nowcoder-oj【面试高频TOP榜单-简单难度(5)5道】
1、NC96 判断一个链表是否为回文结构

import java.util.*; /* * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next = null; * } */ public class Solution { /** * * @param head ListNode类 the head * @return bool布尔型 */ public boolean isPail (ListNode head) { // write code here } }
实现
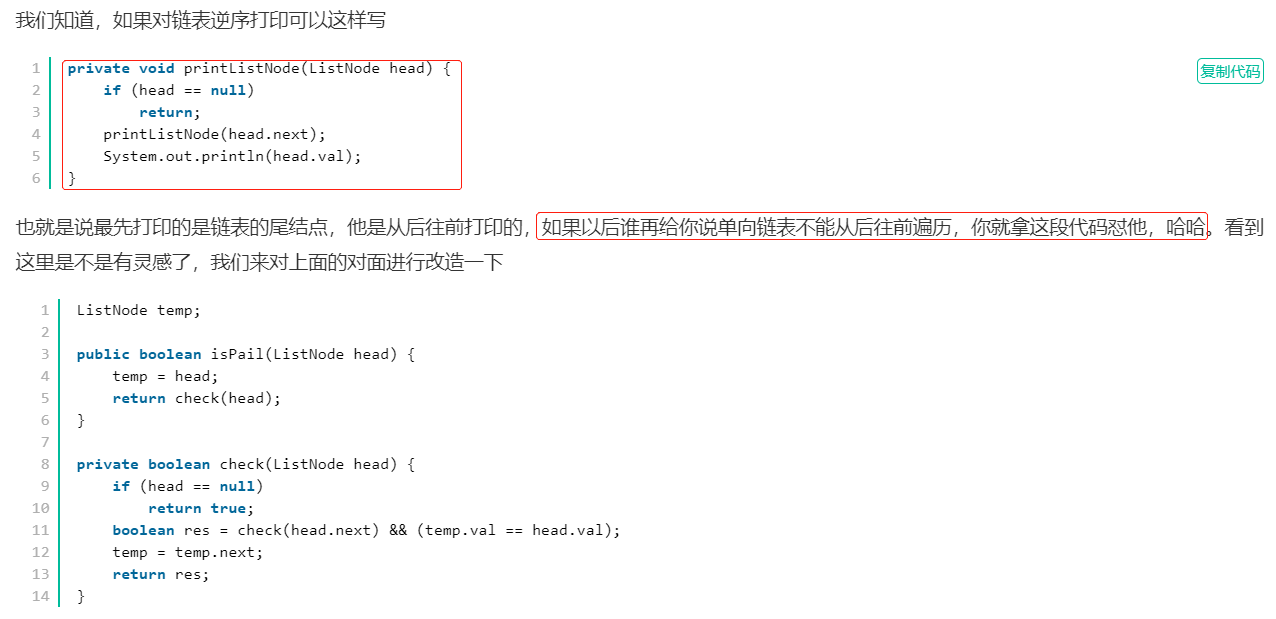
/* * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next = null; * } */ import java.util.*; public class Solution { /** * * @param head ListNode类 the head * @return bool布尔型 */ //未完成:11/13 组用例通过 public boolean isPail (ListNode head) { if(head == null){ return false; } if(head.next == null){ return true; } //思路:遍历单链表,将所有节点的数据存入一个数组/列表,遍历前一半列表,对比后一半中对应位置的数值是否一致 ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); while(head != null){ list.add(head.val); head = head.next; } int len = list.size(); // if(len % 2 == 0){ //偶数个元素 // }else{ //奇数个元素(中间元素不需要参与遍历对比) // } //经过推导发现:以下遍历可以解决奇偶数问题(即i<len/2可以避开奇数列表中的最中间元素) for(int i=0; i<len/2; i++){ if(list.get(i) != list.get(len-i-1)){ //推导出后半段回文对应位置下标为len-i-1 return false; } } return true; } }
参考
【数据结构和算法】判断回文链表,图文详解_牛客博客 (nowcoder.net)

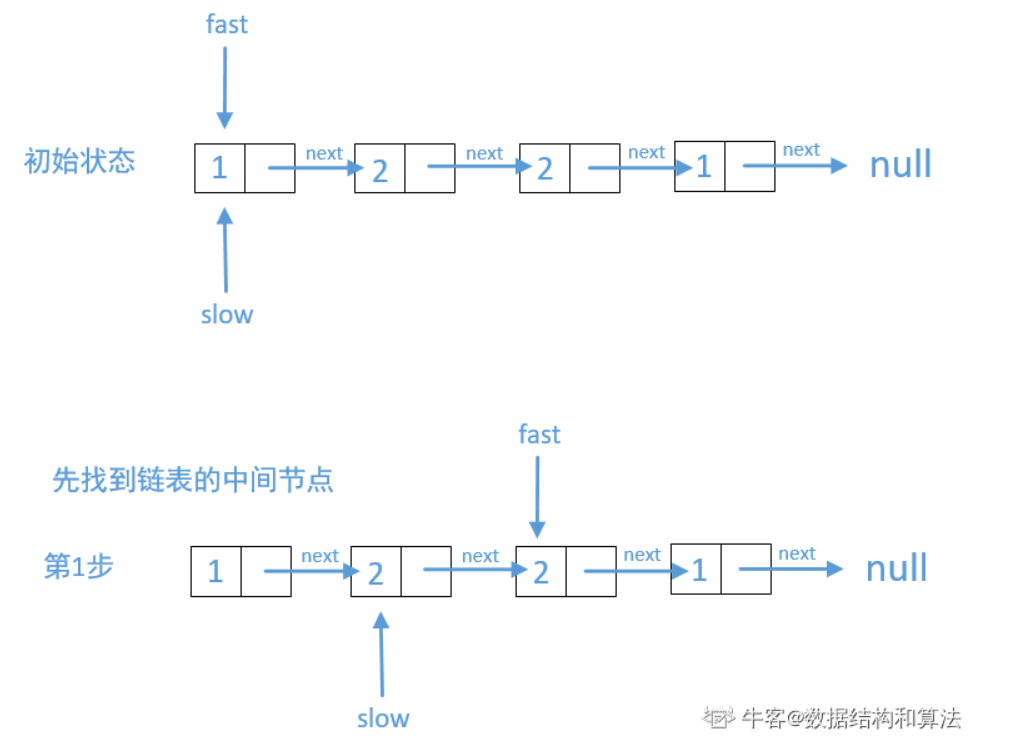
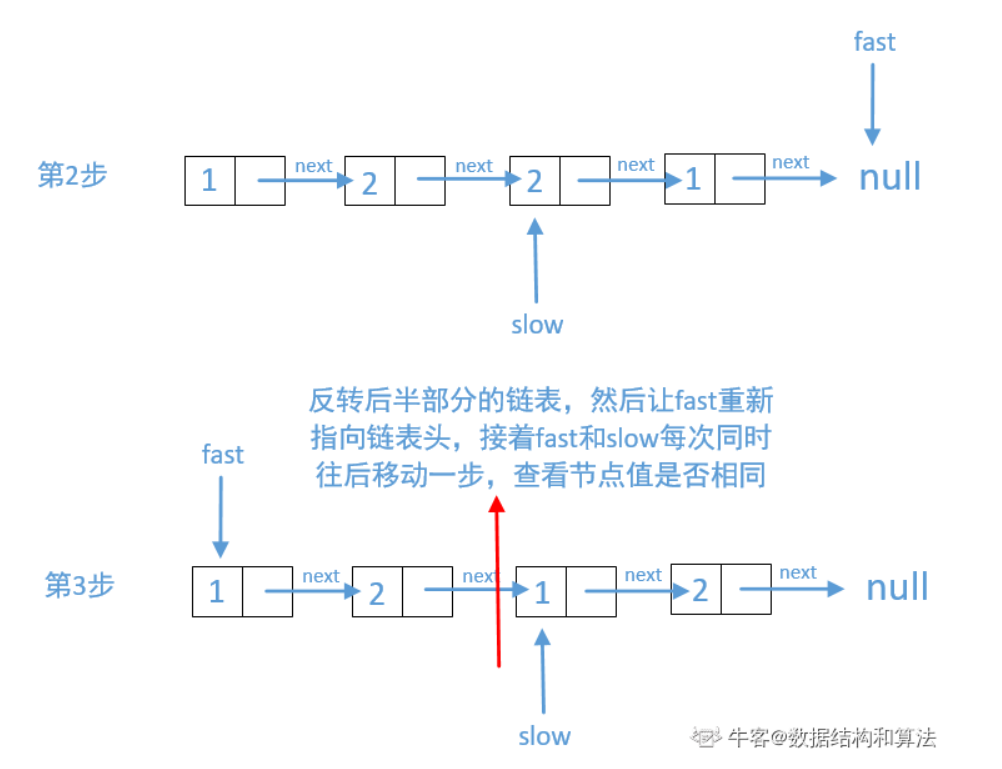
//思路:快慢指针找到单链表的“中间节点”,反转后半部分链表,同步遍历两个小链表,对比对应节点的值 import java.util.*; public class Solution { public boolean isPail (ListNode head) { //通过快慢指针找到中点 ListNode fast = head, slow = head; while(fast != null && fast.next != null){ fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; } //如果fast不为空,说明链表的长度是奇数个 if(fast != null){ slow = slow.next; } //反转后半部分链表 slow = reverse(slow); //前半小链表(逻辑上是两个小链表,其实fast还是原链表但我们只需要其前一半,后半部分是名副其实的反转构造的小链表) fast = head; //遍历,比较对应节点值是否相等 while(slow != null){ if(fast.val != slow.val){ return false; }else{ fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next; } } return true; } public ListNode reverse(ListNode head) { ListNode prev = null; while (head != null) { ListNode temp = head.next; head.next = prev; prev = head; head = temp; } return prev; } }

2、NC34 求路径
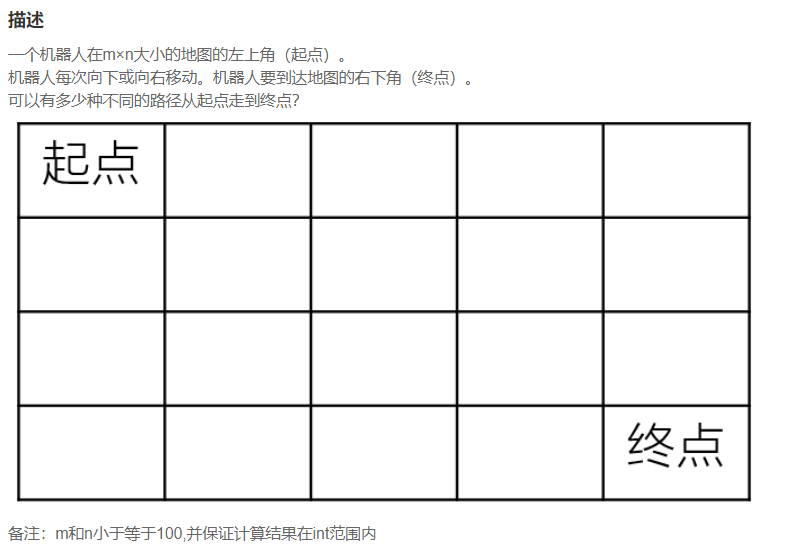

import java.util.*; public class Solution { /** * * @param m int整型 * @param n int整型 * @return int整型 */ public int uniquePaths (int m, int n) { // write code here } }
参考
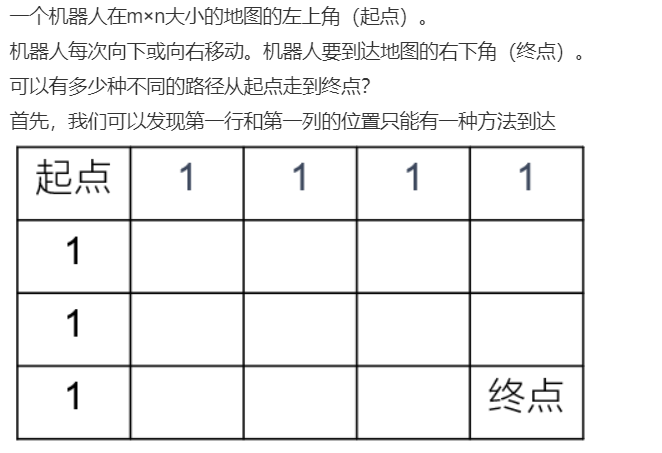
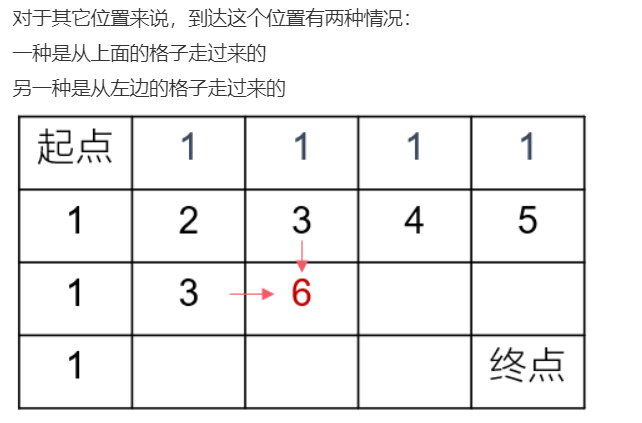
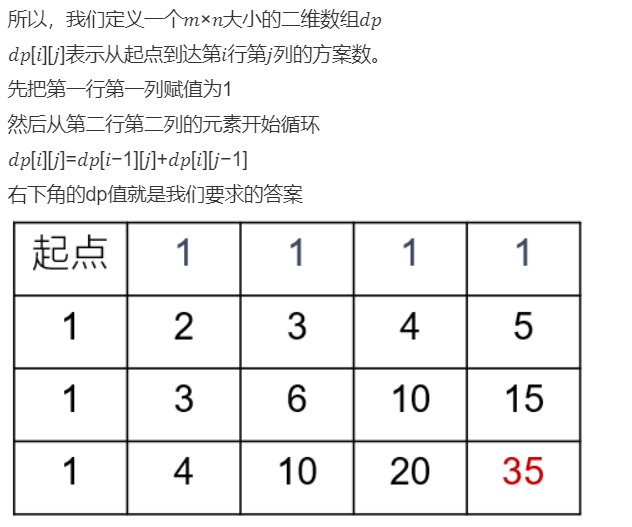
//参考1 public int uniquePaths (int m, int n) { int[][] dp = new int[m+1][n+1]; for(int i=1; i<=m; i++){ //第一列赋值为1 dp[i][1] = 1; } for(int j=1; j<=n; j++){ //第一行赋值为1 dp[1][j] = 1; } for(int i=2; i<=m; i++){ for(int j=2; j<=n; j++){ dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + dp[i][j-1]; } } return dp[m][n]; }

//参考2 public int uniquePaths (int m, int n) { int N = n+m-2; int K = n-1; double num = 1.0; for(int i=1; i<=K; i++){ num = num * (N-K+i) / i; } return (int)num; }
3、NC57 反转数字

import java.util.*; public class Solution { /** * * @param x int整型 * @return int整型 */ public int reverse (int x) { // write code here } }
实现
//19/20 组用例通过 //java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "9876543212" public int reverse (int x) { boolean flag; if(x < 0){ flag = false; }else{ flag = true; } if(!flag){ x = -x; } //不论原始输入的x是正数还是负数,此时x是正数 String strX = String.valueOf(x); StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(strX); String revStrX = sb.reverse().toString(); int res = Integer.parseInt(revStrX); if(!flag){ res = -res; } //左移:num << n,相当于num乘以2的n次方 //右移:num >> n,相当于num除以2的n次方 //2的32次方,相当于32个2相乘,就是1乘以32个2,1<<32 // int temp = 1 << 32; //1,没生效?? if(res < -Math.pow(2,31) || res > Math.pow(2,31)-1){ return 0; } return res; }
参考
【数据结构和算法】反转数字,图文详解_牛客博客 (nowcoder.net)
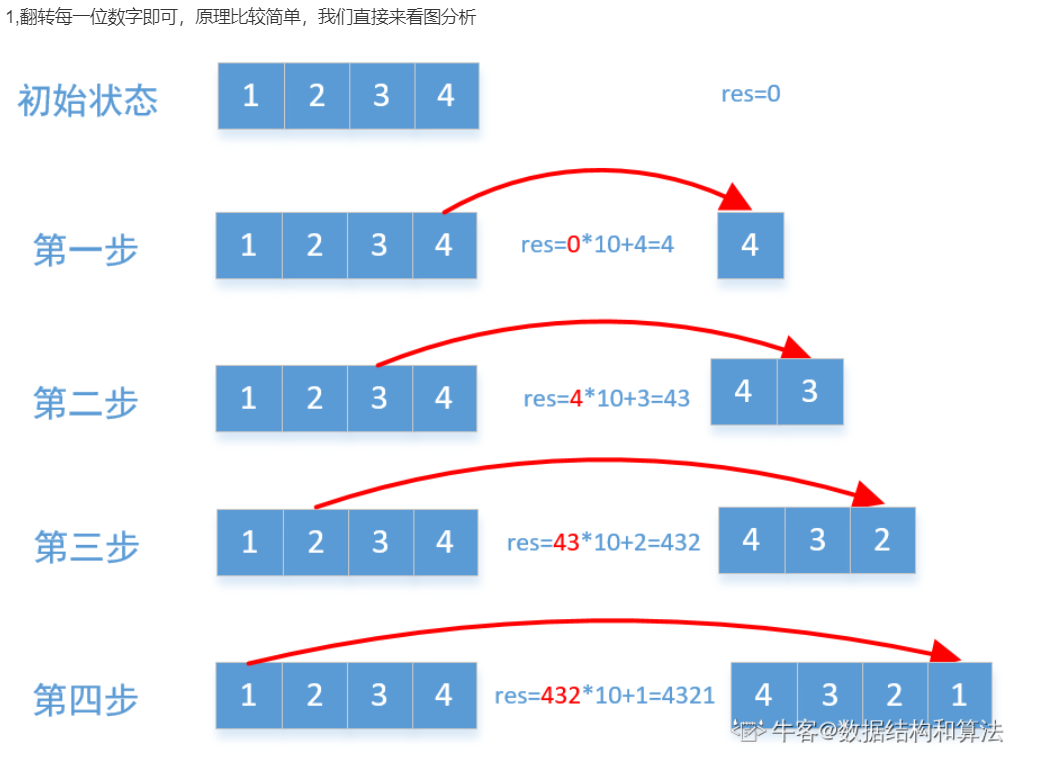
public int reverse(int x) { int res = 0; while (x != 0) { int t = x % 10; int newRes = res * 10 + t; //如果数字溢出,直接返回0 if ((newRes - t) / 10 != res) return 0; res = newRes; x = x / 10; } return res; }

public int reverse(int x) { long res = 0; while (x != 0) { res = res * 10 + x % 10; x /= 10; } return (int) res == res ? (int) res : 0; }
4、NC16 判断二叉树是否对称


import java.util.*; /* * public class TreeNode { * int val = 0; * TreeNode left = null; * TreeNode right = null; * } */ public class Solution { /** * * @param root TreeNode类 * @return bool布尔型 */ public boolean isSymmetric (TreeNode root) { // write code here } }
参考1
判断二叉树是否对称【递归】【迭代】详解!_牛客博客 (nowcoder.net)

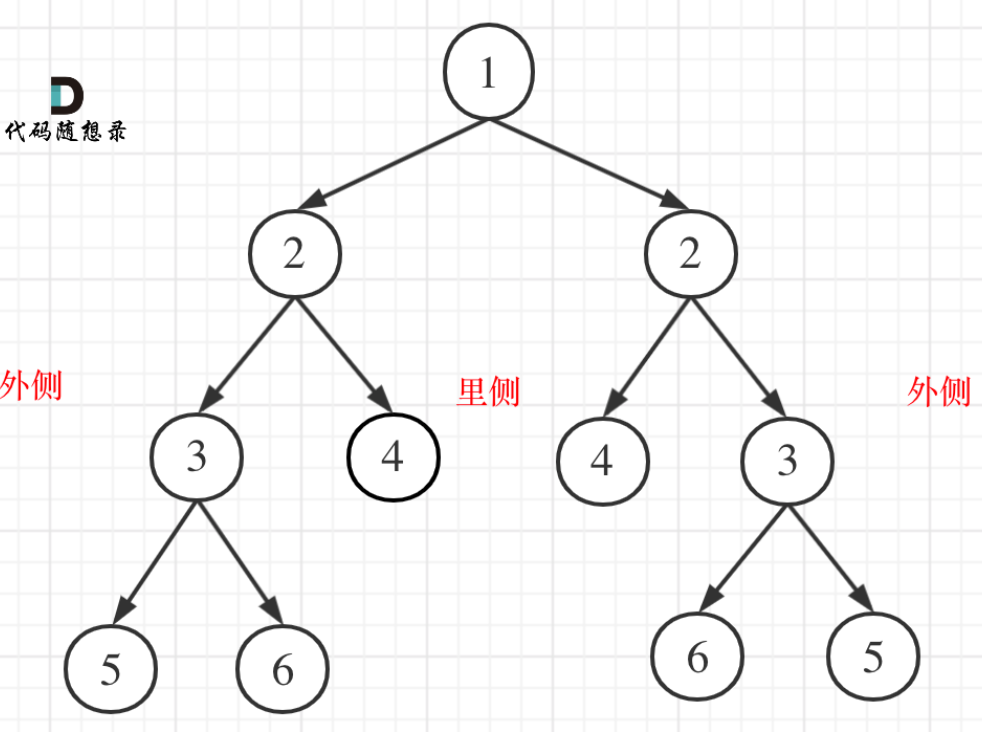

参考2
【数据结构和算法】递归和非递归两种方式解决_牛客博客 (nowcoder.net)
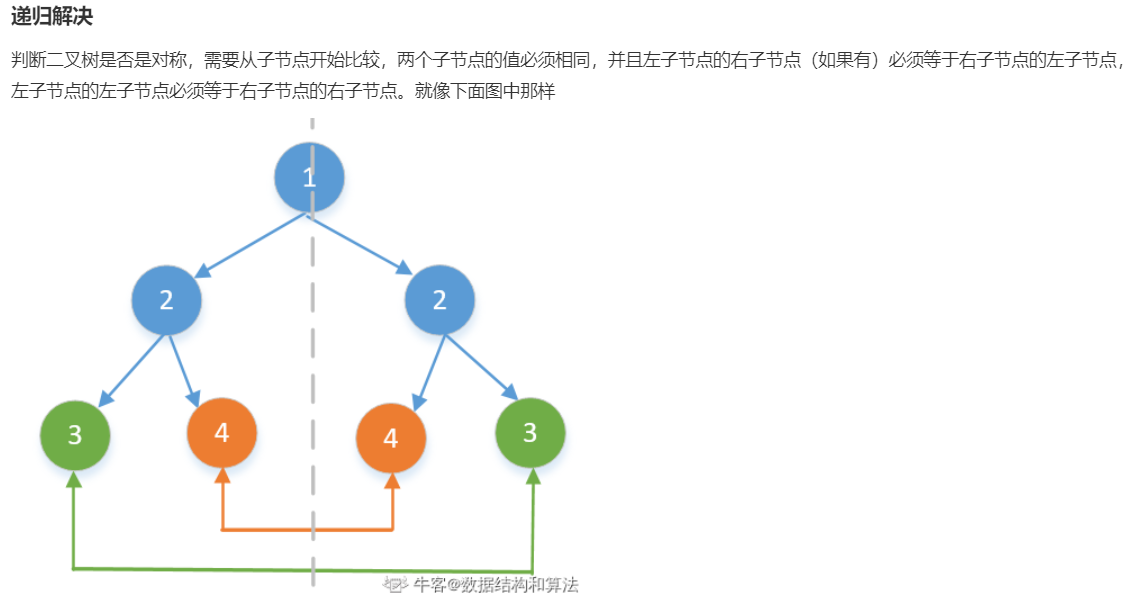
import java.util.*; public class Solution { public boolean isSymmetric (TreeNode root) { if (root == null){ return true; } return isSymmetricHelper(root.left, root.right); //从两个子节点开始判断 } public boolean isSymmetricHelper(TreeNode leftTree, TreeNode rightTree) { if (leftTree == null && rightTree == null){ //如果左右子节点都为空,说明当前节点是叶子节点,返回true return true; } if (leftTree == null || rightTree == null || leftTree.val != rightTree.val){ //如果当前节点只有一个子节点或者有两个子节点,但两个子节点的值不相同,直接返回false return false; } //然后左子节点的左子节点和右子节点的右子节点比较,左子节点的右子节点和右子节点的左子节点比较 return isSymmetricHelper(leftTree.left, rightTree.right) && isSymmetricHelper(leftTree.right, rightTree.left); } }

import java.util.*; public class Solution { public boolean isSymmetric (TreeNode root) { if (root == null){ return true; } Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); //队列 //左子节点和右子节点同时入队 queue.add(root.left); queue.add(root.right); //如果队列不为空就继续循环 while (!queue.isEmpty()) { //每两个出队 TreeNode left = queue.poll(), right = queue.poll(); //如果都为空继续循环 if (left == null && right == null){ continue; } //如果一个为空一个不为空,说明不是对称的,直接返回false if (left == null ^ right == null){ return false; } //如果这两个值不相同,也不是对称的,直接返回false if (left.val != right.val){ return false; } //这里要记住入队的顺序,他会每两个两个的出队。 //左子节点的左子节点和右子节点的右子节点同时 //入队,因为他俩会同时比较。 //左子节点的右子节点和右子节点的左子节点同时入队, //因为他俩会同时比较 queue.add(left.left); queue.add(right.right); queue.add(left.right); queue.add(right.left); } return true; } }

5、NC25 删除有序链表中重复的元素

import java.util.*; /* * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next = null; * } */ public class Solution { /** * * @param head ListNode类 * @return ListNode类 */ public ListNode deleteDuplicates (ListNode head) { // write code here } }
实现
import java.util.*; public class Solution { public ListNode deleteDuplicates (ListNode head) { if(head == null || head.next == null){ return head; } TreeSet<Integer> set = new TreeSet<>(); while(head != null){ set.add(head.val); head = head.next; } ListNode res = new ListNode(-1); //头结点不能为空,因为null.next报空指针,-1不属于结果仅占位用 ListNode move = res; for(int num: set){ ListNode temp = new ListNode(num); move.next = temp; move = move.next; } return res.next; } }
其他1
import java.util.*; public class Solution { public ListNode deleteDuplicates (ListNode head) { if (head == null){ return head; } // a-b-c,三个位置使用三个指针 // 如果 b=c,删除b就可以 // 创建一个虚拟头部 ListNode visual = new ListNode(-1); visual.next = head; ListNode first = visual; ListNode second = head; ListNode third = head.next; while (third!=null){ //相等就进行处理 if (second.val == third.val){ first.next = third; second = third; third = third.next; } else { // 不相等就继续遍历 first = second; second = third; third = third.next; } } return visual.next; } }
其他2

import java.util.*; class Solution { public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) { ListNode dummy = new ListNode(Integer.MAX_VALUE); dummy.next = head; ListNode cur = dummy; while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) { if (cur.next.val == cur.next.next.val) { cur.next = cur.next.next; } else { cur = cur.next; } } return dummy.next; } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号