Map集合
Map集合
Map集合整体框架:
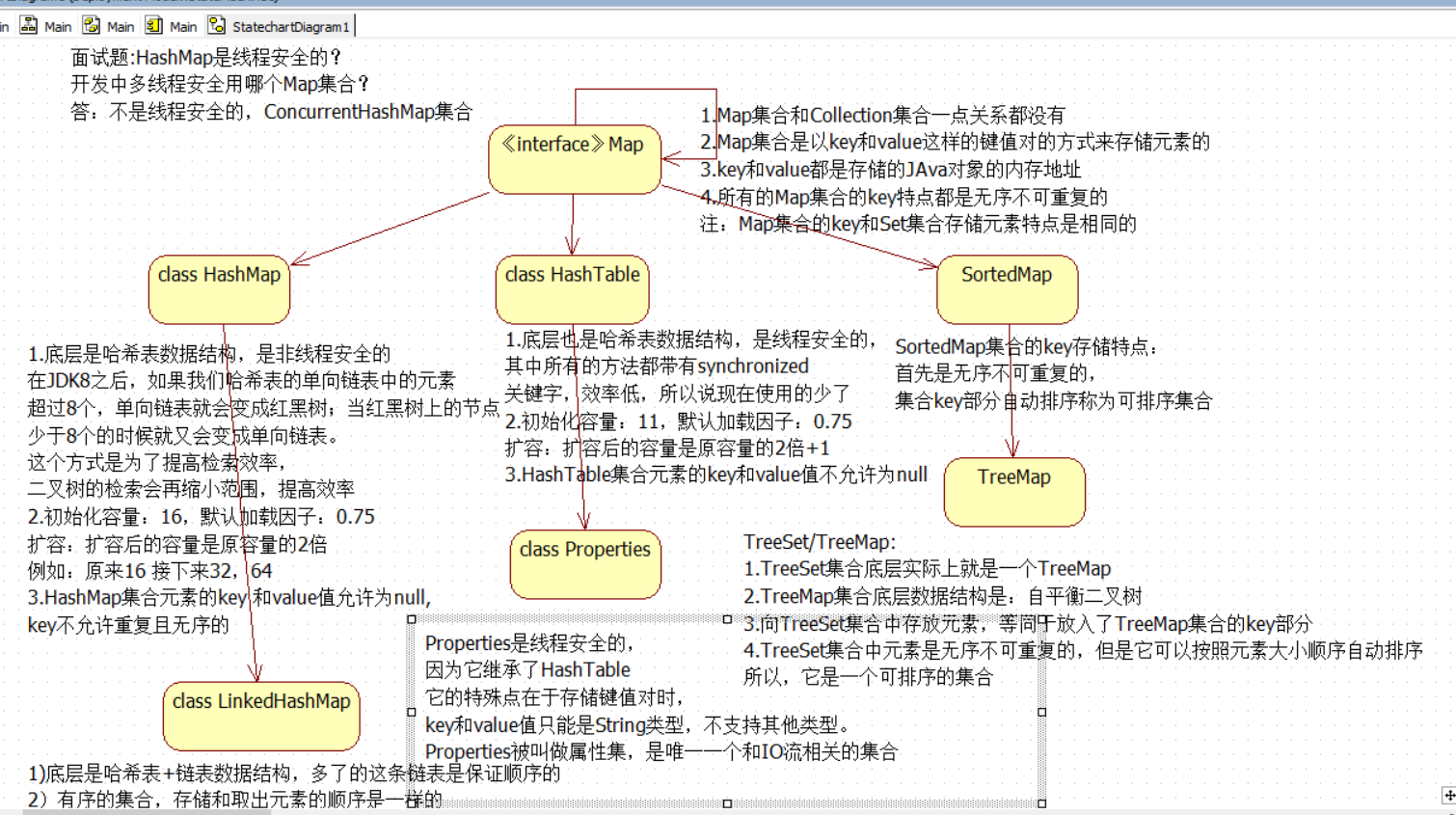
Map<K,V>集合:
特点:
1)双列集合,一个元素包含两个值(key,value)
2)key和value的数据类型可以相同,也可以不同
3)key不允许重复,value是可以重复的
4)key和value是一一对应的
HashMap<K,V>集合:
1)底层是哈希表数据解雇:查询速度非常快
2)无序的集合,存储和取出元素的顺序可能不一样
linkedHashMap<K,V>
1)底层是哈希表+链表数据结构,多了的这条链表是保证顺序的
2)有序的集合,存储和取出元素的顺序是一样的
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class MapTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
show04();
}
/*
boolean containsKey(Object key)如果此映射包含指定键的映射,则返回true
boolean containsValue(Object value)如果此映射将一个或多个键映射到指定的值,则返回true 。
*/
private static void show04() {
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("赵丽颖",168);
map.put("杨颖",165);
map.put("林志颖",155);
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println(map.containsKey("赵丽颖"));
System.out.println(map.containsValue(155));
}
/*
Map集合获取值:
V get(Object key)
注意:key值存在,v返回的是对应的value值
key值不存在,v返回的是null
*/
private static void show03() {
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("赵丽颖",168);
map.put("杨颖",165);
map.put("林志颖",155);
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println(map.get("杨颖"));
System.out.println(map.get("颖"));
}
/*
Map集合删除值:
V remove(Object key)
注意:key值存在,v返回的是删除的值
key值不存在,v返回的是null
*/
private static void show02() {
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("赵丽颖",168);
map.put("杨颖",165);
map.put("林志颖",155);
System.out.println(map);
Integer v1 = map.remove("林志颖");
System.out.println(map);
Integer v2 = map.remove("林志玲");
System.out.println(v2);
}
/*
Map集合添加值:
V put(K key,V value)
key不允许重复,重复的话value会覆盖
*/
private static void show01() {
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("向佐","郭碧婷");
map.put("郑恺","苗苗");
map.put("邓超","嬛嬛");
map.put("邓超","娘娘");
System.out.println(map);
}
}
Map集合的第一种遍历方式:通过键找值的方式:
方法:
Set
实现步骤:
1.使用keySet()方法,把Map集合中的key取出来,存入到一个set
2,遍历Set
3.通过Map集合中V get(Object key),获取到所有的value值,输出
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Set;
public class MapTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1,2);
map.put(2,3);
map.put(3,4);
Set<Integer> set = map.keySet();
for (Integer key : set) {
Integer value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key+"="+value);
}
}
}
Map集合的第二种遍历方式:使用Entry对象遍历
Entry:键值对(key-value)
方法:
Map接口:
方法:
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet()返回此地图中包含的映射的Set视图
java.util Interface Map.Entry<K,V>
K getKey()返回与此条目相对应的键
V getValue()返回与此条目相对应的值。
实现步骤:
1.使用Map集合entrySet()方法,把集合中多个Entry对象取出来,存储到一个Set集合中
2.遍历Set集合,获取到每一个Entry对象
3.调用Map.Entry<K,V>接口中的getKey()和getValue()获取出键和值
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class MapTest03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("赵丽颖",168);
map.put("杨颖",165);
map.put("林志颖",155);
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> set = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : set) {
String key = entry.getKey();
Integer value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key+"="+value);
}
}
}
HashMap<K,V>集合:
key和value是自定义类型
key是自定义类型: 建议实体类重写equals和hashCode方法
value是自定义类型:可以不用重写equals和hashCode方法
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
/*
HashMap<K,V>集合:
key和value是自定义类型
key是自定义类型: 建议实体类重写equals和hashCode方法
value是自定义类型:可以不用重写equals和hashCode方法
*/
public class HashMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
show02();
}
/*
key是自定义类型:
建议实体类重写equals和hashCode方法
*/
private static void show02() {
HashMap<Person,String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(new Person("女王",18),"美国");
map.put(new Person("秦始皇",18),"秦国");
map.put(new Person("普京",30),"俄罗斯");
map.put(new Person("女王",18),"毛里求斯");
Set<Map.Entry<Person, String>> set = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Person, String> entry : set) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"="+entry.getValue());
}
}
/*
value是自定义类型:
*/
private static void show01() {
HashMap<String,Person> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("北京",new Person("张三",18));
map.put("上海",new Person("李四",19));
map.put("广州",new Person("王五",20));
map.put("北京",new Person("张三",18));
Set<String> set = map.keySet();
for (String key : set) {
Person value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key+"="+value);
}
}
}
import java.util.Objects;
//重写过
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Person() {
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (!(o instanceof Person)) return false;
Person person = (Person) o;
return age == person.age &&
Objects.equals(name, person.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
}
linkedHashMap<K,V>集合
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
/*linkedHashMap<K,V>
1)底层是哈希表+链表数据结构,多了的这条链表是保证顺序的
2)有序的集合,存储和取出元素的顺序是一样
*/
public class LinkedHashMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("a","b");
map.put("c","a");
map.put("b","b");
map.put("d","a");
System.out.println(map);// a c b d ____a b c d
LinkedHashMap<String,String> linked = new LinkedHashMap<>();
linked.put("a","b");
linked.put("c","a");
linked.put("b","b");
linked.put("d","a");
System.out.println(linked);
}
}
HashTable:
HashTable:
1.底层也是哈希表数据结构,是线程安全的
从Java 2平台v1.2,如果不需要线程安全的实现,建议使用HashMap代替Hashtable 。 如果需要线程安全的并发实现,那么建议使用ConcurrentHashMap代替Hashtable 。
HashTable在开发中不建议使用,但是它的子类Properties属性集类还在使用。
此类是唯一一个和IO相结合的集合类。
2.HashMap集合元素的key 和value值允许为null,
HashTable集合元素的key和value值不允许为null
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Properties;
public class HashTableTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(null,"a");
map.put("b",null);
map.put(null,null);
System.out.println(map);
Hashtable<String,String > table = new Hashtable<>();
/**
*
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException
*/
table.put(null,"a");
table.put("b",null);
table.put(null,null);
System.out.println(table);
}
}
TreeSet/TreeMap:
1.TreeSet集合底层实际上就是一个TreeMap
2.TreeMap集合底层数据结构是:自平衡二叉树
3.向TreeSet集合中存放元素,等同于放入了TreeMap集合的key部分
4.TreeSet集合中元素是无序不可重复的,但是它可以按照元素大小顺序自动排序
所以,它是一个可排序的集合
public class TreeMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet<Integer> set = new TreeSet<>();
set.add(1);
set.add(10);
set.add(9);
set.add(5);
for (Integer i : set) {
System.out.println(i);//1597
}
}
}
Debug调试程序:
可以让代码直接逐行执行,查看到代码执行的过程,调式过程中出现的bug
使用的方式:
在行号的右边,使用鼠标左键点击,添加断点(每个方法的第一行,哪里有bug添加到哪里)
右键,选择debug运行程序
程序会停留在添加的第一个断点处
执行程序:
Fn+F8:逐行执行程序
Fn+F7:进入到方法中
shift+f8:跳出方法
Fn+F9:跳到下一个断点,如果没有下一个断点,就会结束程序
ctrl+F2:退出debug模式,停止程序




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号