#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
#include<typeinfo>
/*
1.3.4类模板对象做函数参数
类模板实例化出的对象,向函数传参的方式
共有三种传入方式:
1. 指定传入的类型 --- 直接显示对象的数据类型 (最常用)
2. 参数模板化 --- 将对象中的参数变为模板进行传递
3. 整个类模板化 --- 将这个对象类型 模板化进行传递
*/
template<class T1, class T2>
class Person{
public:
T1 name;
T2 age;
Person(T1 _name, T2 _age){
this->name = _name;
this->age = _age;
}
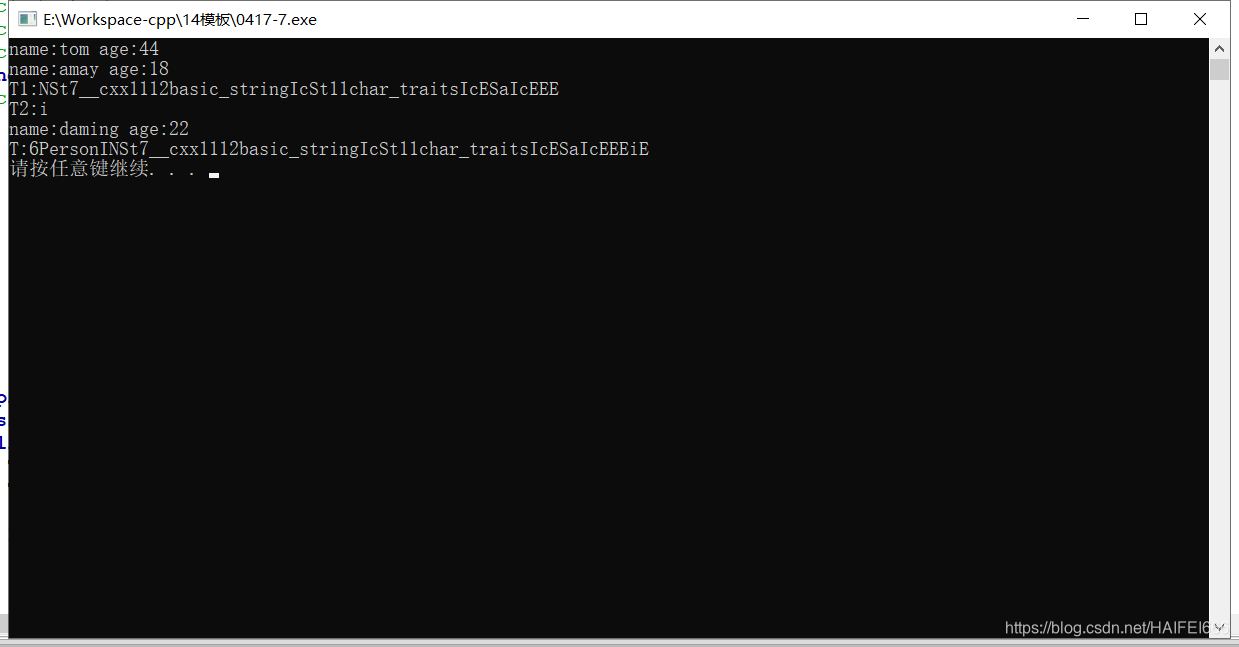
void show(){
cout << "name:" << this->name << " age:" << this->age << endl;
}
};
//1. 指定传入的类型(三种中最常用)
void print_p1(Person<string, int>&p){
p.show();
}
void test(){
Person <string, int> p("tom", 44);
print_p1(p);
}
//2. 参数模板化
template<class T1, class T2>
void print_p2(Person<T1, T2>&p){
p.show();
// 查看编译器推导出来的T的类型
cout << "T1:" << typeid(T1).name() << endl; // 注意要引用头文件<typeinfo>
cout << "T2:" << typeid(T2).name() << endl;
}
void test2(){
Person <string, int> p("amay", 18);
print_p2(p);
}
//3. 整个类模板化
template<class T>
void print_p3(T &p){
p.show();
cout << "T:" << typeid(T).name() << endl;
}
void test3(){
Person <string, int> p("daming", 22);
print_p3(p);
}
int main(){
test();
test2();
test3();
system("pause");
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号