010、分区表
分区表的介绍
分区功能并不是在存储引擎层完成的,因此不只有innodb存储引擎支持分区,常见的存储引擎myisam,NDB等都支持。但也并不是所有的存储引擎都支持,如csv,federated,merge等就不支持。
Mysql数据库在5.1版本时添加了对于分区的支持,这个过程将一个表或者索引物分解为多个更小,更可管理的部分。从逻辑上讲,只有一个表或者一个索引,但是在物理上这个表或者索引可能由数十个物理分区组成,每个分区都是独立的对象,可以独自处理,也可以作为一个更大对象的一部分进行处理。
Mysql数据库支持的分区类型:水平分区,并不支持垂直分区。此外mysql数据库的分区是局部分区索引,一个分区中既存放了数据,又存放了索引。
分区对于某些sql语句性能可能会带来提高,但是分区主要用于高可用性,利于数据库的管理。在OLTP应用中,对于分区的使用应该非常小心。
总之,要了解分区是如何工作的,否则一味地创建,只会对性能产生负面影响。
表分区是一把双刃剑,带来查询性能的提升,但也会使IO过高。
Mysql数据库支持以下几种类型的分区:
- Range分区:行数据基于属于一个给定连续区间的列值放入分区。mysql数据库5.5开始支持range columns的分区。
- List分区:和range分区类似,只是list分区面向的是离散的值。mysql数据库5.5开始支持list columns的分区。
- Hash分区:根据用户自定义的表达式的返回值来进行分区,返回值不能为负数。
- Key分区:根据mysql数据库提供的哈希函数来进行分区。该类型的分区使用的不多。
- MySQL5.5之后又引起了column分区,包括5.5。该版本之前只支持int类型的列分区,该版本之后,支持int和字符型分区。

分区表的实验
实验1
创建分区的注意事项:
如果表中存在主键或者是唯一索引时,分区列必须是唯一索引的一个组成部分。
创建分区表(注意观察报错信息):
mysql> use test;
Database changed
mysql> drop table t1;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
mysql> create table t1(
-> col1 int not null,
-> col2 date not null,
-> col3 int not null,
-> col4 int not null,
-> unique key (col1,col2)
-> )
-> partition by hash(col3)
-> partitions 4;
ERROR 1503 (HY000): A PRIMARY KEY must include all columns in the table's partitioning function以上报错提示主键必须包含表的分区功能中的所有列,换一种说法就是分区列必须是主键或者唯一索引的一部分。
分区的原则:分区列的选择必须是主键或者主键的一部分。分区列的选择,必须是整型字段 (mysql 5.1)。
mysql> create table t1(
-> col1 int not null,
-> col2 date not null,
-> col3 int not null,
-> col4 int not null,
-> unique key (col1,col2)
-> )
-> partition by hash(col2)
-> partitions 4;
ERROR 1659 (HY000): Field 'col2' is of a not allowed type for this type of partitioning修改为按col1分区之后再次创建,并查看数据文件:
mysql> create table t1(
-> col1 int not null,
-> col2 date not null,
-> col3 int not null,
-> col4 int not null,
-> unique key (col1,col2)
-> )
-> partition by hash(col1)
-> partitions 4;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.14 sec)
[root@ning test]# pwd
/u01/data/mysql/test
[root@ning test]# ls -l|grep t1
-rw-rw----. 1 mysql mysql 8650 Apr 7 22:09 t1.frm
-rw-rw----. 1 mysql mysql 32 Apr 7 22:09 t1.par
-rw-rw----. 1 mysql mysql 98304 Apr 7 22:09 t1#P#p0.ibd
-rw-rw----. 1 mysql mysql 98304 Apr 7 22:09 t1#P#p1.ibd
-rw-rw----. 1 mysql mysql 98304 Apr 7 22:09 t1#P#p2.ibd
-rw-rw----. 1 mysql mysql 98304 Apr 7 22:09 t1#P#p3.ibd
--分区的号从p0开始一直到pN实验2
唯一索引是允许null值的,并且分区列只要是唯一索引的一个组成部分,不需要整个唯一索引列都是分区列。
mysql> create table t(
-> col1 int null,
-> col2 date null,
-> col3 int null,
-> col4 int null,
-> unique key(col1,col2,col3,col4) --唯一索引允许null值
-> )
-> partition by hash(col3)
-> partitions 4;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.11 sec)建表时没有指定主键,唯一索引时,可以指定任何一个列为分区列:
mysql> create table t(
-> col1 int null,
-> col2 date null,
-> col3 int null,
-> col4 int null
-> )
-> partition by hash(col3)
-> partitions 4;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.33 sec)range分区
range分区是最常用的一种分区类型,例如:当id<10时,数据插入p0分区,当 10=<id<20插入p1分区:
mysql> create table t(
-> id int
-> )
-> partition by range(id)(
-> partition p0 values less than(10), --注意不要漏掉less关键字
-> partition p1 values less than(20)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.12 sec)插入测试数据:
mysql> insert into t select 9; ---9在p0分区
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.08 sec)
Records: 1 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> insert into t values(10); ---10在p1分区
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> insert into t select 11; ---11在p1分区
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.04 sec)
Records: 1 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0如何查看插入的数据在哪个分区:
mysql> use information_schema;
Database changed
mysql> desc PARTITIONS;
mysql> select TABLE_SCHEMA,TABLE_NAME,PARTITION_NAME,TABLE_ROWS from PARTITIONS where TABLE_SCHEMA='test';
+--------------+------------+----------------+------------+
| TABLE_SCHEMA | TABLE_NAME | PARTITION_NAME | TABLE_ROWS |
+--------------+------------+----------------+------------+
| test | su | NULL | 0 |
| test | t | p0 | 1 |
| test | t | p1 | 2 |
| test | t3 | NULL | 2 |
+--------------+------------+----------------+------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from t partition(p0);
+------+
| id |
+------+
| 9 |
+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from t partition(p1);
+------+
| id |
+------+
| 10 |
| 11 |
+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)添加分区:
mysql> alter table t add partition(
-> partition p2 values less than(30));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.08 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0拆分分区:
mysql> alter table t reorganize partition p0 into(
-> partition p3 values less than(5),
-> partition p4 values less than(10)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.12 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
--注意:原来分区p0的范围是[负无穷-10),所以新拆分的分区范围值最大不能超过10。
[root@localhost test]# ls
t.frm t.par t#P#p0.ibd t#P#p1.ibd t#P#p2.ibd
[root@localhost test]# ls
t.frm t.par t#P#p1.ibd t#P#p2.ibd t#P#p3.ibd t#P#p4.ibd
--拆分分区之后,数据文件也发生变化合并分区:
--对列表分区来说,重新组织的分区必须是相邻的分区:
mysql> alter table t reorganize partition p2,p3,p4 into(
-> partition a values less than(10),
-> partition b values less than(50)
-> );
ERROR 1519 (HY000): When reorganizing a set of partitions they must be in consecutive order
--我实际上相邻在分区是p1,p3,p4
--新的分区范围必须和原本的分区相同,如果不同就会报错:
mysql> alter table t reorganize partition p1,p3,p4 into(
-> partition a values less than(10),
-> partition b values less than(50)
-> );
ERROR 1493 (HY000): VALUES LESS THAN value must be strictly increasing for each partition
mysql> alter table t reorganize partition p1,p3,p4 into(
-> partition a values less than(10),
-> partition b values less than(15)
-> );
ERROR 1520 (HY000): Reorganize of range partitions cannot change total ranges except for last partition where it can extend the range
--改为相同(即原来的p0,p1分区)以后,负无穷 - 20,重新组织分区:
mysql> alter table t reorganize partition p1,p3,p4 into(
-> partition pa values less than(5),
-> partition pb values less than(20)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.21 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0拆分分区和合并分区统称为重新组织分区,原则是:
- 重新组织的分区是由连续的分区组成;
- 重新组织的分区范围要和原来的分区范围保持一致。
创建分区表的时候,一定要指定最大分区范围。如不指定,插入超出范围值的时候,会报错误:
mysql> insert into t select 40;
ERROR 1526 (HY000): Table has no partition for value 40
--添加最大范围分区,对分区添加一个 maxvalue 值的分区, maxvalue 可以理解为正无穷
mysql> alter table t add partition(
-> partition p3 values less than maxvalue
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.13 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> insert into t select 40;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
Records: 1 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
注意:增加分区只能在最大端增加,所以增加了maxvalue分区之后,无法再增加分区:
mysql> alter table t add partition(
-> partition p4 values less than(50)
-> );
ERROR 1481 (HY000): MAXVALUE can only be used in last partition definitionrange分区的使用场景:
主要用于日期列的分区,如对于销售类的表,可以根据年份来存放销售记录:
mysql> use test;
Database changed
mysql> create table sales(
-> money int not null,
-> date datetime
-> )
-> partition by range(year(date))(
-> partition p2014 values less than(2015),
-> partition p2015 values less than(2016),
-> partition p2016 values less than(2017)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.21 sec)
mysql> insert into sales select 100,'2014-01-01';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.06 sec)
Records: 1 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> insert into sales select 100,'2014-02-01';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 1 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> insert into sales select 100,'2015-01-01';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.03 sec)
Records: 1 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> insert into sales select 100,'2016-01-01';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
Records: 1 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0这样创建的好处是:便于对sales这张表的管理,如果我们要删除2014年的数据,
第一种写法:
delete from sales where date>='2014-01-01' and date<='2014-12-31';
第二种写法:
delete from sales where date>='2014-01-01' and date<'2015-01-01';
正确:第一种,第一种写法只需要扫描p2014一个分区。第二种写法需要扫描p2014和p2015两个分区。
删除分区:
更简单的做法是:需要删除2014年数据所在的分区即可:
mysql> alter table sales drop partition p2014;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.11 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> use information_schema
Database changed
mysql> select table_name,partition_name,table_rows from partitions where table_schema='test' and table_name='sales';
+------------+----------------+------------+
| table_name | partition_name | table_rows |
+------------+----------------+------------+
| sales | p2015 | 0 |
| sales | p2016 | 0 |
+------------+----------------+------------+
2 rows in set (0.07 sec)list分区
List分区和range分区非常相似,只是分区列的值是离散的,而非连续的。不同于range分区中定义的values less than语句,list 分区使用value in,所以每个分区的值是离散的,只能是定义的值。
mysql> use test;
Database changed
mysql> drop table t;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.11 sec)
mysql> create table t(
-> a int,
-> b int
-> )
-> partition by list(b)(
-> partition p0 values in(1,3,5,7,9),
-> partition p1 values in(0,2,4,6,8)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.06 sec)插入测试数据:
mysql> insert into t values(1,1);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> insert into t values(1,2);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.02 sec)
mysql> insert into t values(1,3);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> insert into t values(1,4);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from t partition(p0);
+------+------+
| a | b |
+------+------+
| 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 3 |
+------+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from t partition(p1);
+------+------+
| a | b |
+------+------+
| 1 | 2 |
| 1 | 4 |
+------+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)增加分区:
--新增加的分区值不能包含原有分区的值:
mysql> alter table t add partition(
-> partition p3 values in(1)
-> );
ERROR 1495 (HY000): Multiple definition of same constant in list partitioning
mysql> alter table t add partition(
-> partition p2 values in(10,11)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.13 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0重新组织分区:拆分分区
mysql> select * from t;
+------+------+
| a | b |
+------+------+
| 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 2 |
| 1 | 10 |
+------+------+
3 rows in set (0.08 sec)
mysql> alter table t reorganize partition p0 into(
-> partition pa values in(3,5),
-> partition pb values in(7,9)
-> );
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.13 sec)
Records: 1 Duplicates: 1 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from t;
+------+------+
| a | b |
+------+------+
| 1 | 2 |
| 1 | 10 |
+------+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
--观察以上现象,发现数据丢失,合并和拆分分区重新定义的枚举值可以不是原来的值。
--如果原来的枚举值包含了数据而新合并或拆分的分区枚举值又不不包含原来的枚举值会造成数据丢失。重新组织分区:合并分区
--不能跨分区
mysql> alter table t reorganize partition pa,p2 into(
-> partition pc values in(1,3,5,10,11,30)
-> );
ERROR 1519 (HY000): When reorganizing a set of partitions they must be in consecutive order
mysql> alter table t reorganize partition pb,p1 into(
-> partition pc values in(0,2,4,6,8,7,9,30)
-> );
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.16 sec)
Records: 1 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0合并和拆分分区重新定义的枚举值可以不是原来的值,如果原来的枚举值包含了数据而新合并或拆分的分区枚举值又不不包含原来的枚举值会造成数据丢失。
删除分区,数据会一起删除:
mysql> alter table t drop partition pc;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.20 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0对比myisam和innodb不同存储引擎对于分区插入效果的影响:
Myisam:
mysql> create table t(
-> a int,
-> b int
-> )engine=myisam
-> partition by list(b)(
-> partition p0 values in(1,3,5,7,9),
-> partition p1 values in(0,2,4,6,8)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
mysql> insert into t values(1,1),(1,2),(1,10),(1,3);
ERROR 1526 (HY000): Table has no partition for value 10
mysql> select * from t;
+------+------+
| a | b |
+------+------+
| 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 2 |
+------+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
--可以发现,myisam引擎的表,从不符合条件的数据开始,之前的数据被插入到表中,之后的数据即使符合条件,也没有被插入到表中。Innodb:
mysql> create table t(
-> a int,
-> b int
-> )engine=innodb
-> partition by list(b)(
-> partition p0 values in(1,3,5,7,9),
-> partition p1 values in(0,2,4,6,8)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.09 sec)
mysql> insert into t values(1,1),(1,2),(1,10);
ERROR 1526 (HY000): Table has no partition for value 10
mysql> select * from t;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
--数据没有被插入到表中总结:因此在使用分区时,也需要对不同存储引擎支持的事务特性进行考虑。
Hash 分区
按照mod取余来进行分区,mod(column,n),column为分区列,n为分区数量。
Hash分区的目的是将数据均匀地分布到预先定义的各个分区中,保证各分区的数据数量大致都是一样的。在range和list分区中,必须明确指定一个给定的列值或列值集合应该保存在哪个分区中,而在hash分区中,mysql自动完成这些工作,你所要做的只是基于将要被哈希的列值指定一个列值或表达式,以及指定被分区的表将要被分割成的分区数量。
partition by hash(expr):expr是一个返回整数的表达式,也可以是字段类型为整形的列名称。
创建一个hash分区表,按日期列b进行分区:
mysql> create table t_hash(
-> a int,
-> b date
-> )
-> partition by hash(year(b))
-> partitions 4;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.14 sec)插入测试数据:
mysql> insert into t_hash select 1,'2010-04-01';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.09 sec)
Records: 1 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0插入的数据会被放在下列分区中:
mysql> select mod(year('2010-04-01'),4);--数字4代表4个分区
+---------------------------+
| mod(year('2010-04-01'),4) |
+---------------------------+
| 2 |
+---------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)验证数据在哪个分区中:
mysql> select * from t_hash partition(p2);
+------+------------+
| a | b |
+------+------------+
| 1 | 2010-04-01 |
+------+------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select TABLE_NAME,PARTITION_NAME,TABLE_ROWS from information_schema.partitions where table_schema='test' and table_name='t_hash';
+------------+----------------+------------+
| TABLE_NAME | PARTITION_NAME | TABLE_ROWS |
+------------+----------------+------------+
| t_hash | p0 | 0 |
| t_hash | p1 | 0 |
| t_hash | p2 | 1 |
| t_hash | p3 | 0 |
+------------+----------------+------------+
4 rows in set (0.03 sec)HASH分区增加和收缩分区:
增加和收缩分区后原来的数据会根据现有的分区数量重新分布。
增加分区可以通过ALTER TABLE ... ADD PARTITION PARTITIONS num来增加分区,这里是num是在原先基础上再增加的分区数量:
mysql> alter table t_hash add partition partitions 2;
Query OK, 4 rows affected (0.27 sec)
Records: 4 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> show create table t_hash \G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: t_hash
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `t_hash` (
`a` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`b` date DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
/*!50100 PARTITION BY HASH (year(b))
PARTITIONS 6 */
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from t_hash partition(p0);
+------+------------+
| a | b |
+------+------------+
| 1 | 2010-04-01 |
+------+------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)HASH分区不能删除分区,所以不能使用DROP PARTITION操作进行分区删除操作,只能通过ALTER TABLE ... COALESCE PARTITION num来合并分区,这里的num是减去的分区数量:
mysql> alter table t_hash coalesce partition 3;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.25 sec)
Records: 1 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> show create table t_hash \G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: t_hash
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `t_hash` (
`a` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`b` date DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
/*!50100 PARTITION BY HASH (year(b))
PARTITIONS 3 */
1 row in set (0.00 sec)Columns分区
Mysql数据库5.5版本开始支持columns分区,可视为range分区和list分区的一种进化。
columns分区可以直接使用非整型的数据进行分区,分区根据类型直接比较而得,不需要转化为整型。其次,range columns分区可以对多个列的值进行分区。
COLUMNS分区支持以下的数据类型:
- 所有的整型类型,如int,smallint,tinyint,bigint。float和decimal则不支持。
- 日期类型,如date和datetime。其余的日期类型不支持。
- 字符串类型,如char、varchar、 binary、varbinary。blob和text类型不支持。
创建columns分区的表:
mysql> create table t_columns_range(
-> a int,
-> b datetime
-> )
-> partition by range columns(b)(
-> partition p0 values less than('2009-01-01'),
-> partition p1 values less than('2010-01-01')
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.11 sec)
mysql> insert into t_columns_range select 1,'2008-12-30';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.07 sec)
Records: 1 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> insert into t_columns_range select 1,'2009-12-30';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.06 sec)
Records: 1 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from t_columns_range partition(p0);
+------+---------------------+
| a | b |
+------+---------------------+
| 1 | 2008-12-30 00:00:00 |
+------+---------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from t_columns_range partition(p1);
+------+---------------------+
| a | b |
+------+---------------------+
| 1 | 2009-12-30 00:00:00 |
+------+---------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)Key分区
和hash分区相似,不同在于,hash分区使用用户定义的函数进行分区,key分区使用mysql数据库提供的函数进行分区。NDB cluster引擎使用MD5函数分区,对于其他存储引擎,mysql数据库使用其内部的哈希函数,这些函数是基于与password()一样的运算法则。key用得不多,大部分情况下,使用其他分区。
创建key分区的表:
mysql> create table t_key(
-> a int,
-> b datetime
-> )
-> partition by key(b)
-> partitions 4;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.17 sec)子分区
在分区的基础上再进行分区,有时也称这种分区为复合分区,mysql数据库允许在range和list的分区上再进行hash或者是key的子分区。
创建含有子分区的分区表:
mysql> create table ts(
-> a int,
-> b date
-> )
-> partition by range(year(b)) --主分区按range分区
-> subpartition by hash(to_days(b)) --子分区按hash分区
-> subpartitions 2( --子分区有2个
-> partition p0 values less than(1990), --主分区有p0、p1、p2三个
-> partition p1 values less than(2000),
-> partition p2 values less than maxvalue
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.26 sec)查看该表的数据文件:
[root@localhost test]# ls -l|grep ts
-rw-rw----. 1 mysql mysql 8578 Apr 12 15:24 ts.frm
-rw-rw----. 1 mysql mysql 96 Apr 12 15:24 ts.par
-rw-rw----. 1 mysql mysql 98304 Apr 12 15:24 ts#P#p0#SP#p0sp0.ibd
-rw-rw----. 1 mysql mysql 98304 Apr 12 15:24 ts#P#p0#SP#p0sp1.ibd
-rw-rw----. 1 mysql mysql 98304 Apr 12 15:24 ts#P#p1#SP#p1sp0.ibd
-rw-rw----. 1 mysql mysql 98304 Apr 12 15:24 ts#P#p1#SP#p1sp1.ibd
-rw-rw----. 1 mysql mysql 98304 Apr 12 15:24 ts#P#p2#SP#p2sp0.ibd
-rw-rw----. 1 mysql mysql 98304 Apr 12 15:24 ts#P#p2#SP#p2sp1.ibd以上写法看起来逻辑混乱,以下是子分区的正确写法(能一眼看出怎么分区的):
mysql> create table ts(
-> a int,
-> b date
-> )
-> partition by range(year(b)) --主分区按range分区
-> subpartition by hash(to_days(b))( --子分区按hash分区
-> partition p0 values less than(2014)( --第一个主分区
-> subpartition s0, --第一个主分区的子分区1
-> subpartition s1 --第一个主分区的子分区2
-> ),
-> partition p1 values less than(2015)( --第二个主分区
-> subpartition s2,
-> subpartition s3
-> ),
-> partition p2 values less than maxvalue( --第三个主分区
-> subpartition s4,
-> subpartition s5
-> )
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.25 sec)
--使用subpartition来明确定义任何分区,那么就必须定义所有的子分区子分区的建立需要注意的问题:
每个子分区的数量必须相同,如果在一个分区表上的任何分区上,使用subpartition来明确定义任何分区,那么就必须定义所有的子分区,并且子分区的名称不能相同。
分区中的null值
Mysql数据库允许对null值做分区,总是把null值视为小于任何一个非null值,这和mysql数据库中对于null的order by 的排序是一样的。因此对于不同的分区类型,mysql数据库对于null值的处理是不一样的。
- 对于range分区,如果分区列插入null值,则mysql数据库会将该值放入最左边的分区。
- list:针对null值的处理,指定哪里去哪里。
- hash分区:针对null值的处理,把null值当做0来处理。
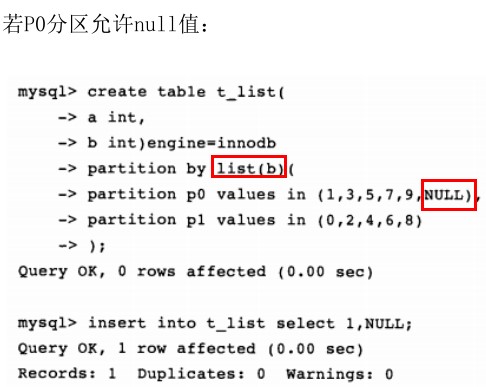
Hash和key分区对于null的处理方式和range分区,list分区不一样。任何分区函数都会将含有null值的记录返回0。
分区的性能:
是把双刃剑,对于使用innodb存储引擎作为OLTP应用的表,在使用分区时,应该十分小心,设计时要确认数据的访问模式,否则在OLTP应用下分区可能不仅不会带来查询速度的提高,反而可能会使你的应用执行得更慢。所以分区表,在前期就要设计好。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号