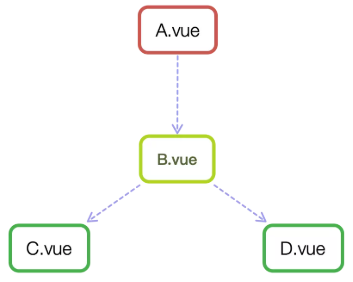
如上图所示,A和B 、 B和C、B和D都是父子关系,C和D是兄弟关系,A和C 是隔代关系
针对不同的使用场景,如何选择行之有效的通信方式? 这是我们要探讨的。vue组件间通信的集中方式,如props、$emit/$on、 vuex、$parent/$children 等
方法一、props / $emit
父组件A通过props的方式向子组件B传递,B to A 通过在B组件中$emit, A 组件中v-on的方式实现。
1. 父组件向子组件传值
接下来我们通过一个例子,说明父组件如何向子组件传递值: 在子组件Son.vue 中如何获取组件Parent.vue 中的数据 users: ['xz,'xp','mimi']
// Parent.vue 父组件 <template> <div id="app"> <Children :users="users"></Children> </div> </template> <script> import Children from './Children' export default { name: "Parent", components: { Children }, data() { return { users: ['zx','zt','zy'] } } } </script> <style scoped> </style>
// 子组件 <template> <div class="hello"> <ul> <li v-for="user in users">{{user}} 我问问</li>// 遍历传递过来的值,然后呈现到页面 </ul> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: "children", props:{ users: { type: Array, required: true } } } </script> <style scoped> </style>

总结: 父组件通过props 向下传递数据给子组件。 注:组件中的数据共有三种形式: data、props、computed
2. 子组件向父组件传值(通过事件形式)$emit
// 子组件 children.vue <template> <div class="hello"> <!-- <ul>--> <!-- <li v-for="user in users">{{user}} 我问问</li>// 遍历传递过来的值,然后呈现到页面--> <!-- </ul>--> <button @click="toParamParent">子向父传值</button> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: "children", // props:{ // users: { // type: Array, // required: true // } // }, methods: { toParamParent() { this.$emit('childrenToParent','ni hao mimi') } } } </script> <style scoped> </style>
// 父组件 <style> #app { margin: 100px; } button { padding: 10px; background: blue; color: #fff; margin:20px; } </style> <template> <div id="app"> <!-- <Children :users="users"></Children>--> <Children @childrenToParent="updateHtml"></Children> <h1>{{title}}</h1> <h2>{{childrenParam}}</h2> </div> </template> <script> import Children from './Children' export default { name: "Parent", components: { Children }, data() { return { users: ['zx','zt','zy'], title: '触发button, 子组件传递数据', childrenParam: '' } }, methods: { updateHtml(e){ // console.log(e) e是传递过来的数据 'ni hao mimi' this.childrenParam = e } } } </script> <style scoped> </style>

总结: 子组件通过events给父组件发送消息,实际上就是子组件把自己的数据发送到父组件
方法二、 bus组件通信 $emit、$on
这种方法通过一个空的Vue实例作为中央事件总线(事件中心), 用它来出发事件和监听事件,巧妙二轻量的实现了任何组件间的通信,包括父子、兄弟、跨级。 当我们的项目比较大时,可以选择状态更好的解决方法vuex。
实现方式
bus
utils - bus.js
import Vue from 'vue' const bus = new Vue() export default bus
一、传值
发送信息 A.vue
import bus from '@/utils/bus'
第一个参数为标志变量,第二个参数为通信的值
bus.$emit('message','hello')
接收信息 B.vue
import bus from '@/utils/bus'
第一个参数为标志变量,第二个参数为通信的值
bus.$on('message', (e)=> {
console.log(e); // 传递过来的值
})
demo:
<div id="itany">
<my-a></my-a>
<my-b></my-b>
<my-c></my-c>
</div>
<template id="a">
<div>
<h3>A组件:{{name}}</h3>
<button @click="send">将数据发送给C组件</button>
</div>
</template>
<template id="b">
<div>
<h3>B组件:{{age}}</h3>
<button @click="send">将数组发送给C组件</button>
</div>
</template>
<template id="c">
<div>
<h3>C组件:{{name}},{{age}}</h3>
</div>
</template>
<script>
var Event = new Vue();//定义一个空的Vue实例
var A = {
template: '#a',
data() {
return {
name: 'tom'
}
},
methods: {
send() {
Event.$emit('data-a', this.name);
}
}
}
var B = {
template: '#b',
data() {
return {
age: 20
}
},
methods: {
send() {
Event.$emit('data-b', this.age);
}
}
}
var C = {
template: '#c',
data() {
return {
name: '',
age: ""
}
},
mounted() {//在模板编译完成后执行
Event.$on('data-a',name => {
this.name = name;//箭头函数内部不会产生新的this,这边如果不用=>,this指代Event
})
Event.$on('data-b',age => {
this.age = age;
})
}
}
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#itany',
components: {
'my-a': A,
'my-b': B,
'my-c': C
}
});
</script>
二、调用方法
一个组件A调用另一个组件B的方法
B组件的方法
import bus from '@/utils/bus'
mounted(){ bus.$on('testA', this.testA) }
testA() { console.log('B组价的方法,由A组件调用') }
A组件调用
import bus from '@/utils/bus'
mounted() { bus.$emit('testA') }
方法三、vuex
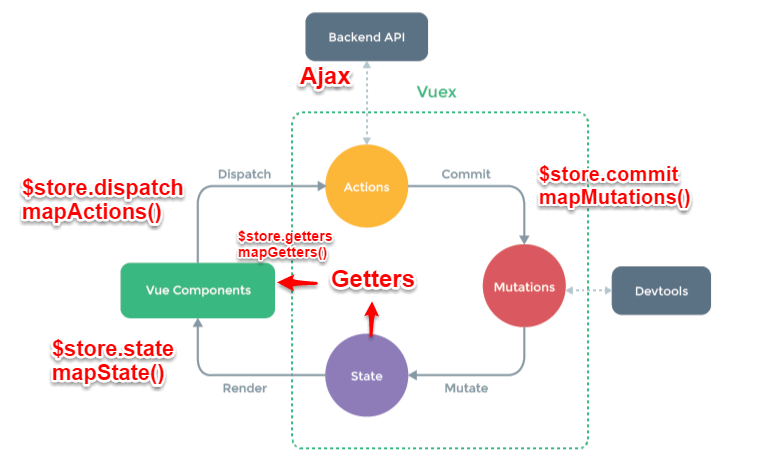
1. 简要介绍Vuex原理
Vuex实现了一个单向数据流,在全局拥有一个State存放数据,当组件要更改State中的数据时,必须通过Mutation进行。Mutation同时提供了订阅者模式供外部插件调用获取State数据的更新。而当所有异步操作(常见于调用后端接口异步获取更新数据)或批量的同步操作需要走Action, 但Action也是无法直接修改State的,还是需要通过Mutation来修改State的数据,最后,根据State的变化,渲染到视图上。
2. vuex中有五种默认的基本属性
1. state: vuex 的基本数据,用来存储变量, 相当于vue中的data
2. mutations: 更改vuex中state的状态唯一方法, 是同步的, 在组件中使用this.$store.commit('',parmas). 这个和我们组件中的自定义事件类似
3. actions: actions提交的就是mutations,而不是直接变更状态,异步操作。 在组件中使用this.$store.dispath("")
4. getters: 对数据获取之前的再次编译,可以理解为store的计算属性。我们在组件中使用$store.getters.fun()
5. module
3. Vuex与locastorage
vuex是vue的状态管理器,存储的数据是响应式的,但是并不会保存起来,刷新之后就回到了初始状态,具体做法应该在vuex里数据改变的时候,把数据拷贝一份保存到localStorage里面,刷新之后,如果localStorage里面有保存的数据,取出来再替换store里的state。
let defaultCity = "上海" try { // 用户关闭了本地存储功能,此时在外层加个try...catch if(!defaultCity) { defaultCity = JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('defaultCity')) } } catch(e){} export default new Vuex.Store({ state: { city: defaultCity }, mutations: { changeCity(state,city) { state.city = city } try{ localStorage.setItem('defaultCity', JSON.stringify(state.city)); // 数据改变的时候把数据拷贝一份保存到localStorage中 } catch(e) { } } })
这里需要注意的是: 由于vuex里,我们保存的状态,都是数组,而localStorage只支持字符串,所以需要JSON转换:
JSON.stringify(state.menuList); // array -> string JSON.parse(window.localStorage.getItem('menuList')); // string --> array
方法四、$attrs/$listeners
1. 简介
多级组件嵌套需要传递数据时,通常使用的方法是通过vuex。但如果仅仅是传递数据,而不做中间处理,使用vuex处理,未免有点大材小用。 为此vue2.4 提供了另一种方法---$attrs/$listeners
· $attrs: 包含了父作用域中不被prop 锁识别的特性绑定(class 和style除外)。 当一个组件没有声明任何prop时,这里会包含所有父作用域的绑定(class 和 style 除外), 并且可以通过v-bind="$attrs" 传入内部组件。通常配合interitAttrs选项一起使用
· $listeners: 包含父作用域中的(不含.native修饰器的) v-on 事件监听器,它可以通过v-on="$listeners" 传入内部组件
跨级组件的通信:
// index.vue <template> <div> <h2>浪里行舟</h2> <child-com1 :foo="foo" :boo="boo" :coo="coo" :doo="doo" title="前端工匠" ></child-com1> </div> </template> <script> const childCom1 = () => import("./childCom1.vue"); export default { components: { childCom1 }, data() { return { foo: "Javascript", boo: "Html", coo: "CSS", doo: "Vue" }; } }; </script>
// childCom1.vue <template class="border"> <div> <p>foo: {{ foo }}</p> <p>childCom1的$attrs: {{ $attrs }}</p> <child-com2 v-bind="$attrs"></child-com2> </div> </template> <script> const childCom2 = () => import("./childCom2.vue"); export default { components: { childCom2 }, inheritAttrs: false, // 可以关闭自动挂载到组件根元素上的没有在props声明的属性 props: { foo: String // foo作为props属性绑定 }, created() { console.log(this.$attrs); // { "boo": "Html", "coo": "CSS", "doo": "Vue", "title": "前端工匠" } } }; </script>
// childCom2.vue <template> <div class="border"> <p>boo: {{ boo }}</p> <p>childCom2: {{ $attrs }}</p> <child-com3 v-bind="$attrs"></child-com3> </div> </template> <script> const childCom3 = () => import("./childCom3.vue"); export default { components: { childCom3 }, inheritAttrs: false, props: { boo: String }, created() { console.log(this.$attrs); // {"coo": "CSS", "doo": "Vue", "title": "前端工匠" } } }; </script>
// childCom3.vue <template> <div class="border"> <p>childCom3: {{ $attrs }}</p> </div> </template> <script> export default { props: { coo: String, title: String } }; </script>


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号