一、python连接mysql时需要导入第三方库——pymysql
在管理员cmd命令行中 pip install pymysql
二、配置文件
1、图一

2、图二
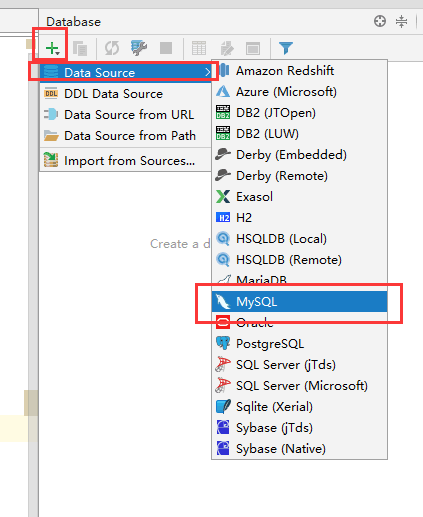
3、图三
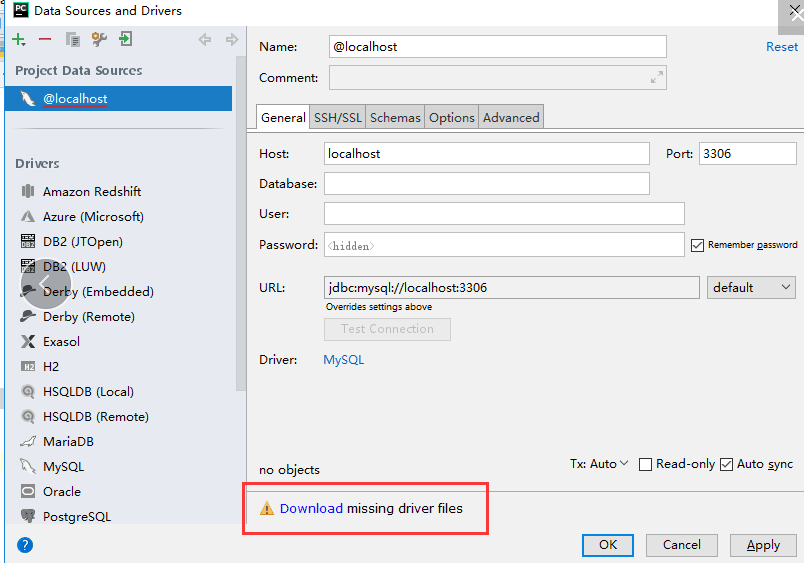
三、基本使用代码
注意:在执行这些代码前,我们需要在MySQL中创建好数据库和表,并且写入数据记录。
1、基本使用
''' 获取用户登录 ''' import pymysql # 1、获取用户登录 name = input('请输入用户名:') pwd = input('请输入密码:') # 判断用户和密码是否正确 # 去数据库查询一下,用户输入的用户名和密码是否正确 # 在python程序中要链接数据库执行sql语句 -->pymysql模块 # 连接数据库,得到一个连接 conn = pymysql.connect( host = '127.0.0.1', port = 3306, user = 'root', password = '123', database = 'day43', charset = 'utf8' # charset=“utf8”,编码不要写成"utf-8" ) # 2 获取光标 cursor = conn.cursor() # 3 执行sql语句 # 3.1 得到sql语句 sql = "select * from userinfo where name = '%s' and pwd = '%s';" %(name,pwd) # print(sql) # 3.2 使用光标对象执行sql语句 ret = cursor.execute(sql) # 关闭 cursor.close() conn.close() # 4 得到结果 if ret: print('登录成功') else: print('登录失败')
注意:

2、mysqlSQL注入

基本语句:预防了恶意注入SQL语句
''' 获取用户登录 ''' import pymysql # 1、获取用户登录 name = input('请输入用户名:') pwd = input('请输入密码:') # 判断用户和密码是否正确 # 去数据库查询一下,用户输入的用户名和密码是否正确 # 在python程序中要链接数据库执行sql语句 -->pymysql模块 # 连接数据库,得到一个连接 conn = pymysql.connect( host = '127.0.0.1', port = 3306, user = 'root', password = '123', database = 'day43', charset = 'utf8' ) # 2 获取光标 cursor = conn.cursor() # 3 执行sql语句 # 3.1 得到sql语句 sql = "select * from userinfo where name = %s and pwd = %s;" # 按照pymysql模块的写法定义好占位符,占位符%s不需要引号 # print(sql) # 3.2 使用光标对象执行sql语句 ret = cursor.execute(sql, [name, pwd]) # 让pymysql模块帮我们拼接SQL语句,执行sql语句 # 关闭 cursor.close() conn.close() # 4 得到结果 if ret: print('登录成功') else: print('登录失败')
四、增删改、查
注意:增删改,涉及数据库的修改,需要提交 conn.commit()
增
import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect( host = '127.0.0.1', port = 3306, user = 'root', password = '123', database = 'day43', charset = 'utf8' ) # 2 获取光标 cursor = conn.cursor() # 3 执行sql语句 # 3.1 得到sql语句 sql = "insert into userinfo(name, pwd) values (%s,%s);" # 按照pymysql模块的写法定义好占位符,占位符%s不需要引号 # print(sql) # 3.2 使用光标对象执行sql语句 ret = cursor.execute(sql, ['Eva_j','456']) # 让pymysql模块帮我们拼接SQL语句,执行sql语句 # 涉及操作数据库的 一定要提交 conn.commit() # 关闭 cursor.close() conn.close()

删
import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect( host = '127.0.0.1', port = 3306, user = 'root', password = '123', database = 'day43', charset = 'utf8' ) # 2 获取光标 cursor = conn.cursor() # 3 执行sql语句 # 3.1 得到sql语句 sql = "delete from userinfo where name = %s;" # 按照pymysql模块的写法定义好占位符,占位符%s不需要引号 # print(sql) # 3.2 使用光标对象执行sql语句 ret = cursor.execute(sql, ['alex']) # 让pymysql模块帮我们拼接SQL语句,执行sql语句 # 涉及操作数据库的 一定要提交 conn.commit() # 关闭 cursor.close() conn.close()

改
import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect( host = '127.0.0.1', port = 3306, user = 'root', password = '123', database = 'day43', charset = 'utf8' ) # 2 获取光标 cursor = conn.cursor() # 3 执行sql语句 # 3.1 得到sql语句 sql = "update userinfo set pwd = %s where name = %s;" # 按照pymysql模块的写法定义好占位符,占位符%s不需要引号 # print(sql) # 3.2 使用光标对象执行sql语句 ret = cursor.execute(sql, ['123','Eva_j']) # 让pymysql模块帮我们拼接SQL语句,执行sql语句 # 涉及操作数据库的 一定要提交 conn.commit() # 关闭 cursor.close() conn.close()

查
1、显示元组为结果的查
import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect( host = '127.0.0.1', port = 3306, user = 'root', password = '123', database = 'day43', charset = 'utf8' ) # 2 获取光标 cursor = conn.cursor() # 3 执行sql语句 # 3.1 得到sql语句 sql = "select * from userinfo;" # 按照pymysql模块的写法定义好占位符,占位符%s不需要引号 # print(sql) # 3.2 使用光标对象执行sql语句 cursor.execute(sql) # 让pymysql模块帮我们拼接SQL语句,执行sql语句 # ret = cursor.fetchall() # 取出所有的数据 # ret = cursor.fetchone() # 取出一条数据 # print(ret) # ret = cursor.fetchone() # print(ret) ret = cursor.fetchmany(2) # 取出n条数据,n为括号内的数值 print(ret) # 关闭 cursor.close() conn.close()
2、显示字典为结果的查,以及指定查询数量和位置的查。
import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect( host = '127.0.0.1', port = 3306, user = 'root', password = '123', database = 'day43', charset = 'utf8' ) # 2 获取光标 cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) # 需要设置默认参数,才可以显示字典 # 3 执行sql语句 # 3.1 得到sql语句 sql = "select * from userinfo;" # 按照pymysql模块的写法定义好占位符,占位符%s不需要引号 # print(sql) # 3.2 使用光标对象执行sql语句 cursor.execute(sql) # 让pymysql模块帮我们拼接SQL语句,执行sql语句 # ret = cursor.fetchall() # 取出所有的数据 # ret = cursor.fetchone() # 取出一条数据 # print(ret) # ret = cursor.fetchone() # print(ret) ret = cursor.fetchmany(2) # 取出n条数据,n为括号内的数值 print(ret) # 关闭 cursor.close() conn.close()
# 查询指定数量的数据
ret = cursor.fetchmany(3)
print(ret)
print(cursor.fetchone())
print(cursor.fetchone())
# cursor.scroll(0, mode='absolute') # 绝对位置,你让光标移动到哪里
# cursor.scroll(-1, mode='relative') # 相对位置,基于光标当前位置移动
print(cursor.fetchone())
五、回滚
import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect( host = '127.0.0.1', port = 3306, user = 'root', password = '123', database = 'day43', charset = 'utf8' ) # 2 获取光标 cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) # 3 执行sql语句 # 3.1 得到sql语句 sql = "insert into userinfo(name, pwd) VALUES (%s,%s);" # 按照pymysql模块的写法定义好占位符,占位符%s不需要引号 # print(sql) # 3.2 使用光标对象执行sql语句 ret = cursor.execute(sql,['ritian','9524']) # 让pymysql模块帮我们拼接SQL语句,执行sql语句 conn.rollback() # 回滚,就是撤销上面增加的命令 conn.commit() # 关闭 cursor.close() conn.close()
六、获取刚才插入的ID值
# 创建一个出版社和书籍 sql1 = "insert into p(name) values ('西里出版社');" cursor.lastrowid # 获取刚才插入到数据库的id值 sql2 = "insert into book(title,p_id) values (%s,%s);" conn.rollback() # 回滚 conn.commit() # 关闭 cursor.close() conn.close()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号