数据库sql基础操作
数据库
存数据的东西
数据库分类
是东西总得分类的,对吧
关系型数据库
数据之间会存在关系,你总得存它吧,所以这种数据库又存数据又存数据之间的关系,代表性的有Oracle、MySQL、SQL sever
非关系型数据库
你数据之间虽然有关系,但是我为什么非要存,麻烦不麻烦,我只存数据,不要以为我只存数据就不行,存我这里可以极大的增加读取速度,特别是高并发的时候,代表性的有Redis
SQL
关系型数据库语言的标准,不分大小写,怎么写都ok
库
最能装的
增
create databases 库名 [character set utf8 collate utf8_bin];
删
删库跑路,晓得伐?
drop databases [if exists] 库名;
改
不能修改名字,只能改校对规则和字符集
alter databases 库名 character set 字符集名;
查
show databases;# 显示所有数据库
show create databases 库名;# 显示某个库的建库语句
表
就是比人家库低一个档次
use 库名;
使用表的时候需要知道在哪个库,然后用这个语句先进库
增
create table 表名 (
#这里可以定义各种属性
);
需要说明的是,定义各种属性的时候,需要给到参数的数据类型,这里的数据类型包括整型、浮点型、时间、字符类型、枚举、集合
整型
与Java一样
浮点型
n float(有效数字数, 小数位数);
时间
-- 设置时区
set time_zone = '+10';
-- 五种类型
time1 year; -- '2021
time2 time; -- '12:00:00'
time3 date; -- '2021-12-31'
time4 datetime; -- '2021-12-31 12:00:00'
time5 timestamp; -- '2021-12-31 12:00:00'
datetime跟着MySQL的时区走的,timestamp跟着系统时间走的,在国内,两个时间是一样,这个时候使用timestamp,在国外,应该跟着当地时间走,一般也是使用timestamp
枚举
example enum('1','2'); -- 只能选一个
集合
example set('1','2','3'); -- 可以选多个
枚举与集合的区别点:枚举为单选,最大能有65535个选项;集合为多选,最大能有64个选项
删
常规操作,都坐下
dorp table 表名;
改
-- 修改名称
rename table 新表名 to 旧表名;
-- 修改字符集
alter table user character set utf8 collate utf8_bin;
-- 修改字段类型
alter table 表名 modify 字段名 字段类型;
-- 修改字段名字
alter table 表名 change 原字段名 新字段名 字段类型;
-- 增加字段
alter table 表名 add 字段名 字段类型, add 字段名 字段类型;
-- 删除字段
alter table 表名 drop 字段名;
查
-- 查询建表语句
show create table 表名;
-- 查询表结构
describe 表名;
desc 表名; -- 缩写形式
数据
增
-- 只增加一个
insert to 表名 value(-- 各种属性);
-- 增加多个
insert to 表名 values (),();
删
delete from 表名 where 字段名 = 具体值;
改
update 表名 set 字段名 = 具体值; -- 该字段名的所有具体值都会变为相同的
update 表名 set 字段名 = 具体值2 where 字段名 = 具体值1; -- 具体值1会替换为具体值2
查
-- 查询所有信息
select * from 表名;
-- 查询部分信息
select 字段名1, 字段名2 from 表名;
-- 查询部分信息并且对信息进行限定
select 字段名1, 字段名2 from 表名 where 字段名 = 限定信息;
select的其他作用
-- 计算表达式
select 3*2;
-- 拼接字符串
select concat('字符串1','字符串2');
-- 查看时间
select now();
-- 修建字符串两边的空白
select trim('字符串');
where的详细说明
-- 比较运算符
select 字段名1, 字段名2 from 表名 where 字段名 > 限定信息;
select 字段名1, 字段名2 from 表名 where 字段名 < 限定信息;
select 字段名1, 字段名2 from 表名 where 字段名 != 限定信息;-- 不等于写法1
select 字段名1, 字段名2 from 表名 where 字段名 <> 限定信息; -- 不等于写法2
select 字段名1, 字段名2 from 表名 where 字段名 between 限定信息1 and 限定信息2;
-- 在这个范围中
select 字段名1, 字段名2 from 表名 where 字段名 in (限定信息1, 限定信息2);-- 在这两个限定中
select 字段名1, 字段名2 from 表名 where 字段名 not in (限定信息1, 限定信息2); -- 不在这两个限定中
select 字段名1, 字段名2 from 表名 where 字段名 is null; -- 该字段为空的时候
select 字段名1, 字段名2 from 表名 where 字段名 is not null; -- 该字段为非空的时候
-- 逻辑运算符
select 字段名1, 字段名2 from 表名 where 字段名 > 限定信息 and 字段名 < 限定信息; -- 与n
select 字段名1, 字段名2 from 表名 where 字段名 > 限定信息 or 字段名 < 限定信息; -- 或
select 字段名1, 字段名2 from 表名 where 字段名 > 限定信息 not 字段名 < 限定信息; -- 非
-- like 模糊查询
select 字段名1, 字段名2 from 表名 where 字段名 like '%字符%'; -- %为通配
select 字段名1, 字段名2 from 表名 where 字段名 like '字符_'; -- _为占位 %和_可以混合使用
其他关键词
distinct
-- 过滤重复数据
select distinct(字段名) from 表名;
limit
-- 限制输出个数
select * from 表名 limit 限制个数;-- 分页时的使用select * from 表名 limit 页码, 每页的行数;
order byasc
-- 排序
-- 单列排序
select * from 表名 order by 字段名 desc;-- 以该字段降序
select * from 表名 order by 字段名 asc; -- 以该字段降序
-- 多行排序
select * from 表名 order by 字段名1 asc, 字段名2 desc; -- 以字段1升序为主,当相同时,以字段名2为辅
as 别名
select (字段名1 + 字段名2) as 字段名3 from 表名 order by 字段名3 asc; -- 在查询输出时创建新字段3,其为字段1与字段2的和,且以此为排序的字段
gourp by
-- 对某个字段进行合并同类项,然后分组
select group_concat(字段1) as 字段1, group_concat(字段2) as 字段2, 字段名3 from 表名 group by 字段名3;
分组前的表
| 序号 | 姓名 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 张三 | A |
| 2 | 李四 | A |
| 3 | 王五 | B |
分组后
| 序号 | 姓名 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|
| 1,2 | 张三,李四 | A |
| 3 | 王五 | B |
聚合函数
一般和group by一起用
max
select 字段1 max(字段2) from 表名 group by 字段1; -- 在字段1的分组下,各组中字段2的最大值
min
select 字段1 min(字段2) from 表名 group by 字段1; -- 在字段1的分组下,各组中字段2的最小值
sum
select 字段1 sum(字段2) from 表名 group by 字段1; -- 在字段1的分组下,各组中字段2的总和select min(字段2) from 表名; -- 字段2的总和
avg
select 字段1 avg(字段2) from 表名 group by 字段1; -- 在字段1的分组下,各组中字段2的平均值
count
select 字段1 count(任意东西) from 表名 group by 字段1; -- 在字段1的分组下,各组的个数
执行顺序
(5) SELECT column_name, ...
(1) FROM table_name, ...
(2) [WHERE ...]
(3) [GROUP BY ...]
(4) [HAVING ...]
(6) [ORDER BY ...];
数据完整性
实体完整性
create table 表名( 字段名 字段属性 primary key auto_increment);
primary key定义了该字段为主键,则限定了这个表中,该字段不允许重复
auto_increment意为当该字段的添加值为null的时候,会根据当前表的情况,自己给其配分值,注意:字符串不可以使用。
域完整性
not null
create table 表名( 字段名 字段属性 not null -- 不允许该字段为空);
unique
create table 表名( 字段名 字段属性 unique -- 不允许该字段有重复元素);
注意:unique和not null可以一起使用
参照完整性
外键
create table 当前表(
字段名 字段属性, -- 与正常无异
constraint 外键名 foreign key(字段名) references 外键表(外键表字段)
);
create table 外键表(
外键表字段 字段属性,
外键表解释字段 字段属性
);
图解
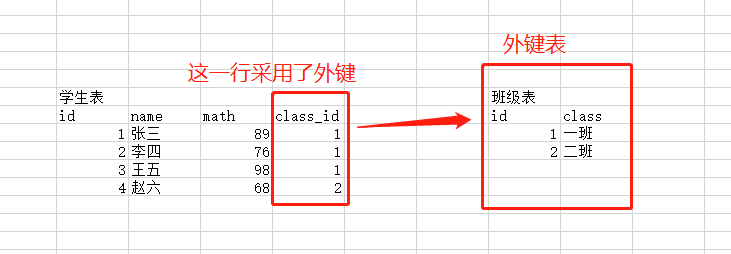
这玩意不好用且浪费数据库性能,很少用
多表设计
一对一
表与表之间的数据为一对一的关系,通常有不可重复的元素进行维护
一对多
表与表之间的关系维护需要在某一个表中单独出一列进行维护
多对多
需要单独建表进行维护
三大范式
第一范式
原子性,表中的字段需要拆分到不能再拆分
第二范式
唯一性,表中需要有一个主键,确保数据之间的差距
第三范式
字段不可冗余,一个表尽量说一件事
三大范式不一定非要遵守
多表查询
连接查询
交叉连接
select * from 表A cross join 表B;
混乱的不行,不知道有啥用
内连接
显式
select * from 表A inner join 表B on 表A.字段 = 表B.字段 where 表A.字段 = '';
隐式
select * from 表A, 表B on where 表A.字段 = 表B.字段 and 表A.字段 = '';
外连接
左
select * from 表A left join 表B on 表A.字段 = 表B.字段
右
select * from 表A right join 表B on 表A.字段 = 表B.字段
子查询
在
where中嵌套使用select语句
select * from 表A where 字段 = (select 字段 from 表B where 字段 = '');
联合查询
相当于or,仅在or不能用的时候使用
select * from 表A where 字段 = ''unionselect * from 表A where 字段 = '';



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号