
package com.example.service.impl;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;
import com.example.dao.UserDao;
import com.example.pojo.User;
import com.example.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author admin
*/
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<UserDao, User> implements UserService {
}
测试
package com.example;
import com.example.pojo.User;
import com.example.service.UserService;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot02IntegrationApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Test
void testGetById(){
User user = userService.getById(1);
System.out.println(user);
}
}
-------------------------------------------
个性签名:独学而无友,则孤陋而寡闻。做一个灵魂有趣的人!
如果觉得这篇文章对你有小小的帮助的话,记得在右下角点个“推荐”哦,博主在此感谢!
万水千山总是情,打赏一分行不行,所以如果你心情还比较高兴,也是可以扫码打赏博主,哈哈哈(っ•̀ω•́)っ✎⁾⁾!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号