期约Promise
期约Promise
Promise的定义
Promise对象用于作为异步任务结果的占位符,它代表了一个异步操作最终完成或者失败。它能把异步操作最终的成功返回值或者失败原因和相应的处理程序关联起来。
//调用Promise构造函数,创建DelayedPromise对象
const DelayedPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log("DelayedPromise executor");
//延时500ms兑现承诺
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("Resolving DelayedPromise");
resolve("DelayedPromise")
}, 500);
});
if(DelayedPromise !== null)
console.log("DelayedPromise is created");
//注册DelayedPromise处理函数
DelayedPromise.then( success => { //定义成功处理函数,success代表成功返回值
console.log("Resolve handled with " + success);
}, err => { //定义失败处理函数,err代表失败原因
console.log(err);
});
//执行结果
//DelayedPromise executor
//DelayedPromise is created
//Resolving DelayedPromise
//Resolve handled with DelayedPromise
调用Promise构造函数并传入执行函数( executor ),此时执行函数会立即被调用,最后再返回DelayedPromise对象。创建完DelayedPromise对象后,调用Promise对象的then方法注册用于处理执行函数结果的回调函数。当执行函数调用resolve时,执行作为传入then方法第一个参数的回调函数;若执行函数捕获到未处理的异常或调用了reject方法,则执行第二个回调函数。
Promise的生命周期
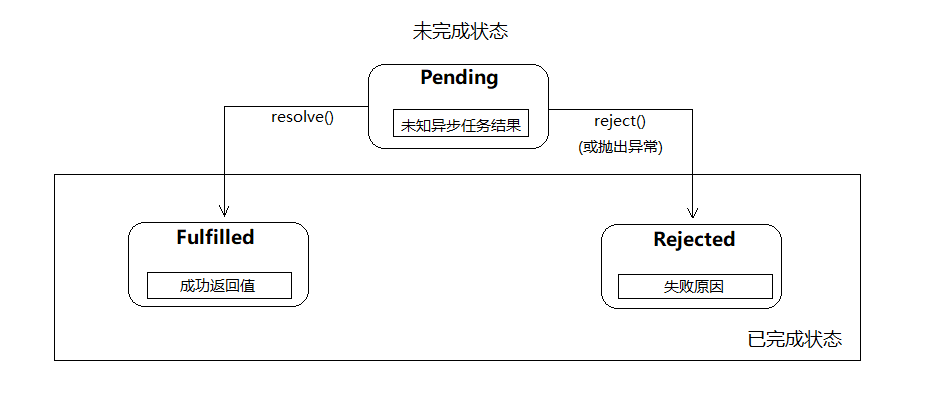
从异步任务是否完成的角度上看,在Promise对象的整个生命周期中,它会经历两种状态——未完成状态和已完成状态。在调用构造函数创建完一个Promise对象后,promise会进入第一个状态——等待(Pending)状态,此时异步任务处于未完成状态,无法得知最终会得到什么结果。
然后调用promise对象的then方法,用于注册一个处理异步操作结果的回调函数。当异步任务调用resolve函数后,promise将进入完成(Fulfilled)状态,此时会调用处理函数中的第一个回调函数并向该函数传递成功返回值;若异步任务调用reject函数或捕获到未被处理的异常时,promise将进入拒绝(Rejected)状态,此时会调用处理函数中的第二个回调函数并向该函数传递失败原因。
一旦异步任务进入到已完成状态时,promise的状态不能再被切换(即完成态和拒绝态不能相互切换)。
Promise执行顺序
console.log("At code end");//标记程序开始
//调用Promise构造函数,创建DelayedPromise对象
const DelayedPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log("DelayedPromise executor");
//延时500ms兑现承诺
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("Resolving DelayedPromise");
resolve("DelayedPromise")
}, 500);
});
if(DelayedPromise !== null)
console.log("DelayedPromise is created");
//注册DelayedPromise处理函数
DelayedPromise.then( success => { //定义成功处理函数,success代表成功返回值
console.log("resolve handled with " + success);
}, err => { //定义失败处理函数,err代表失败原因
console.log(err);
});
//调用Promise构造函数,创建ImmediatePromise对象
const ImmediatePromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log("ImmediatePromise executor");
console.log("Resolving ImmediatePromise");
resolve("ImmediatePromise"); //立即兑现承诺
});
if(ImmediatePromise !== null)
console.log("ImmediatePromise is created");
//注册ImmediatePromise处理函数
ImmediatePromise.then( success => {
console.log("resolve handled with " + success);
}, err => {
console.log(err);
})
console.log("At code end");//标记程序结尾
//运行结果
//At code start
//DelayedPromise executor
//DelayedPromise is created
//ImmediatePromise executor
//Resolving ImmediatePromise
//ImmediatePromise is created
//At code end
//resolve handled with ImmediatePromise
//Resolving DelayedPromise
//resolve handled with DelayedPromise
JavaScript在本次时间循环中的所有代码都执行完毕后(同步执行),再调用then回调函数用于处理promise(异步执行)。由代码的运行结果可知,“resolve handled with ImmediatePromise”与“resolve handled with DelayedPromise”跟setTimeout的回调函数都是在"At code end"之后才执行的,也就是说then方法创建的回调函数都是异步执行的。
Promise的应用
利用Promise实现客户端向服务端请求数据(基于Xhr)
function getJSON(url){
//创建并返回一个promise对象
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//创建XHR对象request
const request = new XMLHttpRequest();
//初始化请求
request.open("GET", url);
request.send();
//服务器端响应后调用
request.onload = function(){
try {
if(this.status == 200){//服务器响应成功且状态码为200时,返回请求值
resolve(JSON.parse(this.response));
}else{ //服务器返回了其他状态码时,调用reject方法,返回状态码和描述
reject(this.status + " " + this.statusText);
}
} catch (e) {//JSON解析异常,调用reject方法,返回错误信息
reject(e.message);
}
}
//无法与服务器通信,调用reject方法,返回状态码和描述
request.onerror = function(){
reject(this.status + " " + this.statusText);
};
})
}
getJSON("http://localhost:3000/data").then(success => {
console.log(success);
}, error => {
console.log(error);
})
Promise的链式调用
promise对象进入已完成(settled)状态执行完相应的回调函数后,会返回一个新的promise对象,此时我们可以对这个新的promise对象调用then方法,在上一个promise对象的处理函数结果的基础上,再进行进一步的操作。
//链式调用
getJSON("http://localhost:3000/ninjas") // [{missionsUrl: "http://localhost:3000/missions"}, {}]
.then(ninjas => getJSON(ninjas[0].missionsUrl))//[{detailsUrl: "http://localhost:3000/details"}, {}]
.then(missons => getJSON(missons[0].detailsUrl))//{mission: "Kill!!"}
.then(misson => console.log(misson))//{mission: "Kill!!"}
.catch(error => console.log(error));
错误传递
对promise对象进行链式调用是串行执行的,每一个promise对象都要等待上一个promise执行完成后才开始执行,若promise进入reject状态,浏览器会顺着promise链寻找下一个失败回调函数或由.catch()指定的回调函数。
//存在失败处理函数
getJSON("http://localhost:3000/ninjas")
.then(ninjas => getJSON(ninjas[0].missionsUrl))
.then(missons => i++)) //出现异常
.then(misson => console.log(misson),
error => consloe.log("rejected:" + error)) //捕获异常,执行失败回调函数 rejected:ReferenceError: i is not defined
.catch(error => console.log("catch:" + error)); //不执行
//存在.catch(),无失败处理函数
getJSON("http://localhost:3000/ninjas")
.then(ninjas => getJSON(ninjas[0].missionsUrl))
.then(missons => i++)) //出现异常
.then(misson => console.log(misson)) //不执行
.catch(error => console.log("catch:" + error)); //捕获异常 catch:ReferenceError: i is not defined



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号