004、MySQL存储引擎和三大特性
一、修改MySQL表的存储引擎
1、在test库中创建表,并查看存储引擎
[root@localhost ~]# mysql -uroot -p
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| test |
+--------------------+
4 rows in set (0.08 sec)
mysql> use test;
Database changed
mysql> show tables;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
mysql> create table t1(id int) engine=myisam;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.14 sec)
mysql> create table t2(id int) engine=myisam;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> create table t3(id int) engine=myisam;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)查看表的存储引擎(就是查看建表语句,\G是用容易看的方式列出):
mysql> show create table t1 \G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: t1
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `t1` (
`id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=MyISAM DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
ERROR:
No query specified修改表的存储引擎,并再次查看:
mysql> alter table t1 engine=innodb;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.13 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> show create table t1 \G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: t1
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `t1` (
`id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
ERROR:
No query specified若有几百张表需要改存储引擎,则需要通过脚本完成。
2、系统层面执行数据库命令
[root@localhost ~]# mysql -uroot -proot -e "show databases";
Warning: Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| test |
+--------------------+3、information_schema库:信息库
相当于数据字典库。
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| test |
+--------------------+
4 rows in set (0.04 sec)
mysql> use information_schema;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed该数据库下,所有的表不能增删改等操作,只能查询。一般查看tables表:
mysql> desc tables;
+-----------------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-----------------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| TABLE_CATALOG | varchar(512) | NO | | | |
| TABLE_SCHEMA | varchar(64) | NO | | | |
| TABLE_NAME | varchar(64) | NO | | | |
| TABLE_TYPE | varchar(64) | NO | | | |
| ENGINE | varchar(64) | YES | | NULL | |
| VERSION | bigint(21) unsigned | YES | | NULL | |
| ROW_FORMAT | varchar(10) | YES | | NULL | |
| TABLE_ROWS | bigint(21) unsigned | YES | | NULL | |
| AVG_ROW_LENGTH | bigint(21) unsigned | YES | | NULL | |
| DATA_LENGTH | bigint(21) unsigned | YES | | NULL | |
| MAX_DATA_LENGTH | bigint(21) unsigned | YES | | NULL | |
| INDEX_LENGTH | bigint(21) unsigned | YES | | NULL | |
| DATA_FREE | bigint(21) unsigned | YES | | NULL | |
| AUTO_INCREMENT | bigint(21) unsigned | YES | | NULL | |
| CREATE_TIME | datetime | YES | | NULL | |
| UPDATE_TIME | datetime | YES | | NULL | |
| CHECK_TIME | datetime | YES | | NULL | |
| TABLE_COLLATION | varchar(32) | YES | | NULL | |
| CHECKSUM | bigint(21) unsigned | YES | | NULL | |
| CREATE_OPTIONS | varchar(255) | YES | | NULL | |
| TABLE_COMMENT | varchar(2048) | NO | | | |
+-----------------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+查看表名,表类型,存储引擎:
mysql> select TABLE_NAME,TABLE_TYPE,ENGINE from tables where TABLE_NAME in ('t1','t2','t3');
+------------+------------+--------+
| TABLE_NAME | TABLE_TYPE | ENGINE |
+------------+------------+--------+
| t1 | BASE TABLE | InnoDB |
| t2 | BASE TABLE | MyISAM |
| t3 | BASE TABLE | MyISAM |
+------------+------------+--------+
3 rows in set (0.07 sec)查看前n行:
mysql> select TABLE_NAME,TABLE_TYPE,ENGINE from tables limit 3;
+---------------------------------------+-------------+--------+
| TABLE_NAME | TABLE_TYPE | ENGINE |
+---------------------------------------+-------------+--------+
| CHARACTER_SETS | SYSTEM VIEW | MEMORY |
| COLLATIONS | SYSTEM VIEW | MEMORY |
| COLLATION_CHARACTER_SET_APPLICABILITY | SYSTEM VIEW | MEMORY |
+---------------------------------------+-------------+--------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)去除框框格式显示:
[root@localhost ~]# mysql -uroot -proot -s -e "select TABLE_NAME,TABLE_TYPE,ENGINE,TABLE_SCHEMA from information_schema.tables where TABLE_NAME in ('t1','t2','t3')"
Warning: Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
TABLE_NAME TABLE_TYPE ENGINE TABLE_SCHEMA
t1 BASE TABLE InnoDB test
t2 BASE TABLE MyISAM test
t3 BASE TABLE MyISAM test去除查询结果中的框框和标题,并将查询结果放到文件中:
[root@localhost ~]# mysql -uroot -proot -s -e "select TABLE_NAME,TABLE_TYPE,ENGINE,TABLE_SCHEMA from information_schema.tables where TABLE_NAME in ('t1','t2','t3')"|grep -v TABLE_NAME > a.txt
[root@localhost ~]# cat a.txt
t1 BASE TABLE InnoDB test
t2 BASE TABLE MyISAM test
t3 BASE TABLE MyISAM test批量修改表存储引擎的脚本:
#目的:批量修改表存储引擎
#作者:张三
#日期:2020.10.20
mysql -uroot -proot -s -e "select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='test' and engine='myisam'"|grep -v TABLE_NAME > a.txt
cat /dev/null > b.txt
for a in `cat a.txt`
do
echo "alter table test.$a engine=innodb;" >> b.txt
done;二、innodb存储引擎的三大特性
1、insert buffer
在应用程序中行记录的插入顺序是按照主键递增顺序插入的,插入聚集索引一般是顺序的,不需要磁盘随机读取。
create table t (id int auto_increment,name varchar(5),primary key (id));
行记录是按照id执行顺序存放,这种情况下插入操作很快,数据页的存放还是顺序的。
非聚集索引(secondary index)插入:
Create table t (id int auto_increment,name varchar(5),primary key (id),key(name));
innodb存储引擎表是索引组织的,因此数据即索引,索引即数据。那么数据段即为B+树的叶节点(leaf node segment),索引段即为B+树的非页节点(non-leaf node segment)。
非聚集索引(就是普通索引)叶子节点的插入不再是顺序的。需要离散地访问非聚集索引页,插入性能下降。
原理:B+树的特性决定了非聚集索引插入的离散性。
工作方式:
对于非聚集索引的插入或者update,purge等操作,并非每一次直接插入索引页,而是把若干对于同一页面的更新缓存起来合并为一次性操作,随机IO—顺序IO 避免随机IO带来性能消耗,提高写性能。--这就是insert buffer的目的。
原理:
a:先判断插入的非聚集索引页是否在缓冲池中
b:如果在,直接插入
c:如果不在,先放入插入缓冲区中,欺骗数据库,这个非聚集的索引已经插入到叶子节点了。
d:然后再以一定频率执行插入缓冲和非聚集索引页子节点的合并操作
插入缓冲使用的满足条件:
1.索引是辅助索引,即不能是主键。
2.索引不是唯一的。
注意:在写密集的情况下,插入缓冲会占用过多的缓冲池内存,默认最大可以占用1/2的缓冲池内存。
2、double write
Double write 带给innodb存储引擎的是数据的可靠性。目的是防止数据库崩溃的时候页损坏,无法恢复数据库数据。
起因:当数据库宕机时,可能发生数据库写一个页面,而这个页只写了一部分,这就是所谓的partial page write(部分页写).
恢复原理:mysql在恢复的时候是通过检查page的checksum来决定这个page是否需要恢复的,checksum就是当前这个page最后一个事务的事务号,如系统找不到checksum,mysql就无法对该行数据执行写入操作。
Double write 是innodb在tablespace上的128个页(2个区)2MB;
原理:为了解决partial page write问题,当mysql将脏数据flush 到data file的时候,先使用memcopy将脏数据复制到内存中的double write buffer,之后通过double write buffer再分2次,每次写入1MB到共享表空间(该过程是顺序写),然后马上调用fsync函数,同步到磁盘上,避免缓冲带来的问题,在这个过程中,doublewrite是顺序写,开销并不大,在完成doublewrite写入后,再将double write buffer写入各表空间文件,这时是离散写入。
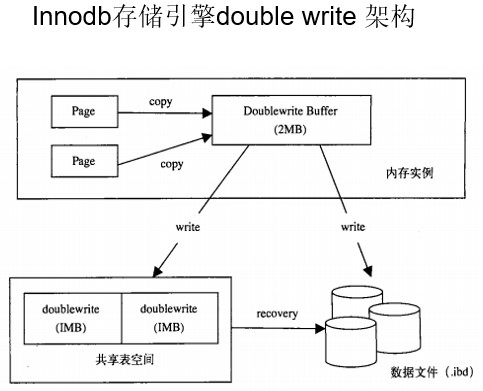
结果:
如果操作系统在将页写入磁盘的过程中崩溃了,在恢复过程中,innodb存储引擎可以从共享表空间中的doublewrite中找到该页的一个副本,将其拷贝到表空间文件,再应用重做日志。
查看数据库相关参数:mysql> show variables;
mysql> show variables like '%double%';
+--------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+--------------------+-------+
| innodb_doublewrite | ON |
+--------------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
--巡检过程中,需要关注double write是否开启3、自适应哈希索引(adaptive hash index)
Innodb存储引擎会监控对表上索引的查找,如果观察到建立哈希索引可以带来速度上的提升,则建立哈希索引,所以称之为自适应的。
自适应哈希索引通过缓冲池的B+树构造而来,因此建立的速度很快。而且不需要将整个表都建hash index,innodb会自动根据访问频率和模式来为某些页建立哈希索引。
启用自适应hash index后,读写速度提高2倍,辅助索引的连接操作,性能提高5倍。
设计思想:数据库自优化,不需我们自己来做!
mysql> show variables like '%hash%';
+-------------------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+-------------------------------+-------+
| innodb_adaptive_hash_index | ON |
| metadata_locks_hash_instances | 8 |
+-------------------------------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql中,一个页的大小16k,64个连续的页组成区(64*16=1M),一个段相当于一个表。表空间>段>区>页>行信息。
innodb存储引擎磁盘读写的最小单位是page,页。
一张大表可以一次性申请4个区,也就是4M。
缓存命中率=内存读/(内存读+磁盘读)。
脏数据:内存(buffer pool)中的数据和磁盘中的数据不一致,这时内存中的数据叫做脏数据。
内存中buffer的三种状态:
1、free 空闲的,一般数据库运行中,这种状态的buffer是不存在的,基本上已经使用。
2、clean,考虑LRU原则,即最近最少被使用的buffer,当需要将磁盘中的数据读入缓存中时,最先被覆盖。
3、dirty 脏数据,还没写入磁盘中的buffer。
数据库内存中链的结构:单向链和双向链。根据数据库内存buffer的状态分为:
1、free list=把free状态的buffer给串起来
2、LRU list=把clean状态的buffer给串起来
2、LRU list=把clean状态的buffer给串起来
3、flush list=把脏数据块串起来,把最近最少被脏的buffer串起来,写入磁盘中。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号