nowcoder-oj【面试高频TOP榜单-简单难度(3)5道】
1、NC66 两个链表的第一个公共结点
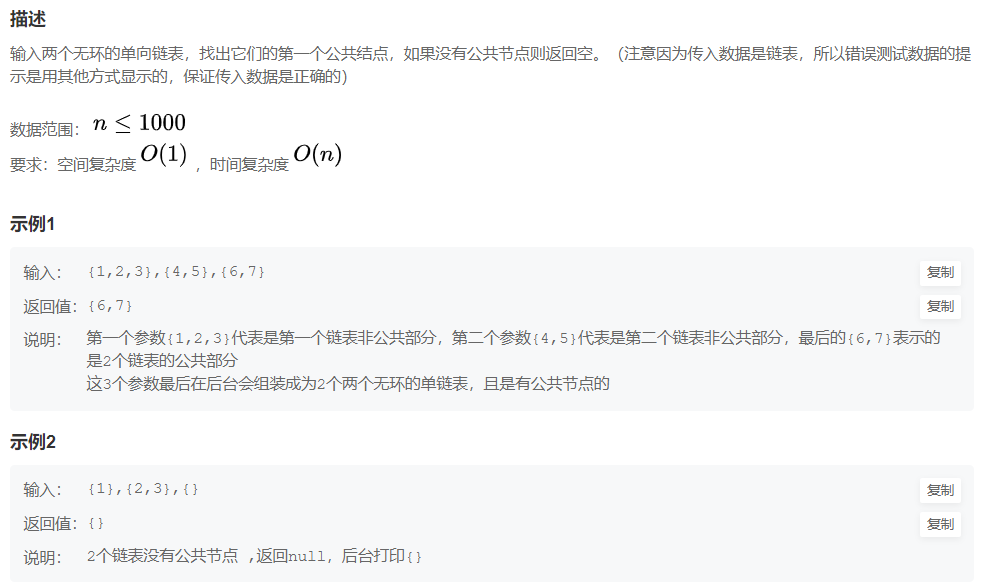

/* public class ListNode { int val; ListNode next = null; ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } }*/ public class Solution { public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) { } }

//0(未实现,4/8 组用例通过) public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) { if(pHead1==null || pHead2==null){ //两个空链表 return null; } if(pHead1.next==null && pHead2.next==null && pHead1.val==pHead2.val){ //两个单节点链表,且节点值相等 return pHead1; } if(pHead1.next==null && pHead2.next==null && pHead1.val!=pHead2.val){ //两个单节点链表,且节点值不等 return null; } //-----------------------------------------逻辑实现有点问题 ListNode res = pHead1; while(pHead1.next != null){ while(pHead2.next != null){ if(pHead1 == pHead2){ ListNode temp = res; res.next = pHead1; temp = res.next; } pHead2 = pHead2.next; } pHead1 = pHead1.next; } return res.next; //----------------------------------------- }
参考1


//参考1
public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {
if(pHead1==null || pHead2==null){
return null;
}
ListNode p1 = pHead1;
ListNode p2 = pHead2;
while(p1 != p2){
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next;
if(p1 != p2){
if(p1 == null){
p1 = pHead2;
}
if(p2 == null){
p2 = pHead1;
}
}
}
return p1;
}
参考2
【宫水三叶の剑指精选】一题五解 :「朴素解法」&「栈解法」&「Set 解法」&「差值法」&「等值法」_牛客博客 (nowcoder.net)


//参考2:朴素解法
public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode a, ListNode b) {
for (ListNode h1=a; h1!=null; h1=h1.next) {
for (ListNode h2=b; h2!=null; h2=h2.next) {
if (h1 == h2){
return h1;
}
}
}
return null;
}

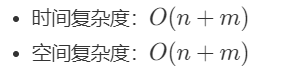
//参考3:栈解法
public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode a, ListNode b) {
Deque<ListNode> d1 = new ArrayDeque<>(), d2 = new ArrayDeque<>();
while (a != null) {
d1.add(a);
a = a.next;
}
while (b != null) {
d2.add(b);
b = b.next;
}
ListNode ans = null;
while (!d1.isEmpty() && !d2.isEmpty() && d1.peekLast()==d2.peekLast()) {
ans = d1.pollLast();
d2.pollLast();
}
return ans;
}

//参考4:Set集合解法
public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode a, ListNode b) {
Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>();
while (a != null) {
set.add(a);
a = a.next;
}
while (b != null && !set.contains(b)){
b = b.next;
}
return b;
}
2、NC32 求平方根

import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param x int整型
* @return int整型
*/
public int sqrt (int x) {
// write code here
}
}
参考1

//参考1:二分查找
public int sqrt(int x) {
if (x <= 0) {
return 0;
}
int left = 1;
int right = x;
while (true) {
int middle = (left + right) >> 1;
if (middle<= x/middle && (middle+1) > x/(middle+1)) {
return (int) middle;
} else if (middle < x/middle) {
left = middle + 1;
} else {
right = middle - 1;
}
}
}
参考2

//参考2:牛顿迭代
public int sqrt(int x) {
if (x <= 0) {
return 0;
}
long r = x;
while (r > x/r) {
r = (r+x/r) / 2;
}
return (int) r;
}
参考3
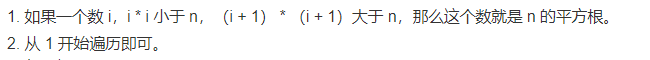
//参考3
public int sqrt(int x) {
if (x <= 0) {
return 0;
}
int i = 1;
for (i=1; i<=x; i++) {
if (i*i<=x && (i+1)*(i+1)>x) {
break;
}
}
return i;
}
3、NC48 在旋转过的有序数组中寻找目标值

1 import java.util.*; 2 3 4 public class Solution { 5 /** 6 * 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可 7 * 8 * 9 * @param nums int整型一维数组 10 * @param target int整型 11 * @return int整型 12 */ 13 public int search (int[] nums, int target) { 14 // write code here 15 } 16 }
实现
//0 public int search (int[] nums, int target) { if(nums.length == 1 && nums[0] != target){ return -1; } if(nums.length == 1 && nums[0] == target){ return 0; } for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++){ if(nums[i] == target){ return i; } } return -1; }
其他
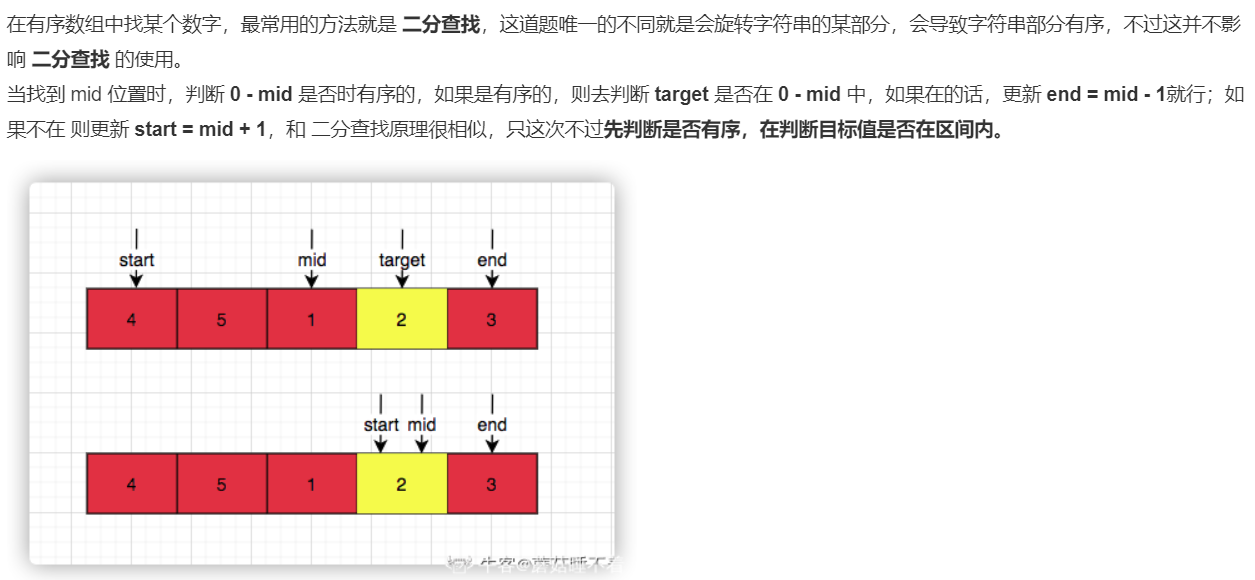


//参考1:二分查找 public int search (int[] nums, int target) { if (nums == null || nums.length < 1) { return -1; } if (nums.length == 1) { return nums[0] == target ? 0 : -1; } int start = 0; int end = nums.length - 1; while (end >= start) { // 找到 左右指针中间位置 int mid = (end + start) >> 1; if (nums[mid] == target) { return mid; } // 在左侧升序数组中 if (nums[0] <= nums[mid]) { // 在开头和 mid 之间,那么 右指针则为 mid -1 if (target >= nums[0] && target < nums[mid]) { end = mid -1; } else { start = mid + 1; } } else { // 如果在 mid 和end 之前,更新 start 为 mid = 1 if (target > nums[mid] && target <= nums[end]) { start = mid + 1; } else { end = mid - 1; } } } return -1; }
4、NC90 包含min函数的栈

import java.util.Stack; public class Solution { public void push(int node) { } public void pop() { } public int top() { } public int min() { } }
参考

同步辅助栈

import java.util.Stack; public class Solution { Stack<Integer> stackTotal = new Stack<Integer>(); Stack<Integer> stackLittle = new Stack<Integer>(); public void push(int node) { stackTotal.push(node); if(stackLittle.empty()){ stackLittle.push(node); }else{ if(node <= stackLittle.peek()){ stackLittle.push(node); }else{ stackLittle.push(stackLittle.peek()); } } } public void pop() { stackTotal.pop(); stackLittle.pop(); } public int top() { return stackTotal.peek(); } public int min() { return stackLittle.peek(); } }
5、NC7 买卖股票的最好时机(股票一次交易)

import java.util.*; public class Solution { /** * * @param prices int整型一维数组 * @return int整型 */ public int maxProfit (int[] prices) { // write code here } }
实现
import java.util.*; public class Solution { /* 分析: 从示例来看,明显数组第一个元素是买入价格,而不是买后的第一天 prices[0]为买入当天(第0天)的价格,即买入价格 在数组prices中找到除了prices[0]外的最大一个元素prices[i] 最大收益=prices[i]-prices[0] PS:百度:当天买入的股票当天是不可以卖出的 */ public int maxProfit (int[] prices) { int length = prices.length; if(length <=1){ return 0; } /* int take = prices[0]; int maxSell = prices[0]; for(int i=1; i<length; i++){ if(prices[i] >= maxSell){ maxSell = prices[i]; } } return maxSell-take; */ /* 仅9/19 组用例通过,复盘发现,审题错了 并不是必须在第一个元素这一天买入 可以在非最后一个元素之前的任一天买入 在买入这一元素之后,至数组最后一个元素(包含)找一个最大的价格卖出即可 */ int max = 0; for(int i=0; i<length-1; i++){ int buy = prices[i]; for(int j=i+1; j<length; j++){ int sell = prices[j]; if(sell-buy > max){ max = sell-buy; } } } return max; } }
其他
【数据结构和算法】动态规划,双指针,单调栈等6种解决方式_牛客博客 (nowcoder.net)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号